Vocabulary Words for January 13 – 17 Water cycle

Vocabulary Words for January 13 – 17
1.
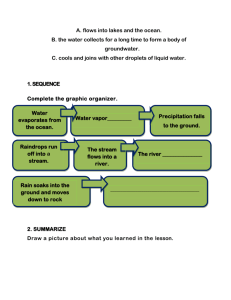
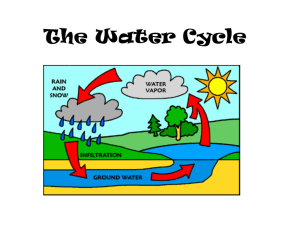
Water cycle – A continuous process that renews the fresh water on Earth.
2.
Evaporation – The process of a liquid turning into a gas. Water is heated by the sun and turned into water vapor.
3.
Condensation – The process of a gas turning into a liquid. As the water vapor rises into the atmosphere, the temperature cools causing the gas to turn back into a liquid. These tiny drops of water, combined with dust particles, form clouds.
4.
Precipitation – A form of water that falls to the Earth. Includes rain, snow, fog, mist, sleet, or hail.
5.
Transpiration – Occurs when plant leaves open and release water into the air. This water can then be evaporated and cycled through the water cycle.
6.
Accumulation – Occurs when precipitated water collects in rivers, ponds, lakes, oceans, and other water sources.
7.
Sun – Star at the center of the solar system that supplies heat and light to
Earth. It is the source of the water cycle.
8.
Fresh water – Water found in lakes, rivers, and streams that does not contain salt.
9.
Salt water – Water found in oceans and seas that contain 3 - 4 % salt.
10.
Warm front – Where a warm air mass moves over cold air mass; hot, humid weather follows; moves slowly; clear and sunny
11.
Cold front – Where a cold air mass moves underneath a warm air mass.
Sinking high pressure; moves quickly, fair cool weather follows; storms and heavy rain
12.
Global Warming – A rise in the average temperatures of Earth’s air and ocean.
13.
Weather – Condition of the air or atmosphere that is constantly changing.
Temperatures rise or fall, air warms or cools, wind can be fast or slow, water in the air can take the form of fog, mist, rain, hail, snow, or sleet.
14.
Climate – Average weather conditions of a region over a period of years.
15.
Temperature – How hot or cold something is.
16.
Humidity – The amount of water vapor in the air.
17.
Air Pressure – A force applied by the weight of air.