Introduction to Linguistics Syllabus
advertisement
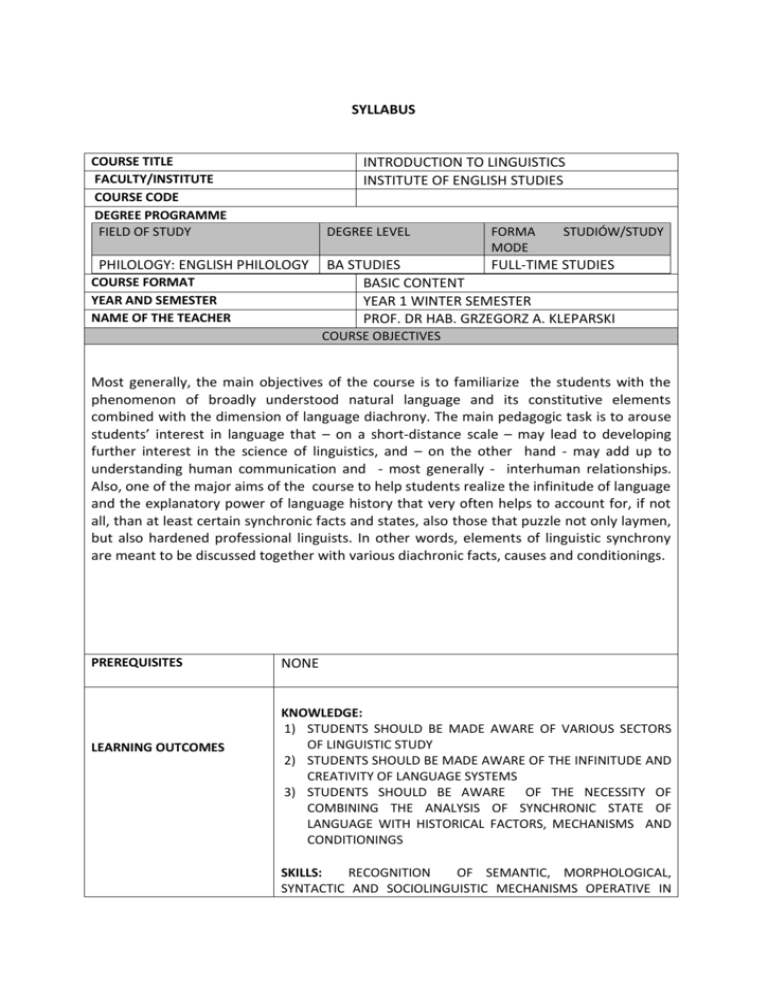
SYLLABUS COURSE TITLE FACULTY/INSTITUTE COURSE CODE DEGREE PROGRAMME FIELD OF STUDY INTRODUCTION TO LINGUISTICS INSTITUTE OF ENGLISH STUDIES DEGREE LEVEL PHILOLOGY: ENGLISH PHILOLOGY COURSE FORMAT YEAR AND SEMESTER NAME OF THE TEACHER FORMA MODE STUDIÓW/STUDY BA STUDIES FULL-TIME STUDIES BASIC CONTENT YEAR 1 WINTER SEMESTER PROF. DR HAB. GRZEGORZ A. KLEPARSKI COURSE OBJECTIVES Most generally, the main objectives of the course is to familiarize the students with the phenomenon of broadly understood natural language and its constitutive elements combined with the dimension of language diachrony. The main pedagogic task is to arouse students’ interest in language that – on a short-distance scale – may lead to developing further interest in the science of linguistics, and – on the other hand - may add up to understanding human communication and - most generally - interhuman relationships. Also, one of the major aims of the course to help students realize the infinitude of language and the explanatory power of language history that very often helps to account for, if not all, than at least certain synchronic facts and states, also those that puzzle not only laymen, but also hardened professional linguists. In other words, elements of linguistic synchrony are meant to be discussed together with various diachronic facts, causes and conditionings. PREREQUISITES LEARNING OUTCOMES NONE KNOWLEDGE: 1) STUDENTS SHOULD BE MADE AWARE OF VARIOUS SECTORS OF LINGUISTIC STUDY 2) STUDENTS SHOULD BE MADE AWARE OF THE INFINITUDE AND CREATIVITY OF LANGUAGE SYSTEMS 3) STUDENTS SHOULD BE AWARE OF THE NECESSITY OF COMBINING THE ANALYSIS OF SYNCHRONIC STATE OF LANGUAGE WITH HISTORICAL FACTORS, MECHANISMS AND CONDITIONINGS SKILLS: RECOGNITION OF SEMANTIC, MORPHOLOGICAL, SYNTACTIC AND SOCIOLINGUISTIC MECHANISMS OPERATIVE IN LANGUAGE, AND THE ABILITY TO ILLUSTATE THEM WITH ILLUSTRATIVE LANGUAGE DATA FINAL COURSE OUTPUT - SOCIAL COMPETENCES 1) AWARENESS OF THE EXISTENCE OF LANGUAGE DIFFERENCES 2) AWARNESS OF THE MANIPULATIVE POWER OF LANGUAGE 3) TOLERANCE FOR OTHER VARIANTS OF THE SAME LANGUAGE (OTHER THAN OWNS OWN) COURSE ORGANISATION –LEARNING FORMAT AND NUMBER OF HOURS LECTURE – 30 HOURS COURSE DESCRIPTION The course starts with the general description of linguistics as a science and a brief account of the history of linguistic analysis Further, the following areas of linguistic enquiry will be covered: 1) Animal systems of communication, 2) Features of natural languages, 3) Theories of language origin, 4) Diachronic, synchronic and panchronic approaches to language analysis, 5) Word-formation and word-formation mechanisms, 6) Semantic relations, 7) The mechanisms of semantic change, 8) Phraseology, 9) Sociolinguistics, 10) Language history and its explanatory power METHODS OF INSTRUCTION REQUIREMENTS AND ASSESSMENTS GRADING SYSTEM TOTAL STUDENT WORKLOAD NEEDED TO ACHIEVE EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES EXPRESSED IN TIME AND ECTS CREDIT POINTS LANGUAGE OF INSTRUCTION INTERNSHIP LECTURE WRITTEN EXAM 60 % PASSMARK 30 HOURS(LECTURE), 60 HOURS (EXAM PREP) 3ECTS ENGLISH NONE MATERIALS PRIMARY OR REQUIRED BOOKS/READINGS: FINEGAN, E. 1. Finegan, E. (1999) Language: Its Structure and Use. Fort Worth. 2. Fromkin, V., Rodman, R. (1993) An Introduction to Language. Fort Worth 3. Kieltyka, R., G.A. Kleparski. (2014) The Rudiments of the History of English. Rzeszów. SUPPLEMENTAL OR OPTIONAL BOOKS/READINGS: 1. Stekauer, P. (1993) Essentials of English Linguistics. Presov. 2. De Saussure, F.: Kurs językoznawstwa ogólnego. Warszawa 2000.