Science - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

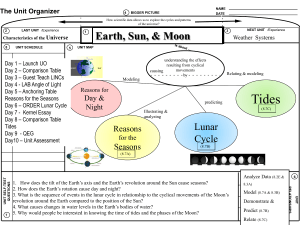
Hearne ISD Science Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Guiding Questions/ Specificity Unit Subtopic: Electromagnetic Spectrum 8.8(C) explore how Guiding Questions: different wavelengths of the electromagnetic How do astronomers spectrum such as light evaluate different types of and radio waves are electromagnetic radiation used to gain to gather information about information about objects in space? distances and properties of Specificity: Properties of waves components in the - amplitude universe; - frequency - wavelength EOC SUPPORTING Transverse/ Longitudinal Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium. Revised Spring 2014 Assessment What does the Redshift of a galaxies spectral lines tell astronomers? a. Galaxies are moving away from each other. b. Galaxies are moving towards each other. c. Galaxies are not moving. d. Galaxies are crashing into each other. Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Wavelengths Days to Teach: 4 Days Electromagnetic Spectrum Amplitude Electromagnetic Pics Frequency Electromagnetic spectrum Electromagnetic Spectrum Poster Electromagnetic waves Resources/ Weblinks APPS: NASA Hubble Top 100 Exoplanet NASA Viz Planets Moon Jog Nog Science Glossary Khan Academy www.glencoe.com/sites/ common_assets/science/ virtual_labs/CT05/CT05 .html Light waves Radio waves EM Spectrum in Space (right click on .jpg, select package object, click yes) Spectrum-space.jpg Vocabulary Concentration http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/00 78617766/171920/index .html Electromagnetic Spectrum Information http://imagine.gsfc.nasa. gov/docs/science/know_ l1/emspectrum.html Hearne ISD Science Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Guiding Questions/ Specificity Unit Subtopic: Components of the Universe 8.8(A) describe What are nebulae and components of the why are they important? universe, including stars, nebulae, and Explain how to use the galaxies, and use HR Diagram to describe models such as the the magnitude and Herztsprung-Russell temperature of stars. diagram for classification; Specificity: Galaxy Types: Elliptical EOC READINESS Spiral Irregular Stars – lifecycle of small and large stars Revised Spring 2014 Assessment Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Days to Teach: 4 Days Many of the stars in the H-R Diagram fall in a diagonal line. What relationship can be seen among surface temperature and brightness in the main sequence stars? a. Surface temperature decreases as brightness decreases. b. Surface temperature increases as brightness decreases. c. Surface temperature decreases as brightness decreases. d. Surface temperature increases as brightness increases. Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Universe The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Reading/Questions HR Diagram Nebulae Make your own HR Diagram Magnitude/ Brightness Main sequence Cluster Constellation Exemplar Lesson “Components of the Universe” TEKS 8.8A Resources/ Weblinks Hearne ISD Science Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Unit Subtopic: Sun 8.8(B) recognize that the Sun is a mediumsized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times closer to Earth than any other star; EOC SUPPORTING Guiding Questions/ Specificity Guiding Questions: Where is the sun located in reference to the earth and to the universe? Specificity: Review 6.11A describe physical properties, locations, and movements of the sun. Describe the properties of the sun using the HR Diagram and the Sun’s lifecycle. Teacher Note: remind students that the Sun is the source of all energy. Assessment What size is the Earth’s sun? a. Small b. Medium c. Large d. Giant Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Days to Teach: 4 Days Suggested Activities: STEMscopes Simple Science Solutions Unit in Google Drive: Middle School Science Folder Notes: Our Sun Astronomy Review Games ELPS Student Expectations: http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us /rules/tac/chapter074/ch 074a.html 4F: Nonlinguistic Rep/Graphic Organizers/Visual/Vid eos 1F: Cornell Notes 2D: KWL Revised Spring 2014 Resources/ Weblinks http://qldscienceteacher s.tripod.com/junior/astr o/sun.html http://reviewgamezone. com/topics.php?id=1&n ame=Astronomy Hearne ISD Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Science Guiding Questions/ Specificity Unit Sub-Topic: Light Years 8.8(D) model and describe Guiding Questions: What unit of measurement how light years are used to is best to use to measure measure distances and distances between objects sizes in the universe. in space? EOC SUPPORTING Specificity: Identify a light year as a measurement of distance, not of time. Speed of light = 300,000 km/s Light year = 9.5 trillion km Teacher Note: Some distant galaxies are so far away that their light takes several billion of years to reach the earth. From Earth we see them as they were in the past. Review 6.11 C concerning history and future of space exploration. Revised Spring 2014 Assessment How long does is take the light from a star that is 11.9 light-years away to reach earth? a. 11.9 years b. 11.9 x 9.5 trillion years c. 11.9 sec d. 11.9 x 9.5 trillion sec Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Light year Days to Teach: 2 Days Suggested Activities: Scientific notation Astronomical Unit (AU) Speed of Light Exemplar Lesson: “Light Years” TEKS 8.8D Light Years Activity Additional Assessment Questions Resources/ Weblinks Stemscopes Hearne ISD Science Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Assessment Guiding Questions/ Specificity Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Unit Sub-Topic: Origin of the Universe 8.8(E) research how scientific data are used as evidence to develop scientific theories to describe the origin of the universe. Guiding Questions: How do scientists use telescopes and microwave radiation to study the origins of the universe? What is the Big Bang Model of the origin of the universe? Days to Teach: 4 Days All the stars we observe from Earth emit light that is shifted, to varying degrees, to longer wavelengths. This evidence is used to support the Big Bang Theory because it shows that stars we observe – a. Specificity: Include several different theories of the origin of the universe Ex: Big Bang, Big Crunch, Inflation Universe, Oscillating Universe Teacher Note: Review TEK 8.3D concepts relating the impact of research on scientific thought and society. Revised Spring 2014 Resources/ Weblinks are all older than our Sun. b. are made up of helium gas. c. use nuclear fusion to make light. d. are moving away from us. Big Bang Theory Stemscopes Red shift www.prometheanplanet.co m/en/Resources/Item/2716 6/the-big-bang Spectroscope Spectrograph The Big Bang Hearne ISD Science Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Guiding Questions/ Specificity Unit Sub-Topic: Lunar Phases 8.7 (B) demonstrate and Guiding Questions: predict the sequence of Predict the next moon events in the lunar cycle phase... EOC READINESS What is the difference between waning and waxing? Assessment Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Days to Teach:– 4 Days The phase immediately following a new moon in the lunar cycle is called a. First quarter b. Waxing gibbous c. Waxing crescent d. Full Moon Lunar Phase Animation of lunar phases http://astro.unl.edu/naap/lp s/animations/lps.html Month http://www.valdosta.edu/~ cbarnbau/astro_demos/fra meset_moon.html Waning What is the difference between rotation and revolution? Waxing Specificity: Review 6.11 B concepts explaining that gravity is the force that governs motion in the solar system Revolution Moon Phases Calendar http://www.middleschools cience.com/moonphase.pd f Rotation Moon Phases www.prometheanplanet.co m/en/Resources/Item/4251 2/moon-phases Period Lunar Lollipops Be sure to illustrate a model of the lunar cycle predicting what comes next and concentrating the position of the moon, earth and sun. http://www.windows2univ erse.org/teacher_resources/ lunar_edu.html http://www.sciencespot.net /Media/moonphases.pdf Phases Poster Exemplar Lesson “Predicting Lunar Cycle” TEKS 8.7B Revised Spring 2014 Resources/ Weblinks Hearne ISD Science Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Unit Sub-Topic: Tides 8.7 C – relate the position of the Moon and Sun to their effect on ocean tides. EOC SUPPORTING Guiding Questions/ Specificity Assessment Guiding Questions: How does the alignment of the sun and moon affect the earth? (oceans). What are the positions of the moon, the sun, and Earth when spring tides occur? a. The sun is perpendicular to the moon and Earth. b. The moon is perpendicular to the sun and Earth c. The moon, the sun, and Earth are in a line with either the moon or the sun in the middle. d. The moon, the sun, and Earth are in a line with either the moon or Earth in the middle. Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Days to Teach: 4 Days Specificity: Show the relationship between the moon phases and the change between spring and neap tide. Emphasize the effects of gravity. (Supports 6.11 B) Show an animation Relationship Tides Animation tides spring neap http://www.valdosta.edu/~ cbarnbau/astro_demos/fra meset_moon.html Tides worksheets location gravity Tides Exemplar Lesson “Tides” TEKS: 8.7C Additional Assessment Questions Revised Spring 2014 Resources/ Weblinks http://www.onr.navy.mil/F ocus/ocean/motion/tides1. htm Hearne ISD Science Course: Eighth Grade Unit: Earth and Space TEKS Unit Sub-Topic: Seasons 8.7 (A) – model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the Sun causing changes in seasons EOC READINESS Guiding Questions/ Specificity Assessment Designated Six Weeks: Third Six Weeks Days to teach: 25 Days Vocabulary Instructional Strategies Days to Teach: 4 Days Guiding Questions: What causes seasons? What causes day and night? What is Earth’s period of revolution? Rotation? Specificity: Review 6.11 A,B A. the characteristics and properties of celestial bodies and B. that gravity is the force that governs motion in our solar system. Which of the following best describes why the Earth has the four seasons? A. The sun is closer to the Earth during summer and farther away during winter B. The sun shines directly onto the equator all year long C. The 23.5° tilt of the Earth is the primary reason for the seasons D. The speed of the Earth's revolution. Rotation Revolution Seasons Seasons Animation Axis Orbit Seasons Activity Ellipse Direct Indirect Exemplar Lesson TEKS 8.7A “Reason for Seasons” Seasons Astronomy Review Games ELPS Student Expectations: http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us/r ules/tac/chapter074/ch074 a.html Revised Spring 2014 Resources/ Weblinks http://www.valdosta.edu/~ cbarnbau/astro_demos/fra meset_moon.html http://reviewgamezone.co m/topics.php?id=1&name =Astronomy