Gravimetric Determination of Iron Lab Report
advertisement
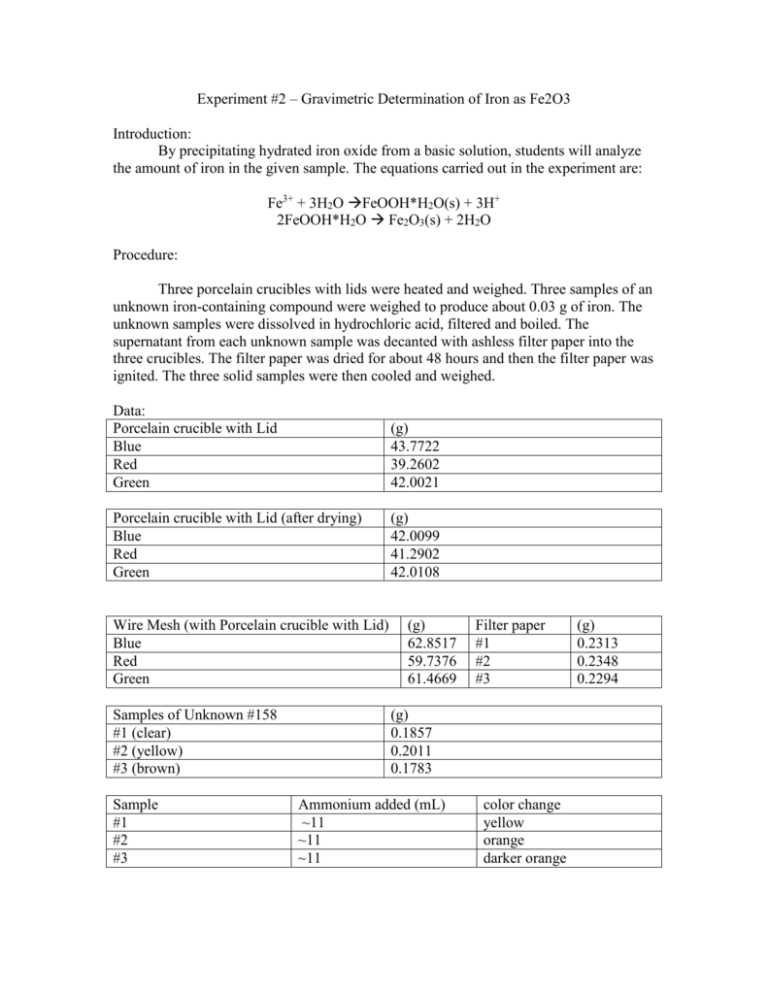
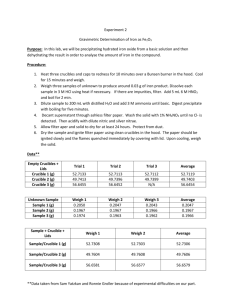
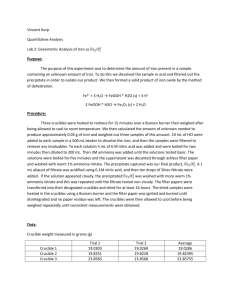
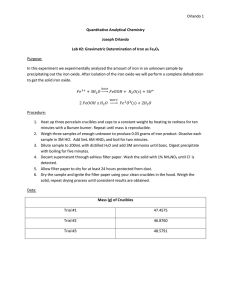
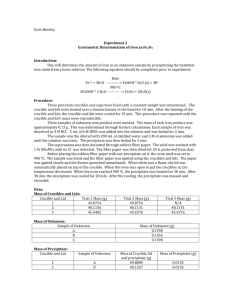
Experiment #2 – Gravimetric Determination of Iron as Fe2O3 Introduction: By precipitating hydrated iron oxide from a basic solution, students will analyze the amount of iron in the given sample. The equations carried out in the experiment are: Fe3+ + 3H2O FeOOH*H2O(s) + 3H+ 2FeOOH*H2O Fe2O3(s) + 2H2O Procedure: Three porcelain crucibles with lids were heated and weighed. Three samples of an unknown iron-containing compound were weighed to produce about 0.03 g of iron. The unknown samples were dissolved in hydrochloric acid, filtered and boiled. The supernatant from each unknown sample was decanted with ashless filter paper into the three crucibles. The filter paper was dried for about 48 hours and then the filter paper was ignited. The three solid samples were then cooled and weighed. Data: Porcelain crucible with Lid Blue Red Green (g) 43.7722 39.2602 42.0021 Porcelain crucible with Lid (after drying) Blue Red Green (g) 42.0099 41.2902 42.0108 Wire Mesh (with Porcelain crucible with Lid) Blue Red Green Samples of Unknown #158 #1 (clear) #2 (yellow) #3 (brown) Sample #1 #2 #3 (g) 62.8517 59.7376 61.4669 Filter paper #1 #2 #3 (g) 0.1857 0.2011 0.1783 Ammonium added (mL) ~11 ~11 ~11 color change yellow orange darker orange (g) 0.2313 0.2348 0.2294 Final Weight (weighed 4 times) (g) Blue Red Green #1 42.1341 39.3058 43.8056 #2 42.1351 39.3067 43.8064 #3 42.1355 39.3070 42.8070 #4 42.1356 39.3073 43.8072 average 42.1351 39.3067 43.8066 Calculations: 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐹𝑒2𝑂3 2 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 256.975 𝑔 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 0.03𝑔 × 159.691 𝑔 𝐹𝑒2𝑂3 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐹𝑒2𝑂3 × 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑜𝑓 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 = 0.1 𝑔 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 With the assumption that the unknown contains ~75% ferrous ammonium sulfate: 0.1𝑔 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 = 0.133 𝑔 𝑢𝑛𝑘𝑛𝑜𝑤𝑛 0.75 𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑢𝑠 𝑎𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑛𝑖𝑢𝑚 𝑠𝑢𝑙𝑓𝑎𝑡𝑒 Post Lab Questions: A. The biggest source of error was losing product due to changing glassware. For example, we moved the solution from Erlenmeyer flasks to beakers. Our results justify this because we had less than we expected. B. Nitric acid is used to precipitate the iron out of the solution in step 3. C. Gravimetric analysis is the method of determining an analyte based on the mass of a solid using quantitative properties. D. Specify the container in which to put the solution and specify how to burning the paper in the crucible, oven vs. Bunsen burner. Conclusions: The experiment was a good representation of the technique of gravimetric analysis. Although some of the results varied greatly (sample 2), the majority of them were sound. It proves that this is a decent demonstration of analysis. Sources of error were all human. There would be no changes to this lab in the future to ensure better results.