Document
advertisement

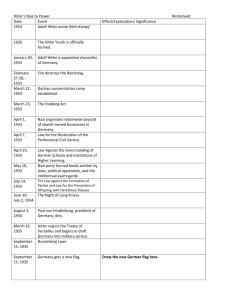
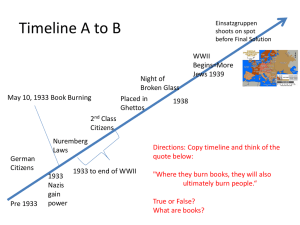
Holocaust • Nature of the Task • Impact – demographic – qualitative destruction – the State of Israel??? Holocaust History • how does it differ from World War II history? • what are its tasks? • impact on Jewish identity has been both immediate and slow: – war against the Jews aimed at extermination – theological -- is there religious significance? – world reaction; nature of international power Stage I (1933-39) • • • • • • Jan. 30, 1933 Nazis come to power c. 500,000 Jews within 65,000,000 April 1, 1933 mass boycott April 4, 1933 eliminated from civil service April 22, 1933 social security eliminated April 26, 1933 quotas in schools Cont. • May 10, 1933 book burning • Sept. 15, 1935 Nuremberg Laws revoke emancipation • 1938 Aryanization of Jewish corporations • Anschluss imposes all laws in Austria Kristallnacht • 1938 Polish Jews expelled and forced into detention centers • November 6, 1938. Hershel Grynspan kills Ernest von Rath in Paris • November 9-10, 1938. Anti-Jewish rampage in Germany. Night of the Broken Glass. Burnings, arrests and beatings Jewish Reaction • 160,000 flee – restrictions in Palestine, America, elsewhere • creation of independent schools and selfhelp organization • suicide Final Solution • not officially adopted until 1941 period of total war Ghettoization • Warsaw: 1940 500,000 in 1500 buildings • questions of Jewish leadership • Chaim Rumkowski (Lodz) Adam Czerniakow (Warsaw) • this is not the pre-modern ghetto • stages: segregation; strangulation; deportation and liquidation • illusory continuity of normalcy Jewish Reactions • the Jews don’t know how to react to this unprecedented institution • initial hope of status quo gives way to snatching at any hope • traditional philosophy of patience is abandoned only gradually • most enlightened are the least able to cope Passivity? • • • • • ability to react is clear experience misleads passive restraint active demoralization by Germans this issue remains as a defining topic in later years Ghettoization (cont.) • education; medical research • inversion of values; smuggling is necessary to survive • competing leadership centers; youth movements • Ghetto humor (“Hitlerplatz”) Jewish Response • • • • organization in the ghettos inversion of moral code and predictability partisans tradition of survival are now useless Massive Exterminations • 1941 Russian invasion: Einsatzgruppen – (cf. Christopher Browning, Ordinary Men, and Daniel Jonah Goldhagen, Hitler’s Willing Executioners) • death camps – Chelmno 1941 – Auschwitz 1942 etc Concentration Camps • loss of personality – Bruno Bettelheim, “Individual and Mass Behavior in Extreme Situations” – Primo Levi, Survival in Auschwitz and The Truce • invention of a rhetoric of suffering and dignity -- “lest we forget” Concentration Camps (cont.) • • • • • • • total loss of personality train ride in box cars ends space demarcations selection; numbered; shorn; Arbeit macht frei; reversal of status and role definitions end of predictability racial anti-Semitism has reached its apex no limit on human behavior; not hell but a toilet Power and Survival • odd cases of Bulgaria, Finland and Denmark • could this have been extended? • internal affair • UN commission for Refugees • international commission 1938 • 1939 white paper • 1938 32-power conference; no quota revision • Britain – 1941 Stürmer sunk – neutrality between Jews and Arabs – Dec. 17, 1942 Parliament stands in silence • April 1943 Bermuda conference