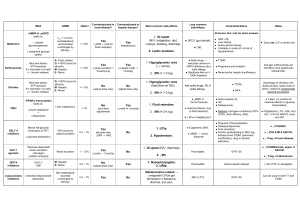
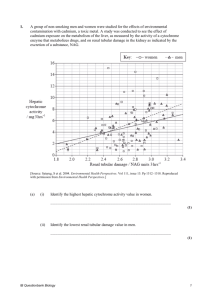
Lung, hepatobiliary, renal MCQ 1. Which of the following usually
advertisement

Lung, hepatobiliary, renal MCQ 1. Which of the following usually presents as nephrotic syndrome a) b) c) d) Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Post infectious glomerulonephritis Membranous glomerulopathy 2. In renal failure a) Chronic renal failure is when the GFR is <25%of normal and kidneys although able to regulate volume are unable to regulate solute composition any longer b) A GFR of <15% of normal, indicates end stage renal disease c) Renal insufficiency is when the GFR is 20-25% of normal amd azotemia appears d) A GFR of around 70% of normal is associated with increasing creatinine levels and indicates diminished renal reserve 3. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis is characterised by a) b) c) d) In situ immune complex formation Loss of foot processes Lipid in tubules Nephritis syndrome 4. Testicular torsion a) b) c) d) Is caused by arterial obstruction Is more common in older adult men Requires surgery within 6hours to remain viable Typicaly has an insidious onset 5. Phimosis is associated with a) b) c) d) Carcinoma Syphilis Condyloma acuminatum Hypospadias 6. Post streptococci glomerulonephritis in children a) b) c) d) Commonly presents with smoky urine 1 month after the resolution of the sore throat Anuria is commonly present Cs serum concentration rises 95% recover with simple conservative treatment aimed at maintaining sodium and water balance 7. Renal artery stenosis a) b) c) d) Is usually secondary to an occlusion of the artery by an atheromatous plaque Fibromuscular dysplasia is the cause seen mostly in the female population Uually is seen in people in their 6th decade of life Bruits over the affected kidney are a common finding 8. Which bug can be associated with the production of magnesium ammonium phosphate stones? a) b) c) d) Klebsiella Streptococci Enterococci Staphylococci 9. Regarding acute respiratory distress a) Neutrophils are thought to play an important role in its pathogenesis b) It is thought that the sole cause is due to the compromised integrity of the microvascular endothelium c) The lungs become stiff late in the disease process d) Resolution requires reabsorption of the transudate 10. Regarding obstructive pulmonary disorders a) COPD is the result of smoking , however 20% of patients that develop the disease are non smokers b) In centrilobular emphysema the lower lobes are mostly affected c) Paraseptal emphysema is associated with α1 antitrypsin deficiency d) Irregular emphysema is usually asymptomatic and clinically insignificant 11. α1 antitrypsin a) b) c) d) Is abnormal in 1% population of patients with emphysema Is associated with the proteinase inhibitor locus found on chromosome 14 Is normally present in macrophages and secreted by neutrophils during inflammation All the above are true 12. Which of the following is correct regarding obstructive pulmonary disease a) b) c) d) Most heavy smokers develop the disease Pulmonary function tests show a reduced forced expiratory volume at 1 sec The source of airway obstruction in these diseases is narrowing of the small airways Most acute exacerbations are due to pneumothorax formation 13. In chronic bronchitis a) There is associated atypical metaplasia and dysplasia of the respiratory endothelium b) As chronic bronchitis persists there is a marked increase in goblet cells predominately in the large airways c) Although there is marked gland hyperplasia the major changes seen are the increased goblet cell numbers d) The role of infection is a secondary feature in the pathogenesis of chronic bronchitis rather than an initiating factor 14. Bronchiectasis a) b) c) d) Has a rare complication of amyloidosis is associated with reversible dilatation of bronchi and bronchioles is most predominately seen in the upper lobes of the lung is most severe in the more proximal bronchi/bronchioles 15. In atelectasis? a) b) c) d) Usually occurs with partial obstruction of the distal airways Mediastinum shifts toward the atelectic side Is typically associated with bronchial neoplasms Is never associated with congenital conditions 16. In haemodynamic pulmonary oedema a) b) c) d) The most common attributing mechanism is decreased hydrostatic pressures Is first seen in the hilar area of the lungs In the acute phase , brown induration of the macrophages is present Hydrostatic pressures are not usually elevated in association with microvascular injury based oedema 17. Regarding pulmonary embolism and infarction a) b) c) d) It accounts for 1% of all inpatient deaths Only 25% of pulmonary emboli cause infarcts 75% of pulmonary infarcts affect the upper lobes Infarcts are usually multiple 18. In pulmonary hypertension, which is incorrect a) b) c) d) It is usually idiopathic Maybe associated with interstitial lung disease Is said to occur when pulmonary pressures reach 25% of systolic blood pressure Death is usually secondary to cor pulmonale 19. The most common form of asthma is a) b) c) d) Occupational Atopic Exertional Intrinsic 20. Regarding lung abscesses a) b) c) d) Those due to aspiration usually occur on the left side Those due to aspiration are usually multiple Those due to pneumonia are usually basal Those due to pneumonia are usually singular 21. The most prevalent chronic occupational disease is associated with exposure to a) b) c) d) Silica Hydrocarbons Coal dust Asbestosis 22. Asbestosis a) b) c) d) Serpentine form is most strongly associated with mesothelioma formation Asbestosis begins as fibrosis around the repiratory bronchiloles and alveolar ducts The least common morphological manifestation is pleural plaques Clinical symptoms commonly occur in less than 10years from first exposure 23. Sarcoidosis a) b) c) d) Is more common in women Cxr changes are found in 50% of cases Clinical splenomegaly is seen in upto 50% of cases Caseating granulomas are the hallmark histological feature 24. Carcinoid tumours a) b) c) d) Represent 10% of all lung tumours Are seen commonly in > 60years of life More common in women 20-40% are found in non smoking patients 25. Regarding community acquired pneumonias a) H. Influenzae is the most common organism b) The unencapsulate b form of H influenza is on the decrease since the introduction of vaccination c) Klebsiella pneumonia is the most frequent G+ve cause of bacterial pneumonia d) H influenza is the most common organism in pneumonia in COPD exacerbations 26. In hepatorenal syndrome a) b) c) d) it occurs in25% of patients with cirrhosis and ascites is heralded by a decrease in blood urea nitrogen and an increase in creatinine is usually associated with a stressor e.g. infection prognosis is good especially in the rapid onset form 27. A post hepatic cause of portal hypertension is usually a) b) c) d) cirrhosis obstructive thrombosis sarcoidosis severe right heart failure 28. Unconjugated bilirubin a) b) c) d) can be excreted in the urine once blood levels become high is closely bound to serum albumin is non toxic is water soluble 29. Which lab finding is not seen in acute pancreatitis a) b) c) d) Increased serum amylase Increased serum lipase Glycosuria Hypercalcemia 30. All of the following are clinical findings/complications of hepatic failure EXCEPT a) b) c) d) Fetor hepaticus is due to hyperammoniaemia Palmer erythemia is associated with hyperestrogenaemia Coagulopathy is due to impaired hepatic synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX,X Hepatorenal syndrome is not associated with any morphological renal cause 31. The most common aetiology of hepatic cirrhosis is a) b) c) d) Alcoholic liver disease Viral hepatitis Drug induced Inherited storage disease 32. Which is true of hepatitis E INFECTION? a) b) c) d) It is often associated with coinfection of hepatitis B Has a mortality rate in pregnant woman of 40% Is associated with chronic liver disease Average post exposure incubation period is 6weeks 33. Fulminent hepatic failure is most commonly due to a) b) c) d) Alcohol Viral hepatitis Drug/chemical toxicity Liver ischaemia secondary to shock 34. The condition most frequently associated with hepatic vein thrombosis is a) b) c) d) Polycythemia rubra vera Pregnancy Intrabdominal carcinoma Oral contraceptive use