Pre-Requisite Unit
advertisement
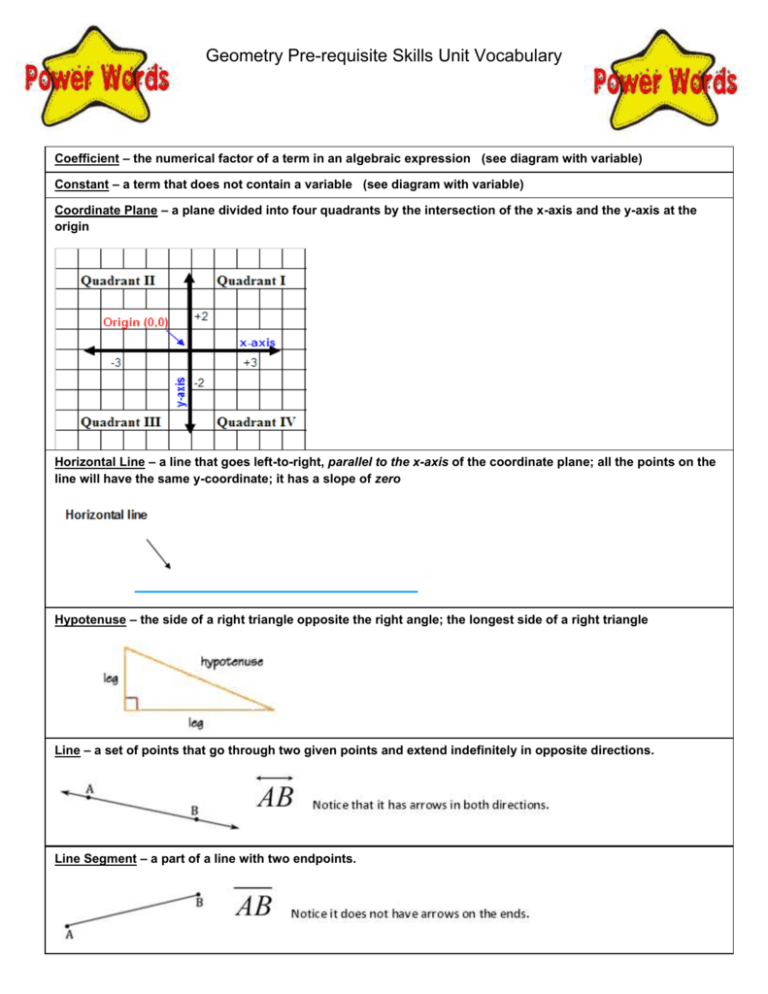
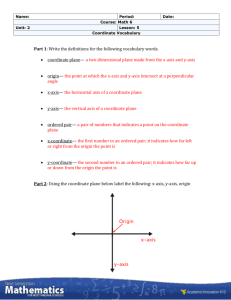
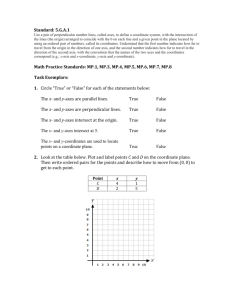
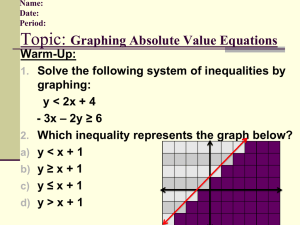
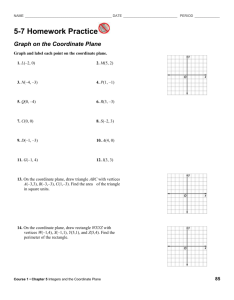
Geometry Pre-requisite Skills Unit Vocabulary Coefficient – the numerical factor of a term in an algebraic expression (see diagram with variable) Constant – a term that does not contain a variable (see diagram with variable) Coordinate Plane – a plane divided into four quadrants by the intersection of the x-axis and the y-axis at the origin Horizontal Line – a line that goes left-to-right, parallel to the x-axis of the coordinate plane; all the points on the line will have the same y-coordinate; it has a slope of zero Hypotenuse – the side of a right triangle opposite the right angle; the longest side of a right triangle Line – a set of points that go through two given points and extend indefinitely in opposite directions. Line Segment – a part of a line with two endpoints. Linear Equation – an equation of degree 1; graph is a line; shows the relationship between two variables; an equation of the form y = mx + b where a and b are real numbers. Origin– the point (0,0) in a coordinate plane where the x-axis and the y-axis intersect (see diagram of coordinate plane) Parallel Lines ( || ) – lines in the same plane that do not intersect; they remain an equal distance apart. (Parallel lines have equal slopes) Perfect Square – a number whose square root is a rational number. Examples of perfect squares: 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, 169, 196, 225, etc Perpendicular Lines – lines that intersect at right angles (Perpendicular lines have negative reciprocal slopes) Plane – a two dimensional surface that extends on all directions. It is defined by 3 points. Point – a location in space. It has no size, and is represented by a dot. Point-Slope Form of a Line – an equation of a line in the for y – y1 = m ( x – x1 ) Pythagorean Theorem – a theorem defining the relationship between the lengths of the three sides of a right triangle; a b c where a and b are the lengths of the legs and c is the length of the hypotenuse (see diagram of right triangle) 2 2 2 Quadrant of a Coordinate Plane – any quarter of a plane divided by an x- and y-axis (see diagram of coordinate plane) radical – the symbol, used to indicate a root Rate of Change – how much a function has changed divided by the length of the interval over which it has changed (slope) Slope – the rate of change; the measure of steepness; the change in the y-coordinates divided by the change in the x-coordinate of a line, rise/run m y1 y 2 x1 x 2 Slope-Intercept form of a line – an equation of a line in the form y = mx + b Term of an Expression – a number, a variable, or a product or quotient of numbers and variables Variable – a symbol used to represent an unknown number that varies, usually a lower case letter Vertical Line – a line that goes up-and-down, parallel to the y-axis of the coordinate plane; all the points on the line will have the same x-coordinate; it is perpendicular to a horizontal line; it has an undefined slope Y-Intercept – the point at which a graph intersects the y-axis