Module 6 Vocabulary
advertisement

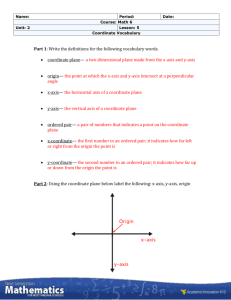
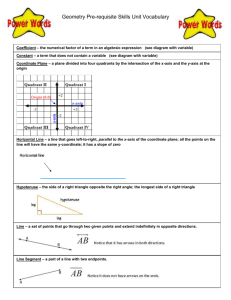
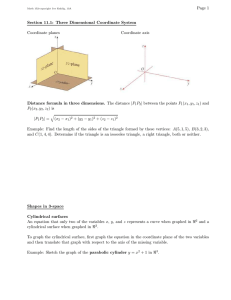
Module 6 Vocabulary Outcomes: The possible results. Probability: A number from 0 to 1 that represents the likelihood of an event. Probability = Experimental probability: The number of desired outcomes divided by the total number of trials. Relative frequency: The number of desired outcomes divided by the total number of trials. Module 6 Advanced Hypotenuse: The longest side of a right triangle; side opposite from the right angle. Legs: The two shorter sides of a right triangle; the sides that meet at 90 degrees. Pythagorean Theorem: a2 + b2 = c2, where a and b are the legs of a right triangle and c is the hypotenuse. Pythagorean triple: A set of positive integers that fits the rule a2 + b2 = c2. Right triangle: A triangle with a 90-degree angle. Two dimensional (2D): An object that has width and length but no thickness (depth); examples include squares, circles, and triangles. Three dimensional (3D): An object that has width, length, and depth; examples include cubes, prisms, spheres, and cones. Coordinate plane (or Cartesian plane): An x-axis and y-axis that meet at a right angle at a center point called the origin; a graph. Ordered pair: A coordinate or point written in the form of (x, y). Origin: The center of a coordinate plane, expressed with the ordered pair (0,0); where the x-axis and y-axis intersect. x-axis: The horizontal number line of the coordinate plane. y-axis: The vertical number line of the coordinate plane. Base: The surface on which an object rests. Cone: A three-dimensional object with one circular base that tapers to a point (vertex) at the other end. Cylinder: A three-dimensional object with a flat, circular base on top and bottom. Diameter: A straight line going from one side of a circle to the other through the center. Height: The vertical distance from top to bottom that creates a 90-degree angle with the base. Radius: The distance from the center to the edge of a circle; half of the diameter. Sphere: A three-dimensional, closed surface that is equally distant from a fixed center. Inverse operation: The opposite of a math operation; the opposite of addition is subtraction and the opposite of multiplication is division. Quizlet- Practice and review here http://quizlet.com/46743603/vocabulary-mj-math-2-v14-module-6-flash-cards/