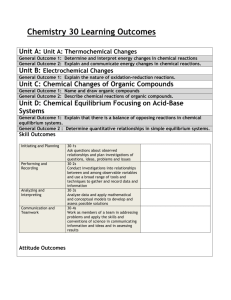
Key Learning of the Unit:
advertisement
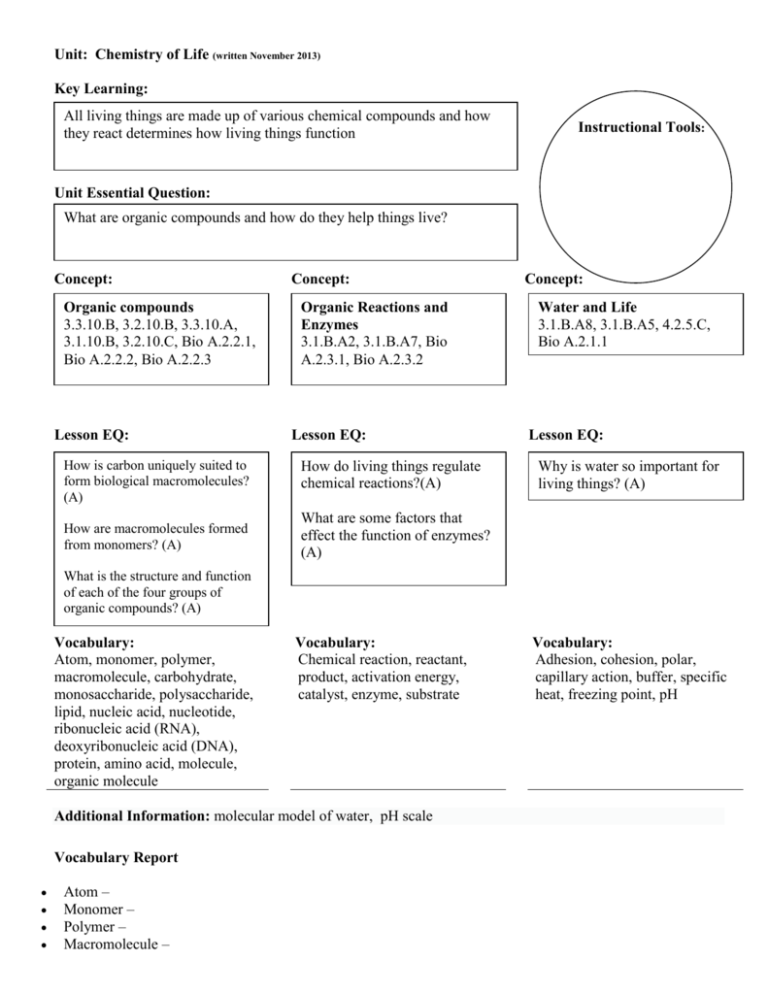
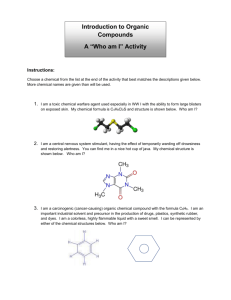
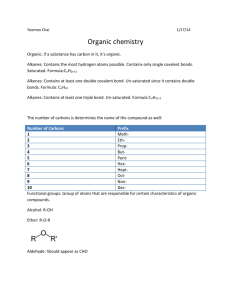
Unit: Chemistry of Life (written November 2013) Key Learning: All living things are made up of various chemical compounds and how they react determines how living things function Instructional Tools: Unit Essential Question: What are organic compounds and how do they help things live? Concept: Organic compounds 3.3.10.B, 3.2.10.B, 3.3.10.A, 3.1.10.B, 3.2.10.C, Bio A.2.2.1, Bio A.2.2.2, Bio A.2.2.3 Lesson EQ: Concept: Organic Reactions and Enzymes 3.1.B.A2, 3.1.B.A7, Bio A.2.3.1, Bio A.2.3.2 Lesson EQ: How is carbon uniquely suited to form biological macromolecules? (A) How do living things regulate chemical reactions?(A) How are macromolecules formed from monomers? (A) What are some factors that effect the function of enzymes? (A) Concept: Water and Life 3.1.B.A8, 3.1.B.A5, 4.2.5.C, Bio A.2.1.1 Lesson EQ: Why is water so important for living things? (A) What is the structure and function of each of the four groups of organic compounds? (A) Vocabulary: Atom, monomer, polymer, macromolecule, carbohydrate, monosaccharide, polysaccharide, lipid, nucleic acid, nucleotide, ribonucleic acid (RNA), deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), protein, amino acid, molecule, organic molecule Vocabulary: Chemical reaction, reactant, product, activation energy, catalyst, enzyme, substrate Additional Information: molecular model of water, pH scale Vocabulary Report Atom – Monomer – Polymer – Macromolecule – Vocabulary: Adhesion, cohesion, polar, capillary action, buffer, specific heat, freezing point, pH Carbohydrate – Monosaccharide – Polysaccharide – Lipid – Nucleic acid – Nucleotide – Ribonucleic acid (RNA) – Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) – Protein – Amino acid – Molecule – Organic molecule – Chemical reaction – Reactant – Product – Activation energy – Catalyst – Enzyme – Substrate – Adhesion – Cohesion – Polar – Capillary action – Buffer – Specific heat – Freezing point – pH