USG - Basic Chemistry
advertisement

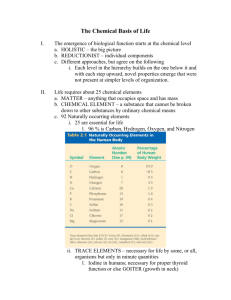
UNIT 1: CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE 1B: Basic Chemistry Roadmap for the year: Themes for the year: Unit 1: Chemical Basis of Life How does this unit contribute to your understanding of the following themes? 1A Characteristics of Living Things 1B Basic Chemistry Life on Earth has various Levels of 1C Biochemistry Organization Unit 2: Ecology and Human Impact The Structure of Living Things Unit 3: Cell Biology leads to their Function Unit 4: Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology Unit 5: Genetics and Evolution Unit 6: Human Body Systems The Big Picture for Unit 1… Science is a body of knowledge and skills acquired through systematic experimentation and observation to describe natural phenomena; or, more simply, it is a “way of knowing”. The diversity of life is the result of ongoing evolutionary change. Species alive today have evolved from ancient common ancestors. All organisms share a set of fundamental characteristics which define “life.” Living organisms are made of molecules that react with each other in predictable ways. There are four main groups of biological molecules that make up the structure of living things and control their functioning. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What is science? What is biology? What does it mean to be ‘alive’? How can species change over time? What are the basic chemical principles that affect living things? How do the unique properties of water make life on earth possible? Why is water so important to organisms? What role do biological molecules play in sustaining and controlling life? How do chemicals combine and break apart inside living things? How do enzymes control the rate of reactions? How does chemical structure lead to biological function? Suggested Resources… Textbook: Biology (Miller and Levine, 2010) (Sections 2.1, part of 2.2, and the Periodic Table of Elements) Websites: www.webelelements.com Directions: Below are check lists of things you should know and things you should be able to do by the end of the unit. Use this tool to help you prepare for the unit assessment. By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: 9. Some covalent bonds don’t share electrons equally and result in molecules which have unequal charge distribution (polar covalent bonds). 1. An atom is the basic unit of matter. An element is a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom. 10.Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, A compound is a substance formed by it is able to form multiple hydrogen the chemical combination of two or bonds, which account for many of its more elements in definite proportions. special properties. A molecule is the smallest unit of most compounds that displays all the 11.Water’s special properties allow it to properties of that compound. act as solvent in which solutions can 2. The basic structure of an atom form. Some molecules (polar) (protons, neutrons and electrons) and dissolve and some (ionic compounds) the charges of the subatomic particles. dissociate. 3. The Periodic Table of the Elements is By the conclusion of this unit, you should an important resource developed as a be able to do the following: result of many scientific discoveries which is crucial to the study of 1. Define atom, element, compound, and chemistry. molecule. 4. Atoms interact based on the number of electrons in their valence level to form 2. Identify the three types of subatomic molecules. particles found in atoms. 5. Atoms may bond with other atoms in order to form stable molecules (i.e., 3. Use the Periodic Table of the covalent bonds form when atoms Elements to determine the reactivity of share electrons). an atom of any particular element and 6. Equations, chemical names, chemical predict the number of bonds which it formulas, structural formulas, will be able to form symbols, subscripts, and/or coefficients can be used to represent 4. Explain why some atoms are more atoms, molecules and/or chemical reactive than others. reactions. 7. Chemical reactions occur when 5. Describe covalent bonding. molecules (reactants) interact and bonds break and reform in new 6. Realize that reactants form products in configurations (products). a chemical reaction and follow the law 8. The Law of Conservation of Matter of conservation of matter. governs chemical reactions. BASIC CHEMISTRY KEY TERMS Words found in the textbook: 1. Atom 2. Molecule 3. Electron 4. Nucleus 5. Element 6. Covalent Bond 7. Reactants 8. Products Words NOT found in the textbook (use your note packet- you may have to generate definition in your own words- give it a try!!) 9. Matter 10. Proton 11. Neutron 12. Valence level 13. Octet Rule 14. Atomic Number 15. Mass Number 16. Atomic Symbol 17. Periodic Table 18. HONC (what does this stand for?) 19. Reactivity 20. Chemical Bond 21. Stable/Unreactive 22. Unstable/reactive 23. Neutral 24. Charge 25. Chemical Formula 26. Chemical Equation 27. Coefficient 28. Structural Formula 29. Subscript 30. Law of Conservation of Matter