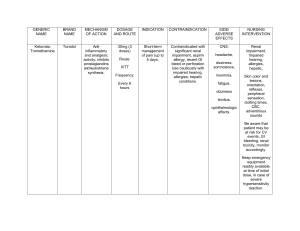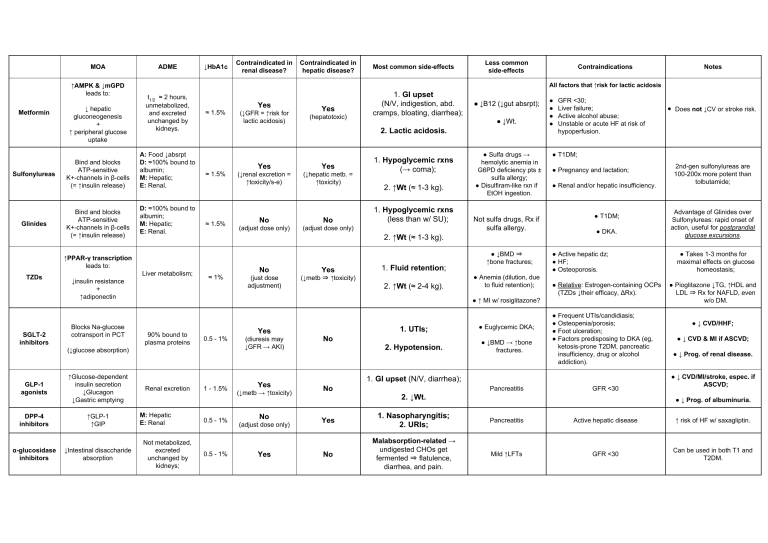
MOA ↑AMPK & ↓mGPD leads to: Metformin Sulfonylureas Glinides ↓ hepatic gluconeogenesis + ↑ peripheral glucose uptake Bind and blocks ATP-sensitive K+-channels in β-cells (= ↑insulin release) Bind and blocks ATP-sensitive K+-channels in β-cells (= ↑insulin release) ADME ↓HbA1c t1/2 ≈ 2 hours, unmetabolized, and excreted unchanged by kidneys. A: Food ↓absrpt D: ≈100% bound to albumin; M: Hepatic; E: Renal. D: ≈100% bound to albumin; M: Hepatic; E: Renal. SGLT-2 inhibitors Liver metabolism; ↓insulin resistance + ↑adiponectin Blocks Na-glucose cotransport in PCT ≈ 1.5% ↑Glucose-dependent insulin secretion ↓Glucagon ↓Gastric emptying DPP-4 inhibitors ↑GLP-1 ↑GIP α-glucosidase inhibitors ↓Intestinal disaccharide absorption Most common side-effects Less common side-effects Yes (↓GFR = ↑risk for lactic acidosis) Yes (hepatotoxic) 1. GI upset (N/V, indigestion, abd. cramps, bloating, diarrhea); ● ↓B12 (↓gut absrpt); ● ↓Wt. 2. Lactic acidosis. ≈ 1.5% ≈ 1.5% Yes Yes (↓renal excretion = ↑toxicity/s-e) (↓hepatic metb. = ↑toxicity) No No (adjust dose only) (adjust dose only) 1. Hypoglycemic rxns (→ coma); 2. ↑Wt (≈ 1-3 kg). 1. Hypoglycemic rxns (less than w/ SU); ● Sulfa drugs → hemolytic anemia in G6PD deficiency pts ± sulfa allergy; ● Disulfiram-like rxn if EtOH ingestion. Not sulfa drugs, Rx if sulfa allergy. 2. ↑Wt (≈ 1-3 kg). ≈ 1% Contraindications No Yes (just dose adjustment) (↓metb ⇒ ↑toxicity) 1. Fluid retention; 2. ↑Wt (≈ 2-4 kg). ● ↓BMD ⇒ ↑bone fractures; ● Anemia (dilution, due to fluid retention); ● ● ● ● GFR <30; Liver failure; Active alcohol abuse; Unstable or acute HF at risk of hypoperfusion. Notes 90% bound to plasma proteins 0.5 - 1% Renal excretion M: Hepatic E: Renal Not metabolized, excreted unchanged by kidneys; 1 - 1.5% 0.5 - 1% 0.5 - 1% Yes (diuresis may ↓GFR → AKI) Yes (↓metb → ↑toxicity) No (adjust dose only) Yes 1. UTIs; ● Euglycemic DKA; 2. Hypotension. ● ↓BMD → ↑bone fractures. No ● Pregnancy and lactation; ● Renal and/or hepatic insufficiency. ● T1DM; ● DKA. ● Active hepatic dz; ● HF; ● Osteoporosis. ● Relative: Estrogen-containing OCPs (TZDs ↓their efficacy, ΔRx). ● Frequent UTIs/candidiasis; ● Osteopenia/porosis; ● Foot ulceration; ● Factors predisposing to DKA (eg, ketosis-prone T2DM, pancreatic insufficiency, drug or alcohol addiction). 1. GI upset (N/V, diarrhea); No Pancreatitis ● Does not ↓CV or stroke risk. ● T1DM; ● ↑ MI w/ rosiglitazone? (↓glucose absorption) GLP-1 agonists Contraindicated in hepatic disease? All factors that ↑risk for lactic acidosis ↑PPAR-γ transcription leads to: TZDs Contraindicated in renal disease? GFR <30 2. ↓Wt. 2nd-gen sulfonylureas are 100-200x more potent than tolbutamide; Advantage of Glinides over Sulfonylureas: rapid onset of action, useful for postprandial glucose excursions. ● Takes 1-3 months for maximal effects on glucose homeostasis; ● Pioglitazone ↓TG, ↑HDL and LDL ⇒ Rx for NAFLD, even w/o DM. ● ↓ CVD/HHF; ● ↓ CVD & MI if ASCVD; ● ↓ Prog. of renal disease. ● ↓ CVD/MI/stroke, espec. if ASCVD; ● ↓ Prog. of albuminuria. Yes 1. Nasopharyngitis; 2. URIs; Pancreatitis Active hepatic disease ↑ risk of HF w/ saxagliptin. No Malabsorption-related → undigested CHOs get fermented ⇒ flatulence, diarrhea, and pain. Mild ↑LFTs GFR <30 Can be used in both T1 and T2DM.