REVIEW: Chapter 8 - Covalent Bonding
advertisement
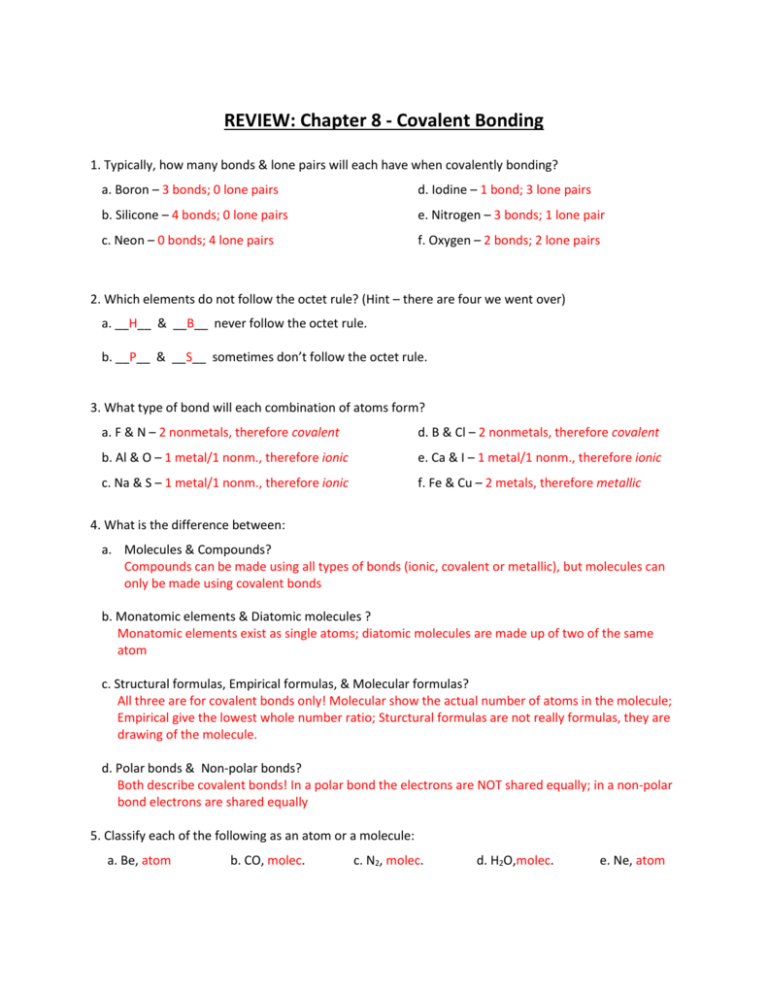
REVIEW: Chapter 8 - Covalent Bonding 1. Typically, how many bonds & lone pairs will each have when covalently bonding? a. Boron – 3 bonds; 0 lone pairs d. Iodine – 1 bond; 3 lone pairs b. Silicone – 4 bonds; 0 lone pairs e. Nitrogen – 3 bonds; 1 lone pair c. Neon – 0 bonds; 4 lone pairs f. Oxygen – 2 bonds; 2 lone pairs 2. Which elements do not follow the octet rule? (Hint – there are four we went over) a. __H__ & __B__ never follow the octet rule. b. __P__ & __S__ sometimes don’t follow the octet rule. 3. What type of bond will each combination of atoms form? a. F & N – 2 nonmetals, therefore covalent d. B & Cl – 2 nonmetals, therefore covalent b. Al & O – 1 metal/1 nonm., therefore ionic e. Ca & I – 1 metal/1 nonm., therefore ionic c. Na & S – 1 metal/1 nonm., therefore ionic f. Fe & Cu – 2 metals, therefore metallic 4. What is the difference between: a. Molecules & Compounds? Compounds can be made using all types of bonds (ionic, covalent or metallic), but molecules can only be made using covalent bonds b. Monatomic elements & Diatomic molecules ? Monatomic elements exist as single atoms; diatomic molecules are made up of two of the same atom c. Structural formulas, Empirical formulas, & Molecular formulas? All three are for covalent bonds only! Molecular show the actual number of atoms in the molecule; Empirical give the lowest whole number ratio; Sturctural formulas are not really formulas, they are drawing of the molecule. d. Polar bonds & Non-polar bonds? Both describe covalent bonds! In a polar bond the electrons are NOT shared equally; in a non-polar bond electrons are shared equally 5. Classify each of the following as an atom or a molecule: a. Be, atom b. CO, molec. c. N2, molec. d. H2O,molec. e. Ne, atom 6. How many diatomic elements are there? __7__ List the diatomic elements: Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, F 7. How many monatomic elements are there? __6__ List them: He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn 8. Complete the table with differences between ionic & covalent compounds: Covalent Ionic Non-metals Metal & non-metal Bond strength… weaker stronger Melting point… Lower Higher Gas or liquid Solid Shared Gained/lost Type of element… State @ room temp… Electrons are… 9. Draw the structure of each covalent molecules. They may contain single, double, or triple bonds: See drawing posted in classroom 10. Would a bond between the following elements be polar or non-polar? a. C & I – non-polar, because they have the same electronegativity & they will share electrons equally b. Si & N – polar, b/c they have diff. electronegatity & nitrogen will ‘hog’ the electrons they are sharing c. H & H – non-polar, b/c they’re the same atom & have the same electronegatity & will share e- equally 11. Draw each molecules; label the dipoles, if any; identify each molecule as polar or non-polar a. PH3 – polar b/c bonds are not all opposite eachother (the lone pair on P is throwing it off) b. CF4 - nonpolar b/c all the bonds are equal and opposite of each other c. SiHF3 – polar b/c the bonds are not all equal (3 are to F, but 1 is to H) d. N2 – nonpolar b/c all the same atom, therefore they share the e- equally e. ClCN – nonpolar, b/c the atoms are different but Cl & N have the same electronegativity, therefore they are equal and opposite each other 12. Write formulas for the following covalent compounds: a. hexaboron nonasilicide – B6Si9 b. chlorine dioxide – ClO2 c. hydrogen diiodide – HI2 d. triIodine octafluoride – I3F8 e. dicarbon monosulfide – C2S f. dinitrogen heptoxide – N2O7 13. Write the names for the following covalent compounds: a. P4S5 – tetraphosphorous pentasulfide b. SeF6 – selenium hexaflouride c. B2Si7 – diboron heptasilicide d. NF7 – nitrogen heptaflouride e. S3O9 – trisulfur nonaoxide f. Si4O8 – tetrasilicon octaoxide 14. Complete the table: Nitrogen Trihydride Dicarbon Dihydride Molecular Formula NH3 C2H2 Empirical Formula NH3 CH Structural Formula Drawing should be: Nitrogen has 1 lone pair, and a single bond to each hydrogen H–C=C–H # Lone Pairs in molecule 1 (on Nitrogen) 0