Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Fourth EditionWAIS-IV
advertisement

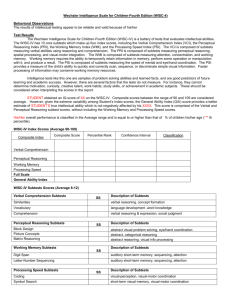
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV) The WAIS-IV is a battery of tests that provides an estimate of general intellectual functioning. Intelligence tests like this one are samples of problem solving abilities and learned facts, and are good predictors of future learning and academic success. However, there are several factors that the tests do not measure. For instance, they cannot determine motivation, curiosity, creative talent, work habits, study skills, or achievement in academic subjects. These should be considered when interpreting the scores in the report. The WAIS-IV has 10 core subtests which make up four index scores, including the Verbal Comprehension Index (VCI), the Perceptual Reasoning Index (PRI), the Working Memory Index (WMI), and the Processing Speed Index (PSI). The VCI is a measure of verbal concept formation, verbal reasoning, and knowledge acquired from one’s environment. The PRI is a measure of perceptual and fluid reasoning, spatial processing, and visual-motor integration. The WMI is a measure of working memory abilities, which involve attention, concentration, mental control and reasoning. Working memory tasks require the ability to temporarily retain information in memory, perform some operation or manipulation with it, and produce a result. The PSI is composed of subtests measuring the speed of mental and eye/hand coordination. The PSI provides a measure of the child’s ability to quickly and correctly scan, sequence, or discriminate simple visual information. This composite also measures short-term memory, attention, and visual-motor coordination. STUDENT obtained a Full Scale IQ score of ******on the WAIS-IV. The chances that his true score is between ******and ******are about 95 out of 100. Composite scores between the range of 90 and 109 are considered average. STUDENT’S overall performance is classified in the Average range and is equal to or higher than that of ******% of children his/her age (******th percentile). Student’s other Index scores are listed in the chart below. Student’s General Ability Index (GAI) is also represented. This score is calculated and derived from the Verbal Comprehension and Perceptual Reasoning subtests only, providing a summary score that is less sensitive to the influence of working memory and processing speed. WAIS-IV Index Scores (Average 90-109) Composite Index Composite Score Verbal Comprehension Perceptual Reasoning Working Memory Processing Speed General Ability Index Full Scale WAIS-IV Subtests Scores (Average 8-12) Verbal Comprehension Subtests Similarities Vocabulary Information Perceptual Reasoning Subtests Block Design Matrix Reasoning Visual Puzzles Working Memory Subtests Digit Span Arithmetic Processing Speed Subtests Symbol Search Coding Interpretation: SS Percentile Rank Confidence Interval Classification Ability measured Verbal reasoning and verbal concept formation Word knowledge and verbal concept formation Ability to acquire, retain, and retrieve general factual knowledge Ability to analyze and synthesize abstract visual stimuli Fluid intelligence, spatial ability, perceptual organization and simultaneous processing Nonverbal reasoning, ability to analyze and synthesize abstract visual stimuli Three memory tasks measure rote learning and memory, attention, auditory processing, mental manipulation, and working memory Mental manipulation, concentration, attention, short and longterm memory, and numerical reasoning Processing speed, short-term visual memory, visual motor coordination, visual discrimination Processing speed, short-term visual memory, psychomotor speed, visual-motor coordination