Science Skeleton Plan. Y6 ELECTRICITY
advertisement
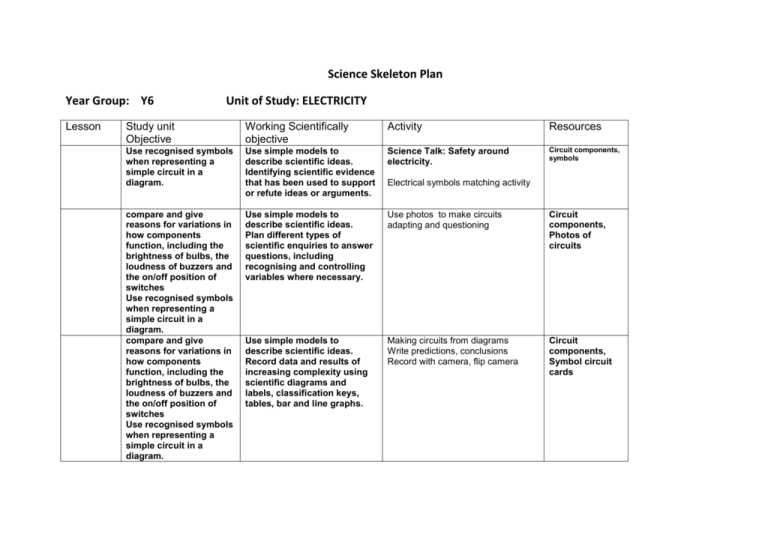
Science Skeleton Plan Year Group: Y6 Lesson Unit of Study: ELECTRICITY Study unit Objective Working Scientifically objective Activity Resources Use recognised symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram. Use simple models to describe scientific ideas. Identifying scientific evidence that has been used to support or refute ideas or arguments. Science Talk: Safety around electricity. Circuit components, symbols compare and give reasons for variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off position of switches Use recognised symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram. compare and give reasons for variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off position of switches Use recognised symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram. Use simple models to describe scientific ideas. Plan different types of scientific enquiries to answer questions, including recognising and controlling variables where necessary. Use photos to make circuits adapting and questioning Circuit components, Photos of circuits Use simple models to describe scientific ideas. Record data and results of increasing complexity using scientific diagrams and labels, classification keys, tables, bar and line graphs. Making circuits from diagrams Write predictions, conclusions Record with camera, flip camera Circuit components, Symbol circuit cards Electrical symbols matching activity compare and give reasons for variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off position of switches Use recognised symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram. associate the brightness of a lamp or the volume of a buzzer with the number and voltage of cells used in the circuit compare and give reasons for variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off position of switches use recognised symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram associate the brightness of a lamp or the volume of a buzzer with the number and voltage of cells used in the circuit compare and give reasons for variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the Use simple models to describe scientific ideas. Plan different types of scientific enquiries to answer questions, including recognising and controlling variables where necessary. Set challenges- volume/ brightness Set up sequence of lights varying battery / voltage Light / wattage (1 min challenge) Make predictions, discuss variables. Record in circuit diagrams Circuit components, timers Use simple models to describe scientific ideas. Use test results to make predictions to set up further comparative and fair tests. Report and present findings from enquiries, including conclusions, causal relationships and explanations of results, in oral and written forms such as displays and other presentations. Planning – Traffic Lights How could it be done? Variables? Hypotheses Plan test record - ICT Circuit components, s Access to all circuit components to select appropriate materials Use simple models to describe scientific ideas. Use test results to make predictions to set up further comparative and fair tests. Report and present findings from enquiries, including conclusions, causal relationships and explanations of results, in oral Carry out investigation and evaluate What would you change? Photo / video evidence Link to ICT program on Control. Circuit components, timers loudness of buzzers and the on/off position of switches use recognised symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram and written forms such as displays and other presentations.