Agricultural Runoff – Cheat Sheet
advertisement

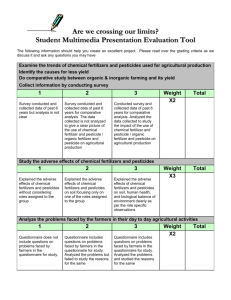
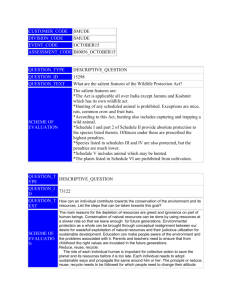
Hauptschein, Dina Koshy, Olivia Xie, Yuan Honors Biology, Period 4 3-10-12 Agricultural Runoff – Cheat Sheet WHAT IS IT? When Pesticides, nutrients, and fertilizers are picked up and then deposited into large bodies of water Type of Nonpoint Source Pollution (The pollutants are picked up and transported during rain and snowmelt events. The rain/snowmelt picks up humans made pollutants and transport them into rivers, lakes, etc.) IMPORTANCE TO BEING STOPPED Deadly effects on human health: Ruin drinking water Destroy rivers, ponds, and wetland’s ecosystems Ruin swimming and boating opportunities When humans are careless they affect ecosystems and habitats in a bad way. This is a problem that could be stopped if take care of. HOW DOES AGRICULTURAL RUNOFF HAPPEN? Sedimentation - Runoff collecting loosen soil and then depositing it in ponds, causing burying of plants, larva, clouds water, can clog gills of fish, and many times fertilizers and pesticides are mixed in this soil. Nutrients – When excess fertilizers are applied the excess is picked up in rainwater, and carried to aquatic ecosystems causing algae bloom, which depletes the oxygen of the pond. It can also run into drinking water creating tainted water with foul orders. Animal Feeding Operations – If farmers keep all their animals in tight confined spaces they create an enormous amount of waste. Runoff from these farms that are badly maintained can carry bacteria, viruses, excess nutrients, and more that can cause problems in the water it is carried to. It can also be carried to drinking water spreading bacteria and viruses. Livestock Grazing – When cattle overgrazes in an area it cause the soil to be exposed making it easier for sedimentation to occur, which can destroy aquatic ecosystems as state above. Irrigation - When crops are overwatered it can cause erosion and carry nutrients and pesticides to aquatic life. Pesticides – When farmers over apply pesticides, they can runoff into aquatic life and drinking water contaminating it. Prevention Sedimentation-Control the flow of water which would help keep the soil in place, reducing sedimentation. Nutrient Overflow-Farmers can create management plans that would make sure not to over use fertilizers, while still maintaining the amount of crops and saving money by not overusing the fertilizers Animal Feeding Operations-Ranches and farmers need to make sure that their animal’s wastes are disposed of in a correct manner, and by managing wastewater. Livestock Grazing- Farmers need to ensure the fact that their animals are not overgrazing an area, which can cause soil to loosen. Provide animals with alternate sources to graze, find shade, water etc. Controlling Irrigation Systems-Control amount of water applied to plants, no need to over water. Also farmers can switch to more efficient irrigation systems Pesticides-Farmers should use Integrated Pest Management. These techniques base the amount of pesticides used on specific soil, climate, pest history, crop conditions etc. o This limits pesticides to only NECCASARY amount WHAT CAN YOU DO? Specifically for Non Agriculture Runoff: GO ORGANIC! Specifically for other Non-Point Source Pollution: Dispose of pet waste, leaves, and debris properly. If not disposed properly, it can end up in outlets that lead directly into ponds, lakes, etc. Don’t over apply fertilizers. Follow directions on the packet. Dispose of household chemicals correctly, such as paint, oil, and antifreeze. For example, household chemicals can lead to spilling which would travel to drains when it rains Clean your car’s oils, grease, and antifreeze. This should be done on grass because the soil absorbs moisture. Use detergents, and cleaning products low in phosphorous and other chemicals. OUTLOOK 1. National Water Program: safe and reliable source of water 2. Farm*A*Syst: preventing pollution on farms, ranches, and in homes using confidential environmental evaluations 3. 2008 NRCS Farm Bill Conservation Programs (Farm and Ranch Lands Protection Program): matches funds to purchase developmental rights to help maintain productive farms and ranchlands in agricultural uses.