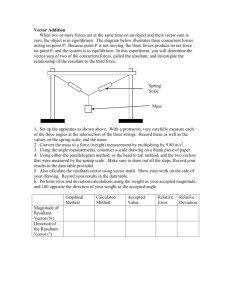
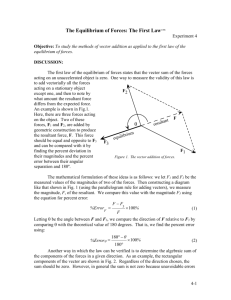
Vector Addition Lab: Methods & Analysis
advertisement
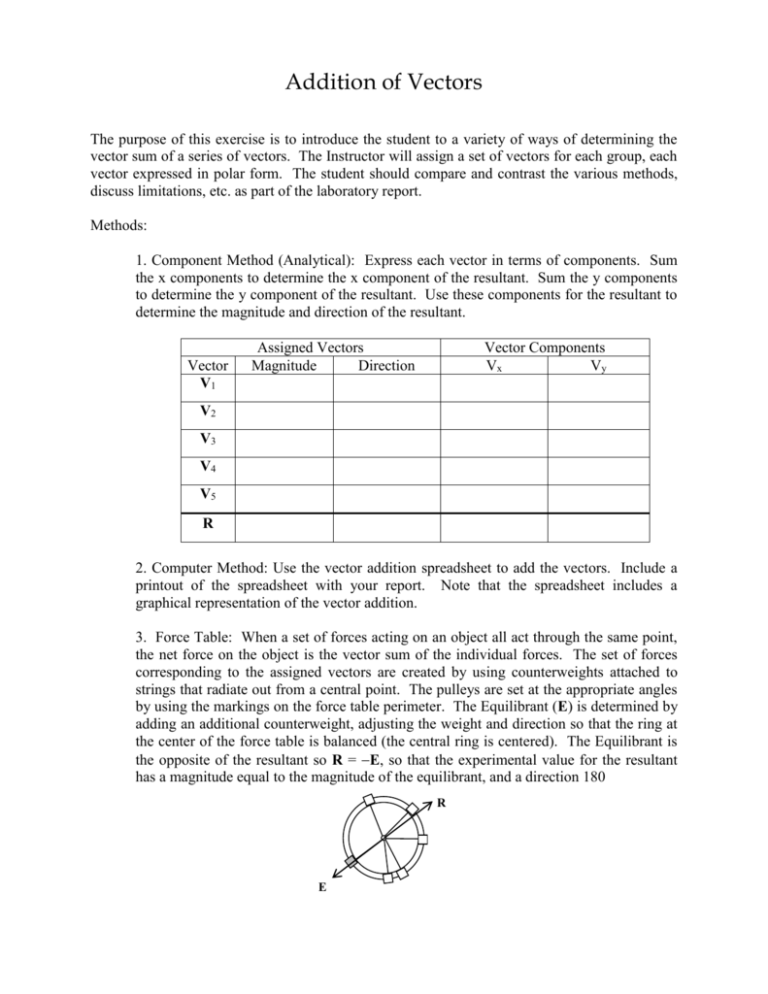
Addition of Vectors The purpose of this exercise is to introduce the student to a variety of ways of determining the vector sum of a series of vectors. The Instructor will assign a set of vectors for each group, each vector expressed in polar form. The student should compare and contrast the various methods, discuss limitations, etc. as part of the laboratory report. Methods: 1. Component Method (Analytical): Express each vector in terms of components. Sum the x components to determine the x component of the resultant. Sum the y components to determine the y component of the resultant. Use these components for the resultant to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant. Vector V1 Assigned Vectors Magnitude Direction Vector Components Vx Vy V2 V3 V4 V5 R 2. Computer Method: Use the vector addition spreadsheet to add the vectors. Include a printout of the spreadsheet with your report. Note that the spreadsheet includes a graphical representation of the vector addition. 3. Force Table: When a set of forces acting on an object all act through the same point, the net force on the object is the vector sum of the individual forces. The set of forces corresponding to the assigned vectors are created by using counterweights attached to strings that radiate out from a central point. The pulleys are set at the appropriate angles by using the markings on the force table perimeter. The Equilibrant (E) is determined by adding an additional counterweight, adjusting the weight and direction so that the ring at the center of the force table is balanced (the central ring is centered). The Equilibrant is the opposite of the resultant so R = E, so that the experimental value for the resultant has a magnitude equal to the magnitude of the equilibrant, and a direction 180 R E 4. Graphical Method: Add the vectors graphically by drawing them to scale on graph paper using a ruler and a protractor. The length of the resultant is measured using the ruler and the direction of the resultant is measured using the protractor. The student must choose an appropriate scale so that the drawing fills the paper. Results: Method Magnitude Analytical Computer Force Table Graphical Direction Resultant x-component y-component