[1] each - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
advertisement
![[1] each - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006734661_1-2b43616198e2c5201f73c2a0c0b29d91-768x994.png)
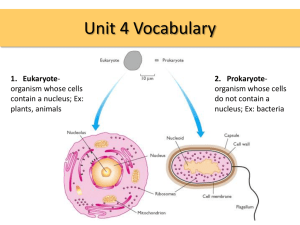
Midterm Review Sheet 2016 1. Cell membrane: label a diagram; Principle components of a cell membrane are proteins and lipids discuss channel proteins and how they are constructed? Channel proteins serve as pumps to move material into and out of the cell easily. They are lined with polar amino acids to enable materials dissolved in water to pass freely. (like dissolves like) 2. What is a tumor A tumor, also known as a neoplasm, is an abnormal mass of tissue which may be solid or fluid-filled. A tumor does not mean cancer - tumors can be benign (not cancerous), pre-malignant (pre-cancerous), or malignant (cancerous). Uncontrolled cell division and may be seen in any organ of the body Compare endocytosis and exocytosis The definitions of exocytosis and endocytosis are as follows: Exocytosis ‘“ the process by which a cell expels molecules and other objects that are too large to pass through the cellular membrane Endocytosis ‘“ the process by which a cell takes in molecules and other objects that are too large to pass through the cellular membrane Both processes require the use of vesicles only in opposite directions Mitosis: # cells produced two daughter cells with identicle nuclei. Phases of mitosis (picture to id) pie chart. ( G1 g2 g0 mitosis) A: interphase / G1, S, G2; B: mitosis / phases of mitosis; Any three of the following [1] each. protein synthesis / translation DNA replication / chromosome replication; cell growth / increase in cell volume; organelle doubling; microtubule formation; respiration / glycolysis; increase energy stores; transcription / mRNA production; Cell organelles, location and identify in a picture, define their function. • Lysosome : hydrolysis / digestion / break down of materials (macromolecules) – including damaged organelles, pathogens (disease causing organisms ex. bacteria), and food materials. • Golgi apparatus : synthesis / sorting / processing/ modifying /transporting / secretion of cell products; • Rough endoplasmic reticulum: site of synthesis of proteins (to be secreted) / intracellular transport of polypeptides to Golgi Apparatus; • Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: synthesizes lipids (phospholipids, steroids (some hormones), triglycerides) • Mitochondrion: (aerobic) respiration / generates ATP (chemical energy used by cell processes); • Chloroplast: photosynthesis (produces glucose needed by mitochondria to produce ATP) • Nucleus : controls cell activities / mitosis / replication of DNA / transcription of DNA (to RNA) / directs protein synthesis; • Centriole/Centrosome: only found in animal cells. Made up of microtubules - responsible for mitotic spindle production for mitosis. And positioning of nucleus. • Peroxisomes: Filled with enzymes. Helps digest fat. Enzymes in peroxisomes depend on peroxisome function. • Ribosome: synthesize proteins. Found on rER and free-floating in cytoplasm. • Cytoplasm: site of chemical reactions (metabolic activity) in the cell. Liquid solution. Holds the cells organelles. Water, ions, glucose, proteins and other organic molecules. • Cell Membrane: regulates the entrance and exit of molecules between the cell and its environment. • Cell Wall: only found in plant cells. Also found in prokaryotes (ex. bacteria). Composed of cellulose. Bacteria cell wall made up of different material. • Cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, micortubules (all made up of protein). Used for cell shape and structure, and movement of substances. Found in both plants and animals. 3. Life functions : list and define 4. Prokaryote vs eukaryote (differences between)( draw each) labelled diagram of generalized prokaryotic (P) and generalized eukaryotic (E) animal cell P is usually smaller in size, E is larger; both have cytoplasm / protoplasm; P has no nucleus / nucleoid region, E has (membranebound) nucleus; P has one chromosome / circular, E has two or more chromosomes; P has DNA only, E has DNA with protein (histones); P has no membrane-bound organelles, E has some membrane-bound organelles; E has mitochondria, P does not; E has other example of organelle, P does not; both can have a flagellum / flagella; if flagella then E has 9+2 fibrils, P does not; P can have pili / slime layer / capsule, E does not; P can have plasmids, E does not; both have ribosomes; P has small ribosomes, E has larger ones; both have cell membrane; P has cell wall, E has no cell wall; E has centriole, P has no centriole. 5. Cell differentiation (what is it) 6. Photosynthesis (factors that affect its rate) where it occurs, pigments involved, explain why a plant is green. 7. DNA base pair 8. Anaerobic vs aerobic respiration ( **chart added) 9. Where does transcription/translation/respiration occur in cells? 10. The structure of fats: made up of 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol. 11. Bonding within the DNA 12. What are the components of a nucleotide: a phosphate, 5 carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base. 13. DNA replication what happens in the correct pathway. (events of) 14. Diagram of glucose/ category 15. Properties of water: Cohesion Adhesion Good coolant 16. Enzyme function: factors that affect the rate, hand and glove model (induced fit model) How will this model effect enzyme action 17. Compare and contrast diffusion and osmosis Must have both for [1]. diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration; osmosis is the diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane; 18. Functions and properties of phospholipids. hydrophillic head groups point outward; hydrophobic tails form a lipid bilayer; forms a (phospholipid) bilayer; ions and polar molecules cannot pass through hydrophobic barrier; helps the cell maintain internal concentration and exclude other molecules;(2 max) hydrophobic tails found in centre (of bilayer) away from water; stability to membrane brought about by attraction between hydrophobic tails / between hydrophilic heads and water; 19. Composition and function of the cell wall cellulose; structural support / protection / maintain turgor pressure; 20. Cell cycle (mitosis) pie chart Cytokinesis events for the animal and plant cell ( differences) plant cells need to produce a cell plate that will go on to form the new cell wall. animal cells: pinching of cell membrane / form cleavage furrow; centrioles; plant cells: cell plate formation; cell wall built (during cytokinesis); 21. Surface area to volume ratio (explain what the numbers indicate) small cells have larger ratio (than larger cells) / ratio decreases as size increases; surface area / membrane must be large enough to absorb nutrients / oxygen / substances needed; surface area / membrane must be large enough to excrete / pass out waste products; need for materials is determined by (cell) volume; cell size is limited (by SA / vol ratio) / cells divide when they reach a certain size; reference to diffusion across / through membrane / surface area; 22. Free ribosome vs attached ribosome (what are the functions of the proteins) free ribosomes produce proteins for inside the cell use attached ribosomes produce proteins for use outside the cell. Difference between globular and fibrous protein (example of each) Protein shape can be categorised as either fibrous or globular. Fibrous proteins tend to be elongated, physically tough and insoluble in water. Collagen found in the skin and keratin found in hair are examples of fibrous proteins. Globular proteins tend to be compact, rounded and water soluble. Haemoglobin and enzymes are examples of globular proteins. fibrous proteins have a long and narrow shape, globular protein have rounded shape; fibrous mostly insoluble in water, globular protein soluble in water; fibrous: collagen / myosin / silk / keratin / other fibrous protein; Globular: immunoglobulin / hemoglobin / catalase / named enzyme / other 23. Functions of proteins 24. Structural Collagen strengthens bones, skin and tendons. Movement Myosin found in muscle fibers causes contraction of the muscle which results in movement. Transport Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to other tissues in the body. Defense Immunoglobulin acts as an antibody. 25. 26. Active vs passive transport: compare and contrast Cell theory principles and exceptions 27. Photosynthesis write the chemical reaction Where does the light independent reaction occur? Significance of the polarity of amino acids for the cell membrane Polar amino acids are found inside membrane proteins and create a channel through which hydrophilic molecules can pass through. polar amino acids are hydrophilic / "water loving"; polar amino acids form hydrophilic proteins / channels; allow hydrophilic / polar / charged particle substances through the membrane; controls shape / function / location of the protein in the membrane; polar amino acids on the surface proteins make them water soluble; Why are different enzymes required either during the various steps of a single reaction or between individual reactions? What will effects be on an enzyme when changing the conditions? (Temp, etc.) The enzyme becomes denatured, the activesite is distorted or damaged and the enzyme no longer functions Compare and contrast DNA with RNA DNA and RNA both consist of nucleotides which contain a sugar, a base and a phosphate group. However there are a few differences. Firstly, DNA is composed of a double strand forming a helix whereas RNA is only composed of one strand. Also the sugar in DNA is deoxyribose whereas in RNA it is ribose. Finally, both DNA and RNA have the bases adenine, guanine and cytosine. However DNA also contains thymine which is replaced by uracil in RNA. What is meant by semiconservative and why this applies to DNA replication. DNA must split and the new DNA will consist of one old strand and one new strand Draw prokaryote and eukaryote, draw stages of mitosis (is interphase a stage and why or why not) List some of the commercial uses of enzymes, Production of lactose free products, cleaning products what is an enzyme inhibitor it is a material that looks just like the substrate and binds to the enzyme in place of the substrate. When this happens the reaction rate does not proceed. and how can I get the reaction to proceed in spite of the presence of this inhibitor. Increase the amount of substrate so the enzyme will find the appropriate substrate instead of the inhibitor. Describe the process of transcription and translation What are the steps to the process of polymerase chain reaction? How is insulin produced? (3 ways) outline the steps for production of insulin within bacteria. Draw a DNA molecule: