Properties_problems 2
advertisement
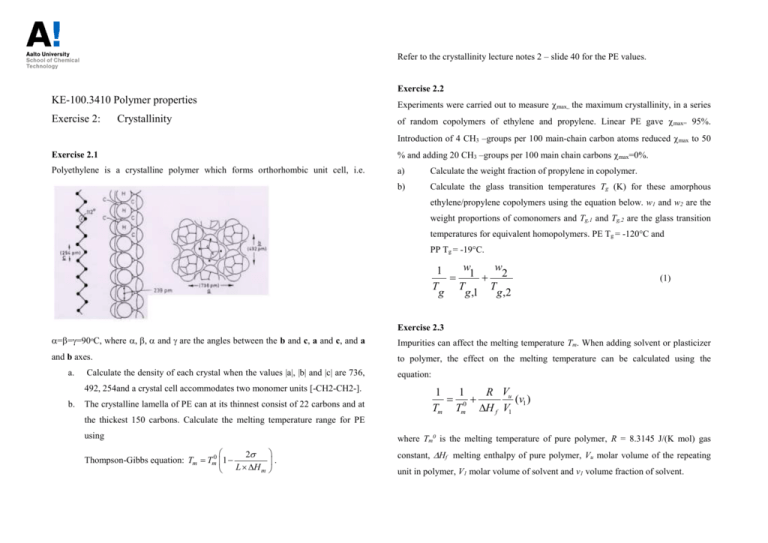
Refer to the crystallinity lecture notes 2 – slide 40 for the PE values. Exercise 2.2 KE-100.3410 Polymer properties Experiments were carried out to measure max,, the maximum crystallinity, in a series Exercise 2: of random copolymers of ethylene and propylene. Linear PE gave max= 95%. Crystallinity Introduction of 4 CH3 –groups per 100 main-chain carbon atoms reduced max to 50 Exercise 2.1 % and adding 20 CH3 –groups per 100 main chain carbons max=0%. Polyethylene is a crystalline polymer which forms orthorhombic unit cell, i.e. a) Calculate the weight fraction of propylene in copolymer. b) Calculate the glass transition temperatures Tg (K) for these amorphous ethylene/propylene copolymers using the equation below. w1 and w2 are the weight proportions of comonomers and Tg,1 and Tg,2 are the glass transition temperatures for equivalent homopolymers. PE Tg = -120°C and PP Tg = -19°C. w w 1 1 2 T T T g g ,1 g ,2 (1) Exercise 2.3 ===90ᵒC, where and are the angles between the b and c, a and c, and a Impurities can affect the melting temperature Tm. When adding solvent or plasticizer and b axes. to polymer, the effect on the melting temperature can be calculated using the a. Calculate the density of each crystal when the values |a|, |b| and |c| are 736, 492, 254and a crystal cell accommodates two monomer units [-CH2-CH2-]. b. The crystalline lamella of PE can at its thinnest consist of 22 carbons and at equation: 1 1 R Vu 0 (v1 ) Tm Tm H f V1 the thickest 150 carbons. Calculate the melting temperature range for PE using 2 Thompson-Gibbs equation: Tm Tm0 1 L H m where Tm0 is the melting temperature of pure polymer, R = 8.3145 J/(K mol) gas . constant, Hf melting enthalpy of pure polymer, Vu molar volume of the repeating unit in polymer, V1 molar volume of solvent and v1 volume fraction of solvent. the Tg of the mixture? Fox-Flory parameters for polystyrene are T g = 373 K, K = Polydecamethyleneadiapate, CO (CH2 )4 CO O (CH2 )10 O n 1.2105. (density 0.99g/cm3) was plasticized using different amounts of dimethylformamide (CH3)2NCHO, (density 0.9445 g/cm3) and the following melting temperatures were Exercise 2.5* The following empirical equation can be applied when calculating the glass transition observed: temperature Tg for copolymers and blends o v1 Tm ( C) 0.079 72.5 0.202 66.5 0.422 61.5 0.603 57.5 w w 1 1 2 Tg Tg ,1 Tg ,2 where w1 and w2 are the weight fractions of polymers and Tg,1 ja Tg,2 are glass What is the melting temperature Tm0 and melting enthalpy H of the pure polymer? transition temperatures of the polymers. The effect of plasticizer on polymer melting temperature Tm can be estimated with the equation: 1 1 R Vu 0 (v1 ) Tm Tm H f V1 1 1 R Vu 0 (v1 12v12 ) Tm Tm H f Vm,1 where Tm0 is the melting temperature of pure polymer, R = 8.3145 J/(K mol) gas Plotting 1/Tm versus V1 should give a straight line: The y-intercept is 1/Tm0 while the slope is equal to: constant, Hf melting enthalpy of pure polymer, Vu molar volume of the repeating unit in polymer, Vm,1 molar volume of the plasticizer, v1 volume fraction of plasticizer and 12 is interaction parameter for polymer-plasticizer. How much plasticizer (Tg = -80oC) should be added to the Nylon 66 sample to obtain Tg of 25oC? What would be the melting temperature? Exercise 2.4* 20 wt.% of a styrene oligomer having a number-average degree of polymerization of Vm,1 = 200cm3/mol and = 0.40, for Nylon66 Hu = 195.6 J/g, = 1.088 g/cm3, Tm0 7 was mixed with a commercial polystyrene sample having a number-average = 265oC, Tg = 50 oC. Density of plasticizer= 1.05 g/cm3. molecular weight of 100 000 g/mol. What is the T g of the styrene oligomer? What is