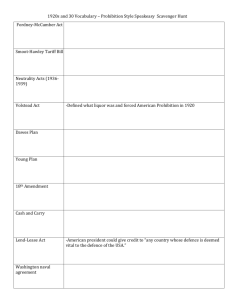
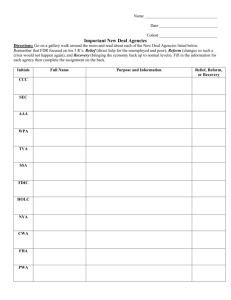
NEW DEAL ALPHABET AGENCIES
advertisement
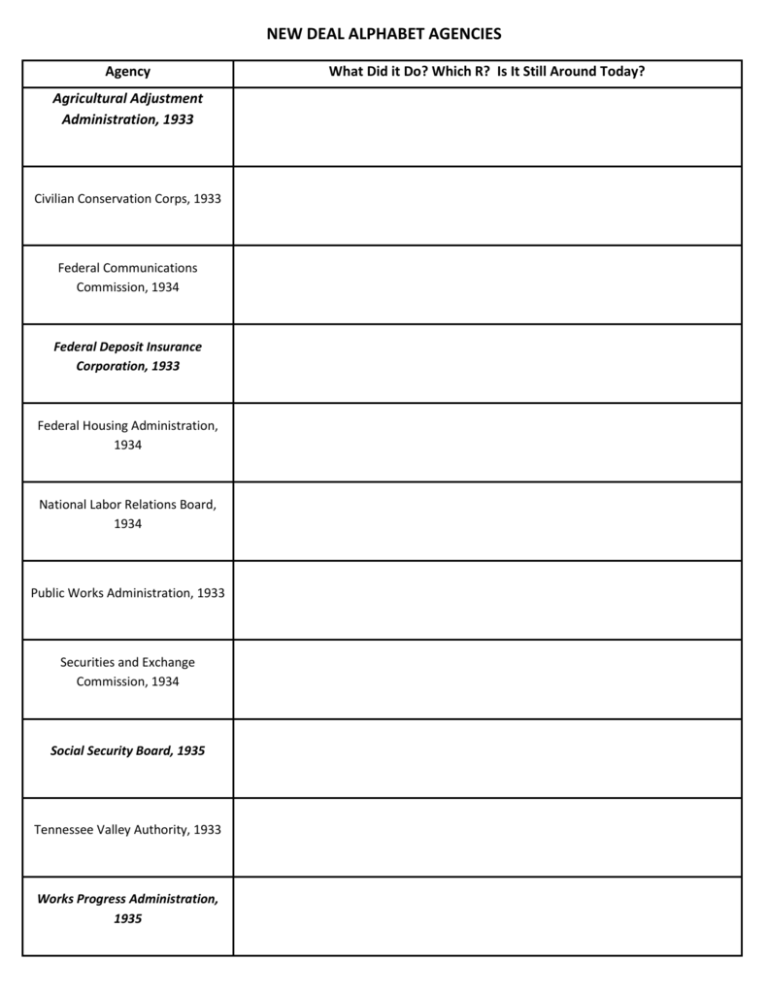
NEW DEAL ALPHABET AGENCIES Agency Agricultural Adjustment Administration, 1933 Civilian Conservation Corps, 1933 Federal Communications Commission, 1934 Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, 1933 Federal Housing Administration, 1934 National Labor Relations Board, 1934 Public Works Administration, 1933 Securities and Exchange Commission, 1934 Social Security Board, 1935 Tennessee Valley Authority, 1933 Works Progress Administration, 1935 What Did it Do? Which R? Is It Still Around Today? Agency Agricultural Adjustment Act, 1933 Civil Aeronautics Authority, 1933 Civilian Conservation Corps, 1933 Civil Works Administration, 1933 Emergency Banking Act, 1933 Farm Credit Administration, 1933 Federal Communications Commission, 1934 What Did it Do restricted agricultural production in the by paying farmers to reduce crop area. Its purpose was to reduce crop surplus so as to effectively raise the value of crops, thereby giving farmers relative stability.The farmers were paid subsidies by the federal government for letting a portion of their fields lie fallow. The money for these subsidies was generated through an exclusive tax on companies which processed farm products gave the authority the power to regulate airline fares and to determine the routes that air carriers would serve; CAA was responsible for air traffic control, safety programs, and airway development. The CAB was entrusted with safety rulemaking, accident investigation, and economic regulation of the airlines; now the FAA a public work relief program for unemployed men, providing vocational training through the performance of useful work related to conservation and development of natural resources in the United States from 1933 to 1942 – Skyline Drive create jobs for millions of unemployed. The jobs were merely temporary, for the duration of the hard winter; ended on March 31, 1934, under the advice of Lewis Douglas, after costing $200 million a month. So much was spent on this administration because it hired 4 million people and was mostly concerned with paying high wages allowed a plan that would close down insolvent banks and reorganize and reopen those banks strong enough to survive; The sense of urgency was such that the act was passed with only a single copy available on the floor and most legislators voted on it without reading it help farmers refinance mortgages over a longer time at below-market interest rates at regional and national banks. This helped farmers recover from the Dustbowl. The Emergency Farm Mortgage Act loaned funds to farmers in danger of losing their properties. The campaign refinanced 20% of farmer's mortgages; still around today jurisdiction over radio licensing Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, 1933 provides deposit insurance, which guarantees the safety of deposits in member banks, currently up to $250,000 per depositor per bank. The FDIC insures deposits at 8,195 institutions.[2] The FDIC also examines and supervises certain financial institutions for safety and soundness, performs certain consumer-protection functions, and manages banks in receiverships (failed banks); 1934 - $2,500; 1935 - $5,000; 1950 - $10,000 Federal Emergency Relief Administration, 1933 the first direct-relief operation under the New Deal; main goal was to alleviate adult unemployment;provided state assistance for the unemployed and their families. From when it began in May 1933 until it closed its operations in December 1935, it gave states and localities $3.1 billion to operate local work projects and transient programs Federal Housing Administration, 1934 Federal Music Project, 1935 intent was to regulate the rate of interest and the terms of mortgages that it insured; new lending practices increased the number of people who could afford a down payment on a house and a mortgage, thereby also increasing the size of the market for single-family homes; goals of this organization are: to improve housing standards and conditions; to provide an adequate home financing system through insurance of mortgage loans; and to stabilize the mortgage market part of the program Federal One, employed musicians, conductors and composers during the Great Depression. People in the music world had been particularly hard-hit by the era's economic downturn. In addition to performing thousands of concerts, offering music classes, organizing the Composers Forum Laboratory, hosting music festivals and creating 34 new orchestras, employees of the FMP researched American traditional music and folk songs; many people visited these symphonies to forget about the economic hardship of the time. Farm Security Administration, 1935 was an effort during the Depression to combat American rural poverty; stressed "rural rehabilitation" efforts to improve the lifestyle of sharecroppers, tenants, and very poor landowning farmers, and a program to purchase submarginal land owned by poor farmers and resettle them in group farms on land more suitable for efficient farming Federal Theatre Project, 1935 project to fund theatre and other live artistic. It was one of five Federal One projects sponsored by the Works Projects Administration (WPA). The FTP's primary goal was employment of out-of-work artists, writers, and directors, with the secondary aim of entertaining poor families and creating relevant art; 1939, the FTP was ended when its funding was canceled, largely attributed to strong Congressional objections to the overtly left-wing political tones of many FTP productions Fair Labor Standards Act, 1938 established a national minimum wage, guaranteed time and a half for overtime in certain jobs, and prohibited most employment of minors in "oppressive child labor," a term defined in the statute; applies to employees engaged in interstate commerce or employed by an enterprise engaged in commerce or in the production of goods for commerce Home Owners Loan Corporation, 1933 purpose was to refinance homes to prevent foreclosure. It was used to extend loans from shorter loans to fully amortized, longer term loans (typically 20-25 years). Through its work it granted long term mortgages to over a million people facing the loss of their homes National Industrial Recovery Act, 1933 authorized the President of the United States to regulate industry and permit cartels and monopolies in an attempt to stimulate economic recovery, and which established a national public works program; devoted to Industrial recovery and created the WPA; struck down as unconstitutional by SCOTUS in 1935 National Labor Relations Board, 1934 National Recovery Administration, 1933 charged with conducting elections for labor union representation and with investigating and remedying unfair labor practices; still around today allowed industries to create "codes of fair competition," which were intended to reduce "destructive competition" and to help workers by setting minimum wages and maximum weekly hours. It also allowed industry heads to collectively set price floors (from NIRA – above) National Youth Administration, 1935 it served 327,000 high school and college youth, who were paid from $6 to $40 a month for "work study" projects at their schools; Another 155,000 boys and girls from relief families were paid $10 to $25 a month for part-time work that included job training; youth normally lived at home, and worked on construction or repair projects Public Works Administration, 1933 concentrated on the construction of large-scale public works such as dams and bridges, with the goal of providing employment, stabilize purchasing power, and contribute to a revival of American industry; The PWA spent over $6 billion, and helped to push industry back toward pre-Depression levels. It lowered unemployment and created an infrastructure that generated local pride in the 1930s and remains vital seven decades later Resettlement Administration, 1935 between April 1935 and December 1936, relocated struggling urban and rural families to communities planned by the federal government; The RA worked with nearly 200 communities on its projects, notably including: Greenbelt, MD (completely planned by RA); Hickory Ridge (now in Prince William Forrest) Rural Electrification Administration, 1935 charged with providing public utilities (electricity, telephone, water, sewer) to rural areas in the United States via public-private partnerships; REA made loans available to local electrification cooperatives, which operated lines and distributed electricity; today is Rural Utilities Service Securities and Exchange Commission, 1934 main reason for the creation of the SEC was to regulate the stock market and prevent corporate abuses relating to the offering and sale of securities and corporate reporting. The SEC was given the power to license and regulate stock exchanges, the companies whose securities traded on them, and the brokers and dealers who conducted the trading Social Security Board, 1935 administers Social Security, a social insurance program consisting of retirement, disability, and survivors' benefits. To qualify for these benefits, most American workers pay Social Security taxes on their earnings; future benefits are based on the employees' contributions; created when social security was created Tennessee Valley Authority, 1933 created by congressional charter in May 1933 to provide navigation, flood control, electricity generation, fertilizer manufacturing, and economic development in the Tennessee Valley, a region particularly impacted by the Great Depression; TVA's service area covers most of Tennessee, parts of Alabama, Mississippi, and Kentucky, and small slices of Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, West Virginia, Indiana and Virginia Works Progress Administration, 1935 was the largest New Deal agency, employing millions to carry out public works projects, including the construction of public buildings and roads, and operated large arts, drama, media, and literacy projects. It fed children and redistributed food, clothing, and housing. Almost every community in the United States had a park, bridge or school constructed by the agency, which especially benefited rural and Western populations. Expenditures from 1936 to 1939 totaled nearly $7 billion; until 1943, the WPA was the largest employer in the country 1. AAA - Agricultural Adjustment Act, 1933 2. CAA - Civil Aeronautics Authority (now Federal Aviation Administration), 1933 3. CCC - Civilian Conservation Corps, 1933 4. CWA - Civil Works Administration, 1933 5. EBA - Emergency Banking Act, 1933 6. FCA - Farm Credit Administration, 1933 7. FCC - Federal Communications Commission, 1934 8. FDIC - Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, 1933 9. FERA - Federal Emergency Relief Administration, 1933 10. FHA - Federal Housing Administration, 1934 11. FMP - Federal Music Project, part of WPA 1935 12. FSA - Farm Security Administration, 1935 13. FTP - Federal Theatre Project, part of WPA 1935 14. FLSA - Fair labor standards act , 1938 15. HOLC - Home Owners Loan Corporation, 1933 16. NIRA - National Industrial Recovery Act, 1933 17. NLRB - National Labor Relations Board, 1934 18. NRA - National Recovery Administration, 1933 19. NYA - National Youth Administration, part of WPA 1935 20. PWA - Public Works Administration, 1933 21. RA - Resettlement Administration, 1935 22. REA - Rural Electrification Administration (now Rural Utilities Service), 1935 23. SEC - Securities and Exchange Commission, 1934 24. SSB - Social Security Board (now Social Security Administration), 1935 25. TVA - Tennessee Valley Authority, 1933 26. USHA - United States Housing Authority, 1937 27. WPA - Works Progress Administration, 1935