Practice bond type - Petoskey Public Schools
advertisement

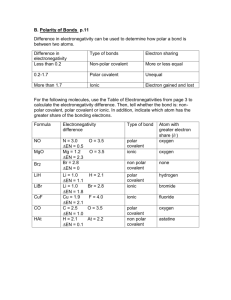
Bond Type Practice Describe the following bond types and tell what type of element(s) are involved: Non-polar Covalent Ionic Metallic Polar Covalent Electronegativities Carbon = 2.5 Cesium = 0.7 Chromium = 1.6 Fluorine = 4.0 Hydrogen = 2.1 Iodine = 2.5 Iron = 1.8 Magnesium = 1.2 Molybdenum = 1.8 Oxygen = 3.5 Phosphorus = 2.1 Silicon = 1.8 Sodium = 0.9 Sulfur = 2.5 Barium = 0.9 Bromine = 2.8 Chlorine = 3.0 Lead = 1.8 Iodine = 2.5 Determine the type of bond (ionic, polar/nonpolar covalent, metallic). If it is polar covalent, determine where the dipoles would be. If it is ionic, denote which would be the positive and negative ions. BaF2 CuPb HBr PH3 SiH4 HCl CH4 SiO2 Au CCl4 SiCl4 PbI Bond Type Practice (Key) Describe the following bond types and tell what type of element(s) are involved: Non-polar Covalent Electrons are shared between the two atoms evenly Ionic Electrons are transferred from one atom to another, creating positive and negative ions that attract each other Metallic A sea of electrons, electrons are shared between all atoms in the piece of metal Polar Covalent Electrons are shared, but not shared evenly, so one atom becomes partially negative (negative dipole) and the other partially positive (positive dipole) Electronegativities Carbon = 2.5 Cesium = 0.7 Chromium = 1.6 Fluorine = 4.0 Hydrogen = 2.1 Iodine = 2.5 Iron = 1.8 Magnesium = 1.2 Molybdenum = 1.8 Oxygen = 3.5 Phosphorus = 2.1 Silicon = 1.8 Sodium = 0.9 Sulfur = 2.5 Barium = 0.9 Bromine = 2.8 Chlorine = 3.0 Lead = 1.8 Iodine = 2.5 Determine the type of bond (ionic, polar/nonpolar covalent, metallic). If it is polar covalent, determine where the dipoles would be. If it is ionic, denote which would be the positive and negative ions. BaF2 Ionic Ba+2, FSiH4 Non-polar Au Metallic CuPb Metallic HCl Polar +---- CCl4 Polar +-- HBr Polar +--- CH4 Polar ---+ SiCl4 Polar +-- PH3 Non-polar SiO2 Ionic Si+4, O-2 PbI Polar +--