Answer - Haiku
advertisement
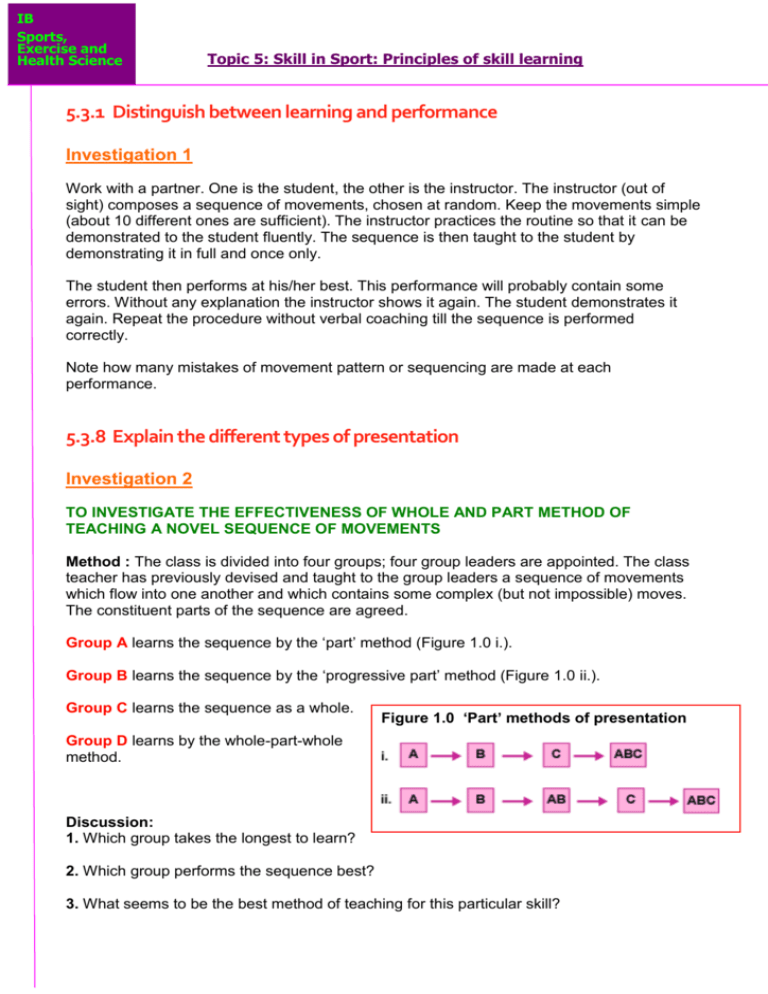
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Topic 5: Skill in Sport: Principles of skill learning 5.3.1 Distinguish between learning and performance Investigation 1 Work with a partner. One is the student, the other is the instructor. The instructor (out of sight) composes a sequence of movements, chosen at random. Keep the movements simple (about 10 different ones are sufficient). The instructor practices the routine so that it can be demonstrated to the student fluently. The sequence is then taught to the student by demonstrating it in full and once only. The student then performs at his/her best. This performance will probably contain some errors. Without any explanation the instructor shows it again. The student demonstrates it again. Repeat the procedure without verbal coaching till the sequence is performed correctly. Note how many mistakes of movement pattern or sequencing are made at each performance. 5.3.8 Explain the different types of presentation Investigation 2 TO INVESTIGATE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF WHOLE AND PART METHOD OF TEACHING A NOVEL SEQUENCE OF MOVEMENTS Method : The class is divided into four groups; four group leaders are appointed. The class teacher has previously devised and taught to the group leaders a sequence of movements which flow into one another and which contains some complex (but not impossible) moves. The constituent parts of the sequence are agreed. Group A learns the sequence by the ‘part’ method (Figure 1.0 i.). Group B learns the sequence by the ‘progressive part’ method (Figure 1.0 ii.). Group C learns the sequence as a whole. Figure 1.0 ‘Part’ methods of presentation Group D learns by the whole-part-whole method. Discussion: 1. Which group takes the longest to learn? 2. Which group performs the sequence best? 3. What seems to be the best method of teaching for this particular skill? IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Topic 5: Skill in Sport: Principles of skill learning 4. You have been investigating teaching methods, but what are the ‘confounding variables’ in this experiment, i.e. factors other than teaching method which may have affected the result? Answers: 5.3.3 Outline the different types of learning curves Learning Curves Curves of learning are based on individuals’ performance at given moments in given situations. There is no single curve of learning – all curves are related to individuals and the skill in question. However, certain types of curves can be identified: Positive acceleration Negative acceleration Linear Plateau Task One: 2. Outline and draw the FOUR different types of learning curves What causes plateau and what can teachers or coaches do to help overcome these? Answer : 3. You see a novice complete a number of tennis serves over a period of 20 minutes of massed practice. a. Sketch a graph, with time in minutes on the horizontal x-axis and success rate on the vertical yaxis, showing the possible changes in performance of the novice over the practice period. (3 marks) Answer : b. Explain the shape of the performance curve on your graph. (4 marks) Answer : Sketch graph 2.0. Success rate against time for a novice tennis player practising a serve IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Topic 5: Skill in Sport: Principles of skill learning c. What strategies might the teacher employ to help improve the performance of any closed skill by a novice during a 20-minute practice session? (4 marks) Answer: 5.3.5 Define the concept of transfer EXAMPLES OF TRANSFER TYPES Put the following pairs of skills into one of three categories (i) very similar (ii) likely to cause interference (iii) dissimilar. Answer: o Tennis serve and volleyball serve = o Long and short serve in badminton = o Golf drive and ten pin bowling = o Straight arm pull and bent arm pull in back crawl = o Rugby League and Rugby Union = o Dismounts from the high bar and the rings in men’s gymnastics o Scottish folk dancing & Latin dancing o Ice hockey and field hockey Notes: = = = IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Topic 5: Skill in Sport: Principles of skill learning 5.3.6 Outline the types of transfer Investigation 3 TO INVESTIGATE POSITIVE TRANSFER EFFECTS IN SKILL LEARNING Method : Select one form of transfer from categories 1 - 5 in Figure 3.0. Select two groups of subjects, Group 1 and Group 2, matched for motor learning ability as far as possible. Using the following two tasks (A and B) o Task A = using non-preferred hand, throwing tennis ball into bin from 2.5m. o Task B = using non-preferred hand, throwing dart into bull of dartboard from 2.5m. Success criteria for: o Task A = 4 successive balls on target. o Task B = 4 successive darts in the bull. Experimental protocol: o Group 1 practises on Task A for 10 minutes. o Group 2 relaxes and waits without practice. o Both groups then begin Task B, and time is taken to successfully complete the task. What might you expect in the learning of Task A to transfer positively to learning in Task B. Figure 3.0 Categories of transfer Decide on the criteria you will use to determine that learning has taken place; for example, you might decide that seven accurate shots out of ten in a novel aiming task constitutes learning. Group 1 learns Task A and then Task B. Group 2 learns only Task B. IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Topic 5: Skill in Sport: Principles of skill learning Results : Determine which group learned Task B more quickly. Table 3.1 Sample results - Times taken to learn task B subject A B C D E F G H mean Group 1 (A + B) subject I J K L M N O P Group 2 (B only) Discussion: Assuming all other variables have been controlled (a dangerous assumption under the circumstances of a class experiment), what do your results tell you about the possibility of transfer between Task A and Task B for Group 1? Answer: How might you improve the experiment so that you could be more confident of your results? Answer: Review Questions 1. Give a sport-related example of a) positive transfer and b) negative transfer. Answer: 2. List the six categories of transfer and give an example for each. Answer: IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Topic 5: Skill in Sport: Principles of skill learning 3. List four requirements for positive transfer to occur. Answer: 4. Give an example of a coach using positive transfer to develop a technique. Answer: 5. How can transfer be detrimental to performance? Give a practical example. (3 marks) Answer: 6. How can a coach ensure that as much positive transfer takes place as possible in a training session? (5 marks) Answer : 7. Define the terms positive transfer and negative transfer in the context of someone learning a sport skill. (2 marks) Answer: IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Topic 5: Skill in Sport: Principles of skill learning 8. Figure 3.2 shows different extents of transfer in different situations labelled A, B, and C, give examples of one pair of games type skills which illustrate the kinds of transfer indicated. (4 marks) Answer: Figure 3.2 Extents of transfer in various situations










