APES CURRICULUM 2011-12
advertisement
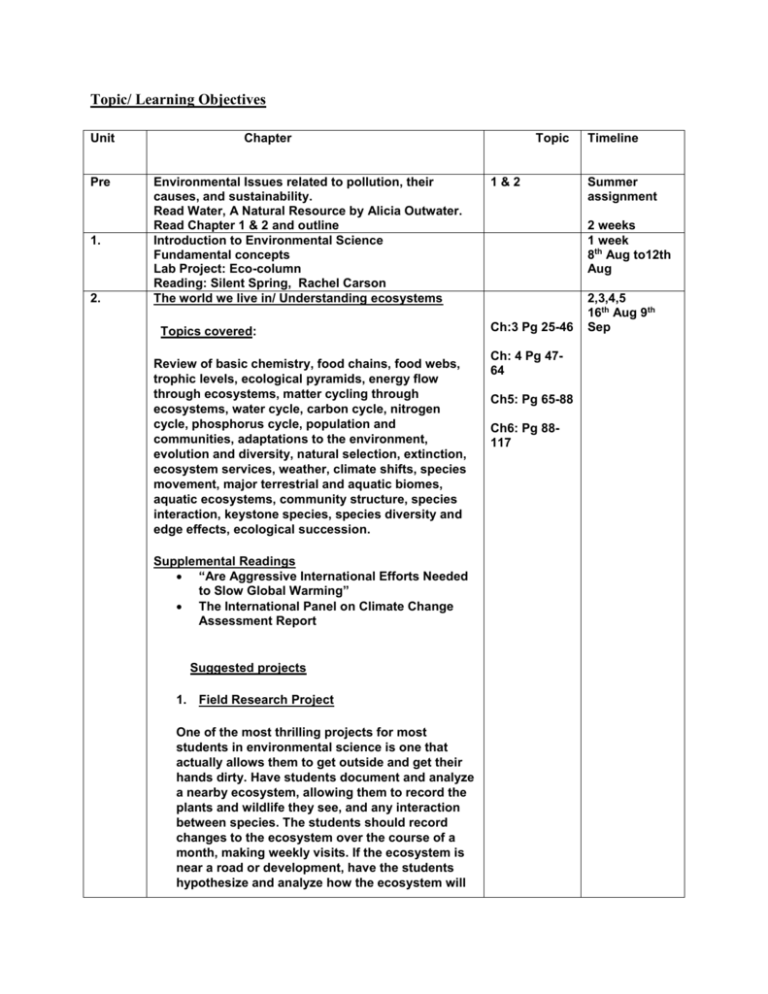
Topic/ Learning Objectives Unit Pre 1. 2. Chapter Environmental Issues related to pollution, their causes, and sustainability. Read Water, A Natural Resource by Alicia Outwater. Read Chapter 1 & 2 and outline Introduction to Environmental Science Fundamental concepts Lab Project: Eco-column Reading: Silent Spring, Rachel Carson The world we live in/ Understanding ecosystems Topics covered: Review of basic chemistry, food chains, food webs, trophic levels, ecological pyramids, energy flow through ecosystems, matter cycling through ecosystems, water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, phosphorus cycle, population and communities, adaptations to the environment, evolution and diversity, natural selection, extinction, ecosystem services, weather, climate shifts, species movement, major terrestrial and aquatic biomes, aquatic ecosystems, community structure, species interaction, keystone species, species diversity and edge effects, ecological succession. Supplemental Readings “Are Aggressive International Efforts Needed to Slow Global Warming” The International Panel on Climate Change Assessment Report Suggested projects 1. Field Research Project One of the most thrilling projects for most students in environmental science is one that actually allows them to get outside and get their hands dirty. Have students document and analyze a nearby ecosystem, allowing them to record the plants and wildlife they see, and any interaction between species. The students should record changes to the ecosystem over the course of a month, making weekly visits. If the ecosystem is near a road or development, have the students hypothesize and analyze how the ecosystem will Topic 1&2 Timeline Summer assignment 2 weeks 1 week 8th Aug to12th Aug Ch:3 Pg 25-46 Ch: 4 Pg 4764 Ch5: Pg 65-88 Ch6: Pg 88117 2,3,4,5 16th Aug 9th Sep be affected. The students should compile their research into a paper equipped with charts, graphs, and tables. This project could be presented to the class with a poster presentation. Labs and Activities a) Nutrient Cycle Presentations b) Quadrant analysis of a vegetative community Lab c) Predator and Prey lab d) Biome Reports/Project e) Water ecosystem Reports f) Measuring Biodiversity with the Shannon Index. g) Quadrat lab: On school grounds/or by visit to a field nearby, students learn how to mark off a quadrat and identify the large plants in the area. Then they graph the area. h) To study the adaptations of xerophytes and hydrophytes 3. Water Resource Global Water Resource and Use/ Aquatic Biodiversity: Water’s importance and unique properties, Supply, renewal and use of water resources, water cycle, Fresh water /salt water, ocean circulation, agricultural, industrial and domestic use, surface and ground water issues, dams and reservoirs, US and global water issues, water management, human impact, conservation and providing a sustainable water supply. Lab: Drinking Water Safety: Coliform (M.Morgan) Lab: National and Local Water Use (Molnar -11) Lab: Introduction to Macro invertebrates as indicator species (M.Morgan) Ch 14: Water Pg 308 to 334 and Ch 6: 117 to 147 Sustaining Aquatic Biodiversity Estuaries, coastal ecosystems, continental Shelf Environments, pelagic ecosystems, benthic ecosystems, fisheries-Tragedy of the Commons, Ocean Pollution Reading: Garret Harding Tragedy of the Commons 1. Water Pollution Topics covered: Ch-22: Water 6,7,8 10th Sep to 30th Sep Labs may be extended to the next week. Types, major sources of water pollution, point vs.nonpoint source pollution, causes and effects of water pollution, eutrophication, groundwater pollution, maintaining water quality, water purification, sewage treatment, septic systems, control and relevant laws. Field trip: Sewage Treatment Plant Lab : a) Lab on Eutrophication: Using water from the school pond, students cause eutrophication and observe the resulting changes in small aquatic organisms. b) Dissolved Oxygen Lab: Students will analyze the dissolved oxygen content in the water samples and study the effect of biodegradable materials on dissolved oxygen. c) Lab: Measuring Water Quality: Chemical and Biological analysis of samples collected from test site. d) Lab to compare contaminant levels present in raw water and effluent water collected from ponds. e) Field trip to an Environmental research centre to analyze water quality. To measure acidity, Ca, Mg, turbidity, BOD, dissolved solids and to compare the results to EPA water quality. Introduction to colorimetric analysis, atomic absorption spectrometer to identify heavy metals in drinking water. Activities Field trip: Wastewater Treatment Plant 4. Pollution-Pg485-506 The Search for Energy Energy Resources and Consumption Topics covered: Energy forms, power, units, conversions, Laws of Thermodynamics, energy consumption, present global energy use, future energy needs, formation of coal, oil, and natural gas, world reserves and global demand, synfuels, environmental advantages and disadvantages of sources, nuclear energy-fission process, production of electricity, types of nuclear reactor, advantages and disadvantages of nuclear fuels, safety issues, radiation and human health, radioactive wastes, 9,10,11 3rd Oct to 21st Oct Ch. 11 Fossil Fuels pgs233 to 259 Ch. 12 Nuclear Energy pgs 259-282 Ch. 13 Renewable Energy and Conservation pgs 282- 308 nuclear fusion, alternative energy sources: wind, water, solar, geothermal, biomass, solar-hydrogen, ocean waves, tidal energy, environmental advantages and disadvantages, energy efficiency. Supplementary Readings “Reinviting the Energy System” Labs and Activities Labs: a) Solar Energy: Solar Oven Design Lab b) Energy conservation Lab c) To study the different characteristics of Fossils. Activities a) Energy Sources Project b) Measuring Household Energy Consumption activity c) Calculate Personal Energy Needs and propose a plan of action to conserve and preserve energy resources. d) Inside a Coal Fired Power Plant Game 5. Holiday Week (Diwali) Food and Soil Resource Food Resource: Food and Nutrition, world food problems, principal types of agriculture, domestication, increasing crop yields, the green revolution, increasing livestock yields, genetic engineering, environmental impacts of agriculture, sustainable agriculture, fisheries of the world, aquaculture. Activity: analysis of organic food. Soil Resources Soil and Soil Dynamics: Rock cycle, formation, composition, physical and chemical properties, main soil types, erosion and other soil problems, soil conservation and regeneration, role of soil in agriculture. Oct 22-30 Ch: 19 Food Resources Pg 427 to 451 Ch15: Soil Resources Pg. 335 to 354 13,14,15 31st Oct to 18th Nov Labs and Activities: a) Soil testing lab (Chemical and Physical properties of soil) b) To identify the horizons in a soil profile. c) Lab to study the water holding capacity of different types of soil. d) To identify the chemical composition of soil. e) Rocks and Rock Cycle Lab Supplemental Readings From the “Sand County Almanac” Pest Management Pesticides types and uses, the case for pesticides and against pesticides, pesticide regulation, alternatives to conventional chemical pesticides. Ch.23 Activity: Industrial vs. organic pesticides Lab: Home hazardous produce survey 6. Geology & Nonrenewable Mineral Sources Minerals: A Nonrenewable Resource Mining: Mineral formation, extraction, global reserves, surface, subsurface, pit, strip mines, acid mine drainage, environmental impact of mining, relevant laws and treaties Labs and Activities Labs Copper Extraction Lab Cookie Mining Lab. Earth Science Concepts: Geologic Time Scale, geologic processes, natural geologic hazards, plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanism. Activity: Global map-Allen Jones, Seismic Eruptions Activity: Plate Tectonics (Molnar -2) Labs and Activities a) Virtual Lab: Plate Tectonics b) Virtual Earthquake Lab Ch.16 Minerals Pg355 to 375 Ch 5 16,17,18 18th Nov to 9th of Dec 23-25 Holidays for Thanks giving. c) Effects of Volcanoes lab (Internet Lab) 7. Semester Examination Winter Break A crowded world Population and Human Health Topics covered : Environmental developments in US and world history, demography, population dynamics, carrying capacity, reproductive strategies, survivorship curves, age structure diagrams, historical population sizes, demographic transition, age structure diagrams, strategies for sustainability, patterns of resource use, quality of life, impacts of population growth, hunger, disease, economic effects. Supplemental Readings From “The Population Bomb” Video: The Environmental Revolution Labs and Activities a) Human Population Lab b) Using the World Population Datasheet from the Population Reference Bureau creating Age Structure Diagrams To calculate percent growth rate and doubling time. c) Duckweed Population Lab: students observe the growth of duckweed, an aquatic angiosperm, and how its growth rate yields a logistic curve, illustrating concepts of population 19 20,21,22 Ch8. Population Change pgs.172-196 Ch9 Addressing Population Issues pgs.196-214 23,24,25,26 9th Jan to 3rd Feb growth rates, carrying capacity, and limiting factors (such as light, pH) d) Lab Age Pyramids: Students use census data of their country to construct age-sex population pyramids. Such pyramids are used to discuss how the population would be affected by natural as well as human-made disasters as well as social, economic, and political changes. e) Data analysis Lab: Human Population Trends f) Field lab Investigation- 60 minutes hands on lab. To calculate the population density and other parameters using quadrant sampling method. To identify stages of succession with in the study area. Human Health and Environmental Toxicology a) b) c) d) Ch: 7 Human Health Risk, Probability, and Hazardous Toxicology: Assessing chemical Hazards Chemical Hazards Risk Analysis Lab Activities: Environmental Justice Project 8. Our Precious Resources Air Pollution and Global climate change 2. Air Pollution and global climate Change Topics covered: A. The Atmosphere: composition, structure, weather and climate, atmospheric circulation and Coriolis Effect, atmosphereocean interactions Atmosphere history, origin, evolution, Ch-20: Air Pollution- Pg 428-452 Ch-21: Global climate change-Pg453-484 27,28 6th Feb to 17th Feb composition, structure, Primary and Secondary pollutants, major air pollutants, measurement units, photochemical smog, acid depositioncauses and effects, heat islands and temperature inversions, indoor and outdoor air pollution, urban air pollution, effects of air pollution on aquatic systems, vegetation, buildings and structures, and wildlife,ozone depletion in the stratosphere – causes and effects of ozone depletion, remediation and reduction strategies, Clean Air Act and other relevant laws, air quality standards, greenhouse effect, climate change and implication, dealing with global climate change, International efforts to reduce greenhouse . Labs and Activities: a) Acid Deposition Lab: The students will study the impact of acid rain on plants. b) The students will also expose the plants to SO2 and then see the effect on the growth of seedlings and infer the effect of acid rain. c) Tropospheric Ozone Lab: In this lab, students will prepare and use chemically reactive paper to measure the concentration of ground-level (tropospheric) ozone. The students will also compare their data with data obtained from the San Diego Air Quality Management District. ( http://www.sdapcd.org/air/data/web/report.txt) d) Airborne Particulate Lab: Every member of the class will measure the particulate concentration inside and outside of their home, and then contribute their individual data to the efforts of the entire class to understand the trends in the distribution patterns of particulates in the community. e) Data analysis Labs: CO2 levels, Global Temperature Trends. f) The Greenhouse Effect Lab: It is simulation lab and students study the effect of greenhouse gas on temperature. Activities: Molnar Global warming Internet activity Global climate change Project. Consequences of Global Warming jigsaw activity 9. Solid and Hazardous waste waste. Waste not, Want not Topics covered: Sources, types of solid and hazardous wastes, metallic and nonmetallic mineral sources, amounts, uses and problems, waste disposal methods and their limitations, solutions: Reduce, Reuse, recycle, treatment and disposal of solid and hazardous waste, cleanup of contaminated sites, biomagnifications, environmental risk analysis, acute and chronic effects, dose response relationships, relevant laws. Ch:24; Solid and Hazardous waste Pg. 557 to 581 Supplemental Readings “Controversy at Love Canal” Hudson River PCB Story- story on the health of the Hudson from Clearwater. Activities Household Hazardous Waste Inventory Personal solid waste Inventory SIMULATION Solid Waste Disposal Landfills The Pesticide Dilemma Topics covered: Ch:23 29,30,31 Feb 20th to Mar 9th Pesticides, types of pesticides, benefits and problems of pesticides, bioaccumulation and biological magnification, risks of pesticides to Human Health, control of pesticides, integrated pest management, relevant laws. Labs : Lab: Toxicology: Students will study the effect of pesticide and determine LD-50 on the given organism. They also produce a dose-response curve as a part of their report. Activities Pesticide Resistance: Pesticide Treadmill Noise Pollution Topics Covered: Sources, effects, and control measures Ch.10 Research project- to design a Business plan to solve a environmental problem in our city 10. Urban land and Land Resource A. Rangeland and other Land Use: overgrazing, deforestation, desertification, rangeland management, federal rangelands, urban land development, suburban sprawl, urbanization, Federal Highway system, transportation infrastructure, ecosystem impacts, wilderness areas, national parks, wildlife refuges, forests, wetlands, preservation of land, remediation, mitigation, restoration, sustainable land-use strategies. Ch 18: Land Resource Pg 401 to 427 32,33 March 12th to 23rd B. Fishing: fishing techniques, overfishing, aquaculture, relevant laws and treaties. The Urban World Urbanization and urban growth, urban resource and environmental problems, transportation and urban development, urban land use planning and control, making urban areas more livable and sustainable. 11. Spring Break Sustaining Biodiversity Species extinction, importance of wild species, extinction threats from habitat loss and degradation, extinction threats from nonnative species, extinction threats from poaching and hunting, other extinction threats, protecting wild species, the sanctuary approach, reconciliation ecology. Lab: Shannon-Weiner Diversity Index (Molnar -18) Environmental laws, Economics, and Ethics Environment and society, Building a sustainable society and sustainable living, Environmental policy making, Our changing world Sustaining Terrestrial Biodiversity: The Ecosystem Approach Human impacts on terrestrial biodiversity, conservation biology, public lands in the United States, and managing and sustaining forests. Ch 10. The Urban World. Pg. 214 to 232 34,35 Ch: 17 Pg 376 to 401 Ch 1 and Ch 2 36,37,38 9th April to 27th April Revision Starts in April Mock Exam Review 12. Tomorrow’s World Living sustainably, eliminating poverty and stabilizing the human population, protecting and restoring Earth’s resources, providing adequate food for all people, mitigating climate change, designing sustaining cities and changing personal attitudes and practices. Mock examination Review and Exam 39






