PowerPoint Presentation - The WISC-IV: Using Intelligence Tests in
advertisement

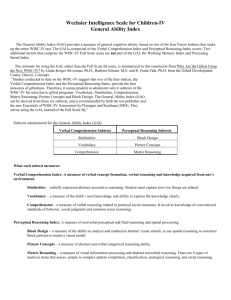
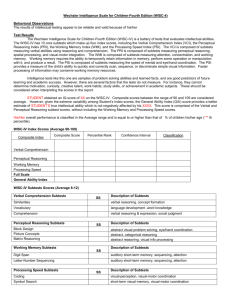
The WISC-IV HT820: Introduction to PsychoEducational Assessment Purpose of the WISC-IV The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for children – Fourth Edition is the latest version of the intelligence test for children ages 6 through 16. The WISC-IV yields measures of general intelligence and specific indices including verbal comprehension, perceptual reasoning, working memory and processing speed Materials Needed Administration and scoring manual Technical and interpretive manual Record form Stimulus book Response booklet 1 and 2 Block design blocks Scoring key for Coding Scoring key for Symbol Search Cancellation scoring template #2 Pencil without eraser Red pencil without eraser Directions for Administration Administer tests in order designated on record form. Start points are age-specific and 6-8 are marked in record form with a black arrow The basal consists of two correct items in a row. If the basal is not reached, reversal items are administered in reverse sequence until basal is reached. Full credit is awarded for all items below basal even if accidentally administered and missed. The ceiling consists of a specified number of incorrect items in a row. Award no credit for items beyond ceiling even if accidentally administered and answered correctly. Scripts are presented in examiner’s manual. WISC-IV Similarities Vocabulary Comprehension Information Word Reasoning Block Design Picture Concepts Matrix Reasoning Picture Completion FSIQ Digit Span Letter-Number Seq. Arithmetic Coding Symbol Search Cancellation Verbal Comprehension Index Similarities (SI): The child is presented with two words that represent common objects or concepts and describes how they are similar. Ex. Milk – Water Frown – Smile Space – Time Verbal Comprehension Index Vocabulary (VC): For picture items, the child names pictures that are displayed in the stimulus book. For verbal items, the child gives definitions for words that the examiner reads aloud. Ex. (picture) train (verbal) umbrella, absorb, garrulous Verbal Comprehension Index Comprehension (CO): The child answers questions based on his or her understanding of general principles and social situations. Ex. Why do people brush their teeth? Other concepts assessed: apologize, copyrights, democracy Verbal Comprehension Index Information (IN): The child answers questions that address a broad range of general knowledge topics. Ex. How many legs does a dog have? Who was Confucius? Where does turpentine come from? Verbal Comprehension Index Word Reasoning (WR): The child identifies the common concept being described in a series of clues. Ex. This is used to dry yourself after a bath. These are protected by skin and bones… And can sometimes be replaced. Perceptual Reasoning Index Block Design (BD): While viewing a constructed model or a picture in the stimulus book, the child uses red-andwhite blocks to re-create the design within a specified time limit. Ex. Perceptual Reasoning Index Picture Concepts (PC): The child is presented with two or three rows of pictures and chooses one picture from each row to form a group with a common characteristic. Ex. student desk candle table lamp beach ball basketball hoop chalkboard Perceptual Reasoning Index Matrix Reasoning (MR): The child looks at an incomplete matrix and selects the missing portion from five response options. Ex. Perceptual Reasoning Index Picture Completion (PCm): The child views a picture and then points to or names the important part missing within a specified time limit. Ex. pencil without lead tip pig without nostril river/bridge without waves on one side Working Memory Index Digit Span (DS): For digit span forward, the child repeats numbers in the same order as presented aloud by the examiner. For digit span backward, the child repeats numbers in the reverse order of that presented aloud by the examiner. Forward length ranges from 2 to 9. Backward length ranges from 2 to 8. Working Memory Index Letter-Number Sequencing (LN): The child is read a sequence of numbers and letters and recalls the numbers in ascending order and the letters in alphabetical order. Ex. 5-A-2-B S-3-K-4-Y-1-G AB25 or 25AB 134GKSY or GLSY134 Working Memory Index Arithmetic (AR): The child mentally solves a series of orally presented arithmetic problems within a specified time limit. Ex. (Picture): How many nuts will be left if each squirrel eats one? (No picture): If I cut an apple in half, how many pieces will I have? Processing Speed Index Coding (CD): The child copies symbols that are paired with simple geometric shapes or numbers. Using a key, the child draws each symbol in its corresponding shape or box within a specified time limit. Processing Speed Index Symbol Search (SS): The child scans a search group and indicates whether the target symbol(s) matches any of the symbols in the search group within a specified time limit. Example: zx target group bvpfk search group YES NO Processing Speed Index Cancellation (CA): The child scans both a random and a structured arrangement of pictures and marks target pictures within a specified time limit. In this exercise, a page is covered with pictures of animals and other common objects, either randomly scattered on the page or arranged in rows and columns. The child then marks through - or cancels - the animals as quickly as possibly. Directions for Scoring Calculate chronological age. Do not round up to nearest month. Raw scores are totaled on each page of the record sheet. Copy raw scores into front cover. Tables in examiner’s manual allow for conversion from raw score to scaled score using age-based norms (Mean 10, SD 3). Scaled scores for 10 core tests are summed to yield a composite Full Scale IQ score (Mean 100, SD 15). Scaled scores contributing to each index are summed and converted to composite scores using tables in examiner’s manual (Mean 100, SD 15). Inside cover provides analysis of discrepancy among scores and strength/weakness profile Validity Report Using factor analysis, studies show that WISC subtests correlate more highly with other subtest in the same index than subtests in different indices. Full scale IQ scores from the WISC-IV are highly correlated with IQ scores from other common IQ tests including: WISC-III, WPPSI-III, WAIS-III, WASI, WIATII, and CMS. The examiner’s manual also presents evidence that the WISC-IV differentiates children who have been diagnosed with mild/moderate mental retardation, ADHD, traumatic brain injury, autism, Asperger’s Syndrome, expressive language disorder, and giftedness. Reliability Report Using the split-half method, internal reliability for subtests ranged from .79 to .90. 243 children in the norm sample were tested a second time to evaluate testretest reliability. Reliability coefficients ranged from .76 on picture concepts to .92 on vocabulary.