AcPChapter 4
advertisement

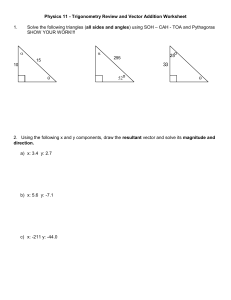
Chapter 4: Forces and the Laws of Motion 4.1 Changes in Motion Force is a vector quantity that causes changes in motion. Force can act either through physical contact of two objects or at a distance Contact Force Field Force Free Body Diagram A Free Body Diagram shows only the forces that act on one object. These are the only forces that affect the motion of that object. Practice: The Physics Classroom - Free Body Diagrams On whiteboards, draw diagrams. 2.2 Newton’s First Law Inertia is the tendency of an object to maintain its state of motion. Object at rest stays at rest Object in motion stays in motion Mass is a measure of inertia. Net External Force The net external force acting on an object is the vector sum of all the forces acting on it. An object is in equilibrium when the net external force acting on it is zero. Practice: The Physics Classroom - Net Force Solve for Net Force More Net Force Often the net force does not lie on the x or y axis. Steps in solving Net Force: Draw a free body diagram and label. Draw the resultant vector for the “triangle”. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the resultant vector force (d2=x2+y2) Use the tangent function to find the angle of the resultant vector and the horizontal or vertical axis. Θ= inv. tan (opposite side/adjacent side) Problem #3 – Example A gust of wind blows an apple from a tree. As the apple falls, the force of gravity on the apple is 9.25 N downward, and the force of the wind on the apple is 1.05 N to the right. Find the magnitude and direction of the net external force on the apple. (Answer: 9.3 N, 6° E of vertical) Draw Free Body Diagram with forces labeled. Draw the triangle Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find “d” Use the tan function to find the angle with respect to the y axis. You Try It! Problem 4 The wind exerts a force of 452 N north on a sailboat, while the water exerts a force of 325N west on the sailboat. Find the magnitude and direction of the net external force. (Answer: 557 N, 35° W or N) Newton’s Second Law Force is proportional to mass and acceleration ΣF= ma Net external force = mass x acceleration Example Problem: The net external force on the propeller of a 3.2 kg model airplane is 7.0 N forward. What is the acceleration of the airplane?(Answer: 2.2 m/s2) A soccer ball kicked with a force of 13.5 N accelerates at 6.5 m/s2 to the right. What is the mass of the ball? Newton’s Third Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. The action-reaction pair objects mutually exert force on each other