2FF_03AP_ILLUSTRATED_Early_transregional_trade
advertisement
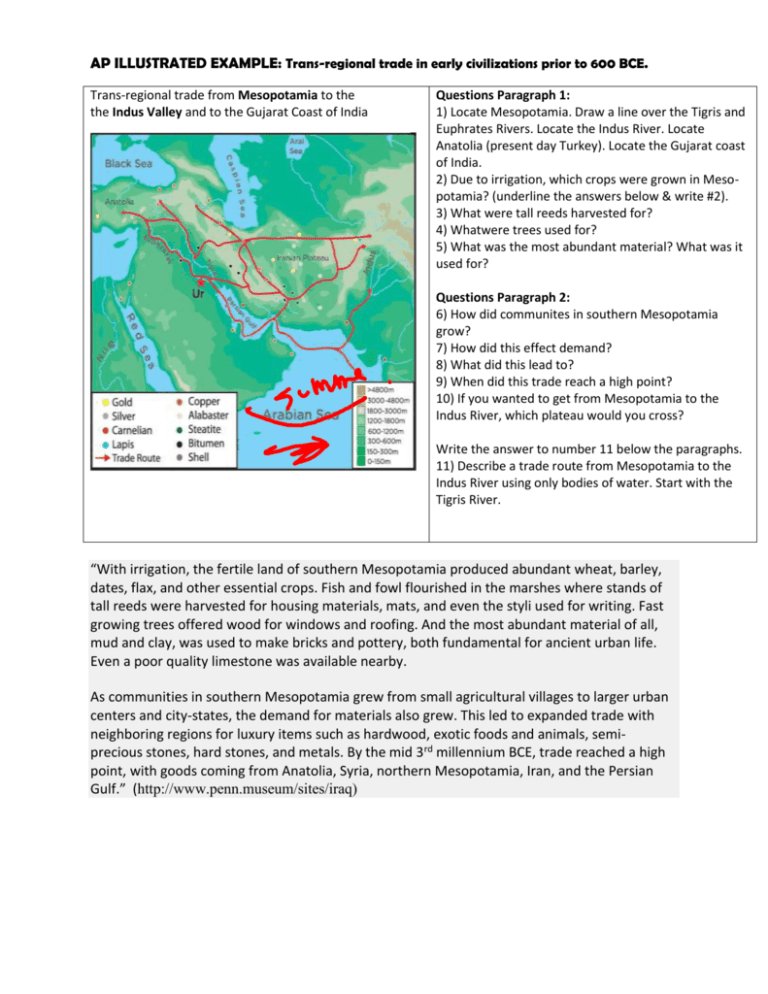
AP ILLUSTRATED EXAMPLE: Trans-regional trade in early civilizations prior to 600 BCE. Trans-regional trade from Mesopotamia to the the Indus Valley and to the Gujarat Coast of India Questions Paragraph 1: 1) Locate Mesopotamia. Draw a line over the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Locate the Indus River. Locate Anatolia (present day Turkey). Locate the Gujarat coast of India. 2) Due to irrigation, which crops were grown in Mesopotamia? (underline the answers below & write #2). 3) What were tall reeds harvested for? 4) Whatwere trees used for? 5) What was the most abundant material? What was it used for? Questions Paragraph 2: 6) How did communites in southern Mesopotamia grow? 7) How did this effect demand? 8) What did this lead to? 9) When did this trade reach a high point? 10) If you wanted to get from Mesopotamia to the Indus River, which plateau would you cross? Write the answer to number 11 below the paragraphs. 11) Describe a trade route from Mesopotamia to the Indus River using only bodies of water. Start with the Tigris River. “With irrigation, the fertile land of southern Mesopotamia produced abundant wheat, barley, dates, flax, and other essential crops. Fish and fowl flourished in the marshes where stands of tall reeds were harvested for housing materials, mats, and even the styli used for writing. Fast growing trees offered wood for windows and roofing. And the most abundant material of all, mud and clay, was used to make bricks and pottery, both fundamental for ancient urban life. Even a poor quality limestone was available nearby. As communities in southern Mesopotamia grew from small agricultural villages to larger urban centers and city-states, the demand for materials also grew. This led to expanded trade with neighboring regions for luxury items such as hardwood, exotic foods and animals, semiprecious stones, hard stones, and metals. By the mid 3rd millennium BCE, trade reached a high point, with goods coming from Anatolia, Syria, northern Mesopotamia, Iran, and the Persian Gulf.” (http://www.penn.museum/sites/iraq) Egypt to Nubia Rough draft: Give information facts 1) In terms of present day locations, Nubia was based in southern Egypt and northern Sudan 2) Early Egyptian settlements started around 5500 BCE. 3) Ancient Egypt lasted from 3000 BCE to 300 BCE. Egypt traded with, and later conquered Nubia. 4) The Kush, a kingdom located in Nubia, later conquered Egypt. 5) Cultural diffusion and trade resulted from these contacts and conquests. 6) Locate the city of Aswan in Upper Egypt. 7) Locate the city of of Cairo in Lower Egypt. 8) The kingdom of Kush reigned from 1070 BCE to 350 CE. 9) This was followed by Axum which reigned from 100-940 CE. Axum also trade extended into the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean. Kingdom of Axum (Axsum) Kingdom of Kush Directions. Do NOT use complete sentences. 1) Circle Nubia on the map. (The kingdom of nubia was in this territory). 2) Why did cultural diffusion between Egypt and Nubia take place? 3) Why is Cairo in lower Egypt and Aswan in upper Egypt? 4) Write the order of rule for Axum, Egypt, and Kush. Don’t give dates, just the order. 5) Where did Axum trade extend to?