5-6 - EDventures
advertisement

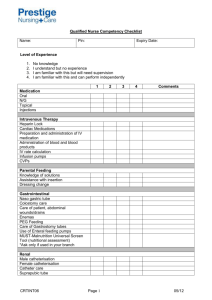
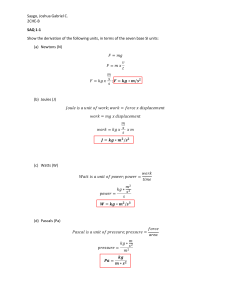
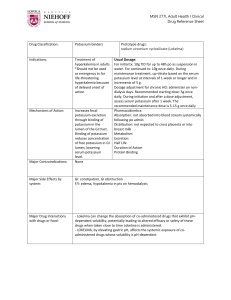
Renal Endocrine Metabolic SAQ 5 A 73 year old female is brought to ED GCS 12 BP 100/70 PR 72 O2sats 97% RR 10 Her ABG is as follows: pH 7.35 pCO2 50 HCO3 24 pO2 113 Na 137 K 4.6 Cl 98 Glucose 72 Urea 28.7 1. What is the primary diagnosis?(2) 2. What parameters would you use to decide ICU disposition? (3) 3. Name six key management priorities? (4) 4. After 4hours repeat bloods show Na 113 and Glucose of 60, what fluid should be used for ongoing maintenance? (1) Renal/ Endocrine SAQ 6 A 35 year old man with a past history of Type I Diabetes presents with a two day history of diarrhoea and vomiting. His BSL on arrival is 40 mmol/L. His observations are GCS 15/15, HR 120 per min, RR 32 per min, BP 100/70 mmHg, SpO2 99% on room air and temperature 37 degrees C 1. After administration of N Saline (0.9%) an arterial gas analysis reveals a serum Potassium of 5.1mmol. Describe how you will manage his serum potassium level over the next three hours (3) 2. List four possible complications of this man’s condition (3) 3. Discuss the utility of an arterial line in this patient (4)