1st 9 weeks review Chapter 1-3 (and a little bit of 4) Name: #27
advertisement

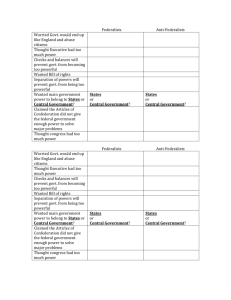
1st 9 weeks review Chapter 1-3 (and a little bit of 4) Name: _______________________ #27 Chapter 1- Government & the State I. What is Government? *Dictator- ruled by single person/small group *Democracy- Power rests with a majority of the people -Direct democracy- people make the laws -Indirect democracy (representative democracy)- elected officials make the laws (U.S.A) *Presidential vs. Parliamentary-Presidential- people elect President and Congress (U.S.A) -Parliamentary- people elect Congress, Congress elects the president *How the American Government began- Social Contract Theory (Preamble) II. The State *State- body of people with a government who has power to make & enforce laws without consent of higher authority Four Characteristics of a state: 1) Population 2) Territory 3) Sovereignty 4) Government Ch. 2 Our Political Beginnings I. Basic Concepts of Government A. Ordered Government -Government = an orderly regulation of relationships B. Limited Government-not all powerful, individual rights C. Representative Government-people should have a voice II. English Documents A. Magna Carta- Great Charter- 1st to limit the power of the King B. Petition of Right- Limited kings power- cannot punish someone for no reason, no martial law in time of peace C. English Bill of Rights- Prohibited a standing army, must listen to parliament for laws & taxes Second Continental Congress May 10, 1775- after Lexington & Concord Reps. from all 13 colonies 1st National government; Raised an army & navy, Raised taxes, Made treaties Declaration of Independence -Declared independence from England with a list of grievances We have natural rights & can destroy gov. if they go against these rights Most included: Popular Sovereignty- government can only exist with the consent of the governed Articles of Confederation A. Congress = sole body created 1. No Executive 2. No Judicial B. Unicameral- each state has one vote C. Presiding Officer elected leader of Congress D. Creates a firm league of friendship -Federal government too weak; cannot tax!! -Constitutional Convention- rewrite the Articles Virginia Plan 3 Branches: Legislative, executive, judicial Legislative = bicameral- Lower House elected in each State; Upper House chosen from list provided by the State Legislatures Smaller states did not like; large states get more power New Jersey Plan Unicameral Congress- each state with equal representation- small states like this plan All 3 branches were included in the plan A. Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise) 2 Houses (Bicameral): -Senate = Equal -House = based on population Made large & small states happy Fight for Ratification A. Federalists and Anti-Federalists: 1. Federalists favored ratification -Madison, Hamilton -Stressed the weakness of the Articles -Wrote the Federalist Papers to encourage ratification -Need VA and NY- largest states by population 2. Anti-Federalists opposed it -Absence of God -Federal Government too strong -No Bill of Rights Bill of Rights First set of basic rights that will be protected by and from the government; First 10 Amendments Chapter 3: The Six Basic Principles 1. Popular Sovereignty- People are the power Government would not exist with the consent of the people; In the Preamble “We the people…” 2. Limited Government Government is not all powerful- Limited Gov’t. Government only has the power given to them by the Constitution *Rule of Law- government is never above the law 3. Separation of Powers Constitution separates the powers of the three independence and coequal branches No one branch can run the country alone 4. Checks and Balances Each branch is subject to a number of constitutional restraints by the other branches Each branch has powers to check the operations of the others 5. Judicial Review Power of courts to determine whether what gov’t does is in accord with what the Constitution says (Unconstitutional) 6. Federalism Division of power among a central government and several regional governments Creates a strong federal gov. while preserving states rights Formal Amendment ProcessChange in the written words of the Constitution Define each of the following (most can be found in the review) 1. Representative government 2. Democracy 3. Presidential government 4. Parliamentary government 5. Federal government 6. Limited government 7. Dictatorship 8. State (list the 4 basic characteristics only) 9. Articles of Confederation 10. Federalists Items to read over before you come to class-How each branch can check each other -First 10 Amendments (Bill of Rights) -Preamble 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. New Jersey Plan Virginia Plan Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise) Three-Fifths Compromise Popular Sovereignty Checks and Balances Bill of Rights Formal Amendment Federalism 1st 9 weeks review Chapter 1-3 (and a little bit of 4) Name: _______________________ #27 Chapter 1- Government & the State I. What is Government? *Dictator- ruled by single person/___________________________________ *Democracy- Power rests with a majority of the people -Direct democracy- people make the laws -Indirect democracy (representative democracy)- elected ______________________________________________ (U.S.A) *Presidential vs. Parliamentary-Presidential- people elect President and Congress (U.S.A) -Parliamentary- people elect Congress, Congress elects the president (Prime Minister) *How the American Government began- ______________________________________________ Theory (Preamble) II. The State *State- body of people with a government who has power to make & enforce laws without consent of higher authority Four Characteristics of a state: 1) Population 2) Territory 3) __________________________ 4) Government Ch. 2 Our Political Beginnings I. Basic Concepts of Government A. Ordered Government -Government = an orderly regulation of relationships B. Limited Government-___________________________________________, individual rights C. Representative Government-people should have a voice II. English Documents A. Magna Carta- Great Charter- 1st to ________________________________________________________________________ B. Petition of Right- Limited kings power- cannot punish someone for no reason, no martial law in time of peace C. English Bill of Rights- Prohibited a standing army, must listen to parliament for laws & taxes Second Continental Congress May 10, 1775- after Lexington & Concord Reps. from all 13 colonies ________________________________________________; Raised an army & navy, Raised taxes, Made treaties Declaration of Independence -Declared independence from England with a _____________________________________________________ We have natural rights & can destroy gov. if they go against these rights Most included: Popular Sovereignty- government can only exist with the consent of the governed Articles of Confederation A. Congress = sole body created 1. No Executive 2. No Judicial B. Unicameral- each state has one vote C. Presiding Officer elected leader of Congress D. ____________________________________________________________________________________ -Federal government too weak; ___________________________________!! -Constitutional Convention- ________________________________________________________________ Virginia Plan 3 Branches: Legislative, executive, judicial Legislative = bicameral- Lower House elected in each State; Upper House chosen from list provided by the State Legislatures Smaller states did not like; large states ________________________________________________________________ New Jersey Plan Unicameral Congress- each state with equal representation- _________________________________________________________ All 3 branches were included in the plan A. Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise) ____________________ (Bicameral): -Senate = Equal -House = based on population Made large & small states happy Fight for Ratification A. Federalists and Anti-Federalists: 1. Federalists favored ratification -Madison, Hamilton -Stressed the weakness of the Articles -Wrote the __________________________________ to encourage ratification -Need VA and NY- largest states by population 2. Anti-Federalists opposed it -Absence of God -Federal Government too strong -No _________________________________________ Bill of Rights First set of basic rights that will be protected by and from the government; First ________________________________ Chapter 3: The Six Basic Principles 1. Popular Sovereignty- __________________________________________________ Government would not exist with the consent of the people; In the Preamble “We the people…” 2. Limited Government Government is not all powerful- Limited Gov’t. Government only has the power given to them by the Constitution *Rule of Law- government is _____________________________________________________ 3. Separation of Powers Constitution separates the powers of the three independence and coequal _________________________ No one branch can run the country alone 4. Checks and Balances Each branch is subject to a number of constitutional restraints by the other branches Each branch has powers to check the _______________________________________________________________ 5. Judicial Review Power of courts to determine whether what gov’t does is in accord with what the Constitution says (_________________) 6. Federalism Division of power among a central government and several regional governments Creates a strong federal gov. while ____________________________________________________________________ Formal Amendment ProcessChange in the written words of the______________________________ Define each of the following (most can be found in the review) 1. Representative government 2. Democracy 3. Presidential government 4. Parliamentary government 5. Federal government 6. Limited government 7. Dictatorship 8. State (list the 4 basic characteristics only) 9. Articles of Confederation 10. Federalists Items to read over before you come to class-How each branch can check each other -First 10 Amendments (Bill of Rights) -Preamble 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. New Jersey Plan Virginia Plan Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise) Three-Fifths Compromise Popular Sovereignty Checks and Balances Bill of Rights Formal Amendment Federalism A. Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise) ____________________ (Bicameral): -Senate = Equal -House = based on population Made large & small states happy Fight for Ratification A. Federalists and Anti-Federalists: 1. Federalists favored ratification -Madison, Hamilton -Stressed the weakness of the Articles -Wrote the __________________________________ to encourage ratification -Need VA and NY- largest states by population 2. Anti-Federalists opposed it -Absence of God -Federal Government too strong -No _________________________________________ Bill of Rights First set of basic rights that will be protected by and from the government; First ________________________________ Chapter 3: The Six Basic Principles 1. Popular Sovereignty- __________________________________________________ Government would not exist with the consent of the people; In the Preamble “We the people…” 2. Limited Government Government is not all powerful- Limited Gov’t. Government only has the power given to them by the Constitution *Rule of Law- government is _____________________________________________________ 3. Separation of Powers Constitution separates the powers of the three independence and coequal _________________________ No one branch can run the country alone 4. Checks and Balances Each branch is subject to a number of constitutional restraints by the other branches Each branch has powers to check the _______________________________________________________________ 5. Judicial Review Power of courts to determine whether what gov’t does is in accord with what the Constitution says (_________________) 6. Federalism Division of power among a central government and several regional governments Creates a strong federal gov. while ____________________________________________________________________ Formal Amendment ProcessChange in the written words of the______________________________ Define each of the following (most can be found in the review) 1. Representative government 11. New Jersey Plan 2. Democracy 12. Virginia Plan 3. Presidential government 13. Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise) 4. Parliamentary government 14. Three-Fifths Compromise 5. Federal government 15. Popular Sovereignty 6. Limited government 16. Checks and Balances 7. Dictatorship 17. Bill of Rights 8. State (list the 4 basic characteristics only) 18. Formal Amendment 9. Articles of Confederation 19. Federalism 10. Federalists 20. Concurrent Powers Items to read over before you come to class-How each branch can check each other -Formal Amendment Process -First 10 Amendments (Bill of Rights) -5 informal Amendments -Preamble