pubdoc_12_3142_450
advertisement

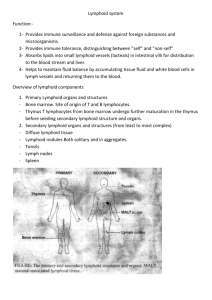
Lymphoid Organs : Lymphoid organs refer to the anatomical aspects of the immune system, whereas immunity refers to the functional aspect of lymphoid organs. Lymphoid organs are classified as: 1-Primary(generative) lymphoid organs: Where lymphocytes first express antigen receptors and attain phenotypic and functional maturity. The major primary lymphoid organs are thymus and bone marrow. 2-Secondary(peripheral) lymphoid organs: Where lymphocytes respond to foreign antigens. These organs include spleen, lymph nodes, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues(MALT). Lymphoid Organs : Lymphoid organs refer to the anatomical aspects of the immune system, whereas immunity refers to the functional aspect of lymphoid organs. Lymphoid organs are classified as: 1-Primary(generative) lymphoid organs: Where lymphocytes first express antigen receptors and attain phenotypic and functional maturity. The major primary lymphoid organs are thymus and bone marrow. 2-Secondary(peripheral) lymphoid organs: Where lymphocytes respond to foreign antigens. These organs include spleen, lymph nodes, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues(MALT). Thymus: The thymus is the site of T cell maturation and education (learn to discriminate between self and nonself antigens) by process positive and negative selection .The lymphocytes (thymocytes) are T cells at various stages of maturation .The most immature T cells enter the thymic cortex through the blood vessels .Maturation begins in the cortex ,then thymocytes migrate toward the medulla ,so that the medulla contains mostly mature T cells. After puberty, Thymus atrophies.