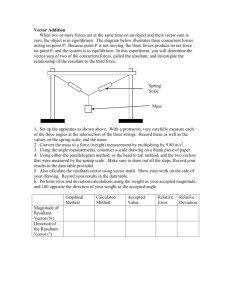
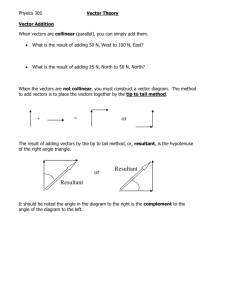
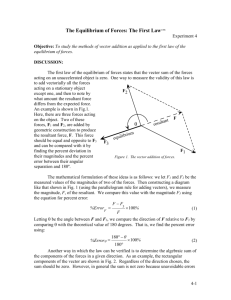
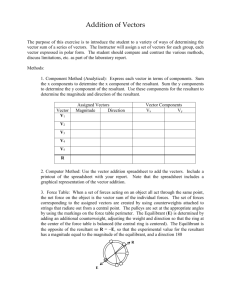
Vector Resolution Skill Builder
advertisement

Resultant Forces Skill Development 1. a) b) c) An object has a mass of 23.6 kg. What is its weight? In order to accelerate at 2.15 m/s2, 7.39 kg mass requires a specific force. What is that force? How much mass will accelerate at 3.11 m/s2 when a 3.65 N force is applied? 2. A mass is suspended with a string. Draw a free-body diagram showing the forces acting on the mass. 3. An 11.0 kg block is on a frictionless table. The block has an applied force of 18.0 N force applied to it. What is its acceleration? Draw a free-body diagram for this situation. 4. Two forces are applied to a 3.25 kg block on a frictionless surface. The first force of 12.9 N [E] acts simultaneously with another force of 7.32 N [W] (think tug-of-war). a. Place the block at the origin of the number line and draw the vector diagram for these forces. b. Write the vector equation for the sum of these two forces. c. Find the sum of the forces algebraically. 5. A block has a 16.4 N force acting at an angle 43.0 ° 𝑆 𝑜𝑓 𝑊. Use the space provided. a. Place the block at the origin of the Cartesian plane and draw the vector diagram for this force. b. Draw the x-component of this force. Is it a positive or negative component? c. Draw the y-component of this force. Is it a positive or negative component? d. What is the standard angle equivalent of this angle? e. Calculate the magnitude of the x-component of this force. Show your work. f. Calculate the magnitude of the y-component of this force. Show Resultant Forces Skill Development your work. g. Write the vector equation for this diagram. h. What is the acceleration of the block if its mass is 3.69 kg? Resultant Forces Skill Development 6. Two forces act on a 7.32 kg mass. One force is 6.42 N from the North and the other is 9.12 N from the East. a. Draw the vector diagram for this problem. b. Write the vector equation for the addition of these two forces? c. Show the Pythagorean formula for these forces. d. Rewrite the formula and solve for the resultant force. e. Write the trigonometric formula that will let you solve for the direction of the resultant force. f. What is the angle of the resultant force? g. What is the (vector) acceleration of this mass? 7. Two forces act on a 9.65 kg mass. One force is 45.60 N 27.0° 𝑁 𝑜𝑓 𝑊and the other is 28.12 N 15.5° 𝑆 𝑜𝑓 𝑊. a. Draw the vector diagram for this problem. b. Measure the vector length and angle from this diagram. c. Write the vector equation for the addition of these two forces? d. Find the x-components of each of these vectors. e. Find the y-components of each of these vectors. f. Find the sum of the x-components. g. Find the sum of the y-components h. Show the diagram for the vector sum of the these two summation vectors (x-, and y-components.) i. Show the Pythagorean formula for the sum of these two components. j. Rewrite the formula and solve for the resultant force. k. Write the trigonometric formula that will let you solve for the direction of the resultant force. l. What is the angle of the resultant force? m. What is the (vector) acceleration of this mass? 8. A 3.78 kg mass is acted upon by two forces to give it a net acceleration of 5.48 m/s2 at an angle of 30.0 ° N of E. If one of the forces is 38.4 N acting toward the East, what is the magnitude and direction of the other force?