Ch 20 Redox
advertisement

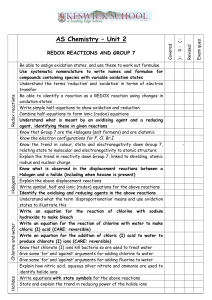
NAME: Ch 20 Oxidation/Reduction - REDOX Period: STUDY GUIDE Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. A. oxidation number C. oxidizing agent B. half-reaction D. reducing agent ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. 2. 3. 4. substance that accepts electrons substance that donates electrons integer related to the number of electrons under an atom's control reaction showing either the reduction or the oxidation reaction Match each item with the correct statement below. A. Choose coefficients to make the change in oxidation number equal to 0. B. Make the electron changes of both half-reactions equal. C. Assign oxidation numbers to all the atoms. D. Write the equation showing ions separately. ____ ____ ____ ____ 5. 6. 7. 8. the first step in balancing a redox reaction by the oxidation-number-change method the next-to-the-last step in balancing a redox reaction by the oxidation-number-change method the first step in balancing a redox reaction by the half-reaction method the next-to-the-last step in balancing a redox reaction by the half-reaction method Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 9. If an atom is reduced in a redox reaction, what must happen to another atom in the system? A. It must be oxidized. B. It must be reduced. C. It must be neutralized. D. Nothing needs to happen to another atom in the system. 10. Which of these metals tends to resist losing electrons to corrosion? A. aluminum B. iron C. platinum D. zinc 11. Which type of reaction is the conversion of iron oxide to iron and oxygen? A. oxidation B. reduction C. neutralization D. combination 12. In which of the following types of reaction are electrons gained? A. decomposition B. oxidation C. neutralization D. reduction 13. What change occurs during oxidation? A. gain of hydrogen B. loss of oxygen C. gain of electrons D. loss of electrons 14. What particles are transferred in an oxidation-reduction reaction? A. protons B. ions C. electrons D. atoms 15. Which element is reduced in the following reaction? 2PbSO4 + 2H2O Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 A. lead B. sulfur C. hydrogen D. oxygen /69 ____ 16. Which element is oxidized in the following reaction? 2PbSO4 + 2H2O Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 A. lead B. sulfur C. hydrogen D. oxygen ____ 17. In the following reaction, which term applies to chlorine? Ca + Cl2 CaCl2 A. oxidizing agent B. reducing agent C. spectator D. accelerator ____ 18. Why does aluminum tend not to corrode as much as iron when it is exposed to moist air? A. A layer of aluminum oxide protects the metal beneath. B. Aluminum does not lose electrons easily. C. Aluminum does not react with oxygen unless salt is present. D. Energy must be added to cause aluminum to corrode. ____ 19. How does a block of zinc attached to a steel ship hull protect the hull from corrosion? A. Zinc is a better reducing agent so it corrodes instead of the iron corroding. B. Zinc is a better oxidizing agent so it corrodes instead of the iron corroding. C. The zinc carries electrons toward the iron so that the iron cannot react. D. The zinc carries electrons away from the iron so that the iron cannot react. ____ 20. In the reaction of hydrogen with iodine, which is the reducing agent? A. hydrogen B. iodine C. hydrogen ion D. iodide ion ____ 21. Cu Cu + 2 eThe equation above represents a reaction that can be classified as ____. A. redox B. hydrolysis C. reduction D. oxidation ____ 22. Which type of reaction does Sn Sn represent? A. oxidation B. reduction C. hydrolysis ____ 23. What is the reducing agent in the following reaction? 2Na + 2H O 2NaOH + H A. Na B. H O C. NaOH D. redox D. H ____ 24. What is the reducing agent in the following reaction? 2Na + S Na S A. Na B. S C. Na S D. Na ____ 25. What is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? CH + 2O CO + H O A. CH B. O C. CO D. H O ____ 26. Which statement is true about the following reaction? S + Cl SCl A. Sulfur is reduced to SCl . C. Chlorine is oxidized to SCl . B. Chlorine is reduced to SCl . D. Sulfur is the oxidizing agent. ____ 27. What process occurs during the corrosion of iron? A. Iron is oxidized. C. Iron (III) is oxidized. B. Iron is reduced. D. Iron (III) is reduced. ____ 28. Why is oxygen reduced in the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen to make water? A. Oxygen pulls electrons toward itself. B. Oxygen pushes electrons toward the hydrogens. C. Oxygen absorbs a proton. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. ____ 33. ____ 34. D. Oxygen releases a proton. The oxidation number of magnesium in magnesium chloride is ____. A. –1 B. 0 C. +1 D. +2 The oxidation number of hydrogen when it is in a compound other than a hydride is ____. A. –2 B. –1 C. 0 D. +1 The oxidation number of bromine in bromine gas is ____. A. +1 B. –1 C. 0 D. –2 What is the oxidation number for each atom in NH Cl? A. N = +3, H = –4, Cl = +1 C. N = +3, H = +1, Cl = –1 B. N = –3, H = +1, Cl = –1 D. N = –3, H = –1, Cl = +1 In general, what is the charge an atom would have in a compound if its bonding electrons were assigned to the more electronegative atom? A. reduction number C. valence B. oxidation number D. electropositivity In which of the following species is the oxidation number of sulfur less than 6? A. SO B. Na SO C. SO D. S O ____ 35. In which of the following compounds does the oxidation number of nitrogen have a negative value? A. NO B. N O C. NH Cl D. Ca(NO ) ____ 36. Identify the atom whose oxidation number increases in the following redox reaction. 2MnO + 2K CO + O 2KMnO + 2CO A. Mn B. O C. K D. C ____ 37. Which atom has a –3 change in oxidation number during the following redox reaction? K Cr O + H O + S KOH + Cr O + SO A. K B. Cr C. O D. S ____ 38. In the following unbalanced reaction, which atom is reduced? H O + Cl + SO HCl + H SO A. hydrogen B. oxygen C. chlorine D. sulfur ____ 39. In the following unbalanced reaction, which atom is oxidized? HNO + HBr NO + Br + H O A. hydrogen B. nitrogen C. oxygen D. bromine ____ 40. Which of the following chemical equations represents an oxidation-reduction reaction? A. Mg(OH) + 2HCl MgCl + 2H2O C. CH4 + 2O2 CO + 2H2O B. BiCl + Na SO 2NaCl + BiSO D. 3NaOH + H PO Na PO + 3H O ____ 41. Which element increases its oxidation number in the following reaction? 3KOH + H PO K PO + 3H O A. oxygen C. phosphorus B. potassium D. no changes in oxidation number ____ 42. The oxidation number of what atom or ion decreases in the following reaction? I + 2KCl 2KI + Cl A. iodine atom B. potassium atom C. chlorine ion D. potassium ion ____ 43. Which of the following chemical equations represents a redox reaction? A. 2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2 B. HCl + KOH KCl + H2O C. AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) + H2O(l) D. Fe3+ + 3NO3– + 3Na+ + 3OH– Fe(OH)3 + 3Na+ + 3NO3– ____ 44. Which of the following types of reactions is always a redox reaction? A. acid-base C. combustion B. double-replacement D. neutralization ____ 45. What is the coefficient for H when this half-reaction is balanced? H + MnO Mn + H O A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 ____ 46. What is the reduction half-reaction for the following unbalanced redox equation? Cr O + NH Cr O + N A. Cr O Cr O C. NH N B. Cr O Cr O D. N NH ____ 47. What is the oxidation half-reaction for the following unbalanced redox equation? Cr O + Fe Cr + Fe A. Cr Cr O C. Fe Fe B. Fe Fe D. Cr O Cr ____ 48. What is the key factor in defining a reaction as an oxidation-reduction reaction? A. transfer of electrons between atoms B. oxygen as one of the reactants C. making and breaking ionic bonds D. precipitation of solid from the reaction solution ____ 49. The half-reaction method is particularly useful for balancing which type of equation? A. dissociation B. acid-base C. redox D. combustion ____ 50. What is the ionic form of the following unbalanced equation? MnO + HNO Mn(NO ) + H O A. MnO + HNO ® Mn + NO + H O B. MnO + H + NO MnNO + H O C. MnO + H + NO Mn + NO + H O D. Mn + O + H + NO Mn + NO + H O ____ 51. Which term describes the following process? 2Fe(s) + O (g) + 2H O(l) 2Fe(OH) (s) 4Fe(OH) (s) + O (g) +2H O(l) 4Fe(OH) (s) A. salt hydrolysis B. electrolysis C. corrosion D. buffering ____ 52. Which of the following is an oxidation half-reaction? A. Sn Sn + 2e C. O + 4H + 4e 2H O B. Cl + 2e 2Cl D. Fe + e Fe ____ 53. What is a balanced equation for the redox reaction represented by the two half-reactions below? Br + 2e 2Br Na Na + e A. Na + Br + e Na + 2Br B. Na + Br Na + 2Br C. 2Na + Br 2Na + 2Br D. Na + Br + 2e Na + 2Br + e ____ 54. Which of the following is a reduction half-reaction? A. Zn Zn C. Na Na B. NO + 2H O N + 4H D. 2H H Numeric Response 55. What is the oxidation number of magnesium in magnesium iodide? 56. What is the sum of the oxidation numbers in lithium carbonate? 57. What is the sum of the oxidation numbers in calcium carbonate? 58. What is the sum of the oxidation numbers in the chlorate ion? 59. What is the change in oxidation number of chromium when Na Cr O becomes CrI ? 60. In the following reaction, what is the total decrease in oxidation number for the reduced element? 2HNO + 6HI 2NO + 3I +4H O 61. What coefficient of H balances the atoms in the following half-reaction? H + PbO Pb + 2H O 62. What is the total increase in oxidation number for the atom that is oxidized in the following redox reaction? Cr O + 8H + 3SO 2Cr + 3SO + 4H O 63. What is the change in oxidation number of aluminum in the reaction of aluminum with oxygen to make aluminum oxide? 64. What is the change in the oxidation number of chromium when K Cr O becomes CrCl ? 65. What is the change in oxidation number of manganese when MnO becomes Mn O ? 66. What will the coefficient of HNO be when the following equation is completely balanced using the smallest whole-number coefficients? HNO + MnCl + HCl NO + MnCl + H O 67. In the following reaction, what is the total increase in oxidation number for the oxidized element? 2H O + Cl + SO 2HCl + H SO 68. In the following reaction, what is the total decrease in oxidation number for the reduced element? 2HNO + 6HBr 2NO + 3Br + 4H O 69. What number of electrons balances the charges in the following half-reaction? SO + 2H O SO + 4H