motor neurons that info
advertisement
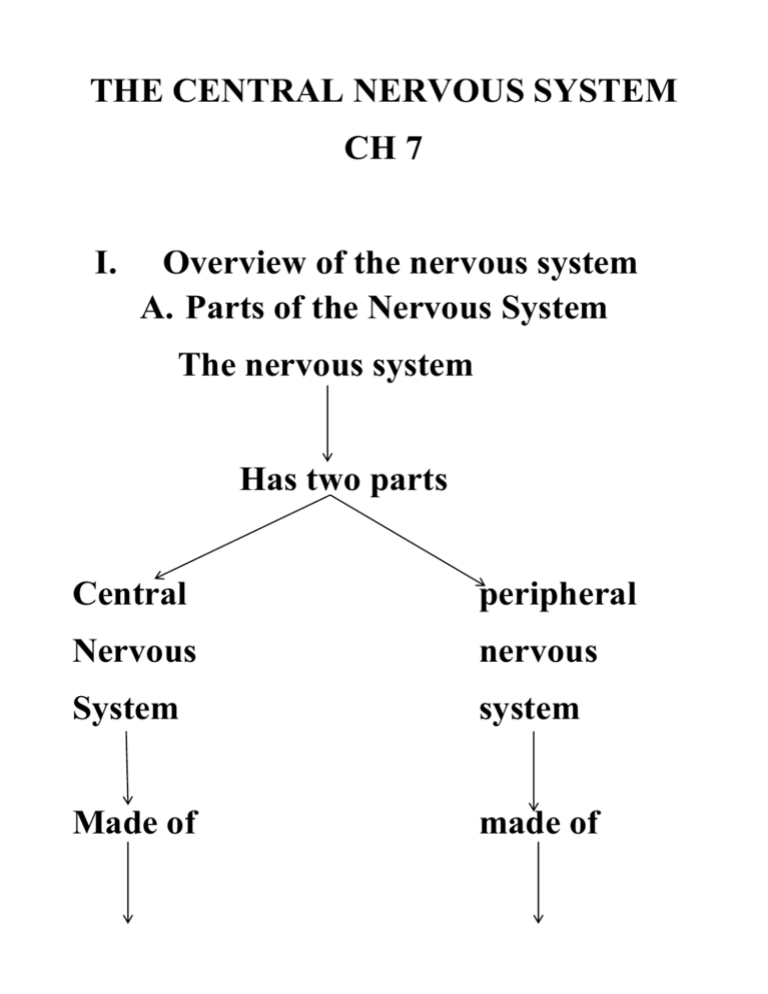
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM CH 7 I. Overview of the nervous system A. Parts of the Nervous System The nervous system Has two parts Central peripheral Nervous nervous System system Made of made of Brain and spine all other nerves B. Overview of How the Nervous System Works Receptors in sense organs pick up info from environment They send info to sensory neurons in the peripheral nervous system Sensory neurons send info to brain /spine in central nervous system Interneurons of the central nervous system processes the info and sends it to motor neurons in peripheral nervous system Motor neurons activate muscles to contract C. Structure of a Neuron dendrites Cell body axon Axon terminal Collateral branch Presynaptic cell Postsynaptic cell Dendrites: receive info from sense receptors or other neurons Cell body: contains all the organelles Axon: send info to other neurons or to muscle cells Axon terminals: where the neuron comes in contact with the next cell Synapse: the gap between 2 cells where the neuron communicates with another cell Presynaptic cell: the cell sending the info Post synaptic cell: the cell receiving the info D. Anatomical classes of Neurons Unipolar neuron: sense neurons that send info to CNS are unipolar Bipolar neuron: rare and found in sense organs Multipolar neuron: motor neurons that receive info from CNS are multipolar E. Neuroglia of the CNS: cells that support and protect the neurons of the CNS Ependymal cells: line the fluid filled cavity that the brain and spine sit in. This cavity has cerebrospinal fluid Microglia: cells that get rid of waste and foreign invaders from the CNS Oligodendrocytes: make myelin that forms myelin sheath o Myelin sheath: speeds up the transmission of nerve impulses F. Neuroglia of the PNS: Schwann cells: form a sheath around the axons of peripheral neurons Satellite cells: surround cell body of peripheral neurons II. How the Nervous System Sends Information Resting Membrane potential: the difference in charge between the inside of the neuron and its surrounding environment When the neuron is stimulated it disrupts this resting membrane potential sending a “wave” down the neuron called the action potential The action potential starts in the dendrites, moves through the cell body, and down the axon When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, neurotransmitters are released into the synapse and start the action potential in the next neuron http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__the_nerve_im pulse.html http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__chemical_synapse__quiz_2 _.html III. Anatomy of the CNS A. The Main Parts of the Brain cerebrum diencephalon midbrain cerebellum pons Medulla oblongata Cerebrum: highly convoluted. Involved in conscious thought, memory storage and processing, sensory processing, regulation of skeletal muscle Cerebellum: involved in coordinating the motor commands from the cerebrum Midbrain: processes visual and auditory stimuli. Controls reflexes Pons: connects cerebellum to brain stem Medulla oblongata: regulates breathing, heart rate, and digestive system activities B. The Parts of the Cerebrum Parietal lobe Frontal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Frontal lobe: reasoning, planning, problem solving, speech Parietal lobe: movement, orientation, recognition, perception Occipital lobe: visual processing Temporal lobe: auditory perception memory, speech http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vy8 EvyQoQIE C. What protects the brain? Bones of the cranium Cerebrospinal fluid: the fluid that surrounds the brain and spine Cranial meninges: connective tissue that separates the cranium from the brain and contains the cerebrospinal fluid D. The Cerebrum has 2 hemispheres Each hemisphere controls specific functions not performed by the other hemisphere The two hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum The right visual field is in left hemisphere The motor cortex that controls left hand is larger in right hemisphere Are left handed people more artistic and right handed people more analytical? IV. The Spinal Cord Contains the nerves that control the body At various points on the spinal cord, a pair of spinal nerves branches off Each pair of spinal nerves controls a different part of the body There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves