Samples_and_Studies 12_1
advertisement

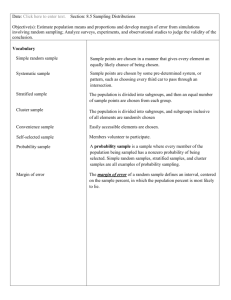
NAME _____________________________________________ DATE ____________________________ PERIOD _____________ 12-1 Study Guide and Intervention Samples and Studies Sampling A population consists of all of the members of a group of interest. Since it may be impractical to examine every member of a population, a sample or subset is sometimes selected to represent the population. Sample Definition Simple random Each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Systematic Members are selected according to a specified interval from a random starting point. Self-selected Members volunteer to be included. Convenience Members that are readily available are selected. Stratified The population is first divided into similar, nonoverlapping groups. Members are then randomly selected from each group. Example: SCHOOL The principal of a high school wanted to know if students in the school liked the attendance policy. He decided to survey the students in the third-hour study hall about whether they like the attendance policy. Fewer than one fourth of the students in the school have a study hall. a. Identify the sample, and suggest a population from which it was selected. The sample includes only those students in the third-hour study hall. The population is the entire student body. b. Classify the sample as simple, systematic, self-selected, convenience, or stratified. Explain your reasoning. This sample is a convenience sample because it is convenient to sample students in a study hall during a certain period of the day. Exercises Identify each sample, and suggest a population from which it was selected. Then classify the sample as simple, systematic, self-selected, convenience, or stratified. Explain your reasoning. 1. SHOPPING Every tenth person leaving a grocery store was asked if they would participate in a community survey. 2. GARDENING A gardener divided a lot into 25-square-foot sections. He then took two soil samples from each and tested the samples for mineral content. 3. SCHOOL The counselors of a high school sent out a survey to senior students with questions about their plans for college. 40% of the seniors sent responses back. Chapter 12 5 Glencoe Algebra 1 NAME _____________________________________________ DATE ____________________________ PERIOD _____________ 12-1 Study Guide and Intervention (continued) Samples and Studies Studies Information is collected from samples using one of the following study types. Type Definition Survey Data are collected from responses given by a sample regarding their characteristics, behaviors, or opinions. Observational Study Members of a sample are measured or observed without being affected by the study. The sample is divided into two groups: Experiment • an experimental group that undergoes a change, and • a control group that does not undergo the change. The effect on the experimental group is then compared to the control group. Example: Determine whether each situation describes a survey, an observational study, or an experiment. Explain your reasoning. a. SHOPPING The manager of a department store wants to analyze customers’ overall shopping experience. Checkout clerks distribute a questionnaire to all shoppers that make a purchase. This is a survey. The data are gathered from responses given by members of the sample. b. MARKETING A marketing group places new displays for a product in selected stores and then observes shoppers’ reactions as they pass by a display. This is an observational study. The data are gathered from observing the shoppers. Exercises Determine whether each situation describes a survey, an observational study, or an experiment. Explain your reasoning. 1. UNIFORMS An athletic trainer is testing a new fabric. He has half of the football team wear their normal uniforms and the other half wears uniforms made from the new fabric. He observes and analyzes the mobility of the players. 2. FOOD A researcher from a pet food manufacturer places multiple bowls of its several flavors of dog food in a room with 20 dogs. The researchers records which foods the dogs eat. 3. EVALUATION At the end of the school year, each teacher distributes 10 standard questions to each of their students that ask the students to rate their teachers’ guidelines and classroom practices on a 5-point scale. Chapter 12 6 Glencoe Algebra 1