ch. 5 notes
advertisement

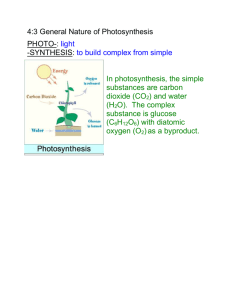
Matter and Energy Pathways in Living Systems – Con’t Photosynthesis - Process that converts energy from the sun into chemical energy that is used by living cells. - Occurs mostly in plants and certain bacteria. These can be found on land as well as in oceans, lakes, streams and rivers. - Organisms convert carbon dioxide into organic molecules using light energy captured by chlorophyll. - Most important process on earth - Humans are completely dependent on this process for the air we breathe and the food we eat. - Water, carbon dioxide and energy → glucose and oxygen Cellular Respiration - Releasing stored energy - Mitochondria in the cells of multicellular organisms break down carbohydrates to generate molecules of ATP. 1 ATP and ADP (p. 163) - ATP (adenosine triphosphate) supplies energy for cellular activities. o Active transport of ions and molecules across cell membranes o Moving chromosomes during cell division o Causing cilia and flagella to move o Causing muscles to contract o Synthesizing compounds such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats and nucleic acids. 2 - ATP is always being used, yet cells maintain a constant supply. o When the bond to the third phosphate group in ATP breaks, energy is released. This chemical energy that is released enables most life-sustaining cellular activities to take place. o This reaction produces ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and a free phosphate group. o ATP is then regenerated by the addition of a free phosphate group to ADP – a process that requires energy. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bbtqF9q_pFw&feature=related Section 5.1 REVIEW p. 168 #’s 2-10 Read 169- 177 complete questions 12→24 & 27 +28 3 Chloroplasts and photosynthetic pigments - Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) eg. X-rays, microwaves, radio waves. - EMR occurs in individual bundles of energy called photons - Each photon corresponds to a small unit of energy of a particular wavelength. Those with short wave lengths have high energy those with long wave lengths have low energy. - Light from the sun is a mixture of different wave lengths. - When passed through a spectroscope, wave lengths are sorted according to their energies, forming an electromagnetic spectrum. - Light travels in waves. One wavelength corresponds to a photon. - Light is the visible portion of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum. - Our eyes perceive photons of different wavelengths or energies as different colors. (p. 171) - Sun is the ultimate source of energy - Photosynthetic organisms capture solar energy and then store it as chemical energy in the bonds of glucose molecules. - These organisms are the first level in the food web. Their stored energy is passed on to other organisms through the food chain. - All organisms release the energy in glucose molecules by cellular respiration. - Photosynthesis occurs only in green plants and some photosynthetic organisms like algae. - These organisms capture photons from solar energy to begin reactions that make up the photosynthesis process. Chlorophyll - Plants that carry out photosynthesis contain the green colored pigment: chlorophyll. - Chlorophyll absorbs photons from solar energy and begins the process of photosynthesis. - Chlorophyll A – (blue-green) - Chlorophyll B – (yellow – green) - All photosynthetic organisms use chlorophyll A as the primary light absorbing pigment. 4 - Chlorophyll A and B absorb photons with energies in the blue-violet and red regions of the spectrum and reflect those with wavelengths of about 500nm and 600nm which we see as green light. - Using a spectrophotometer (the absorption spectrum of pigments) like chlorophyll A and B can be determined with accuracy. - Chlorophyll A is the only pigment that can transfer energy from sunlight to the reactions of photosynthesis. - Chlorophyll B acts as an accessory pigment, absorbing photons that chlorophyll A absorbs poorly or not at all. - Carotenoids also act as accessory pigments. These will usually transfer the energy they absorb back to a molecule of chlorophyll A. - In the spring and summer, leaves appear green because of high amounts of chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of the leaves. - In autumn, plants stop producing chlorophyll and disassemble those already in the leaves. This causes the other colors (brown, red, orange, yellow) to become visible. 5 - - Chloroplasts Leaves are the primary photosynthetic organ in most plants In order for photosynthesis to occur, a plant must contain chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water, as well as capture solar energy from the environment. Plant cells contain chlorophyll within the photosynthetic membrane of chloroplasts. Since chloroplasts are found only in leaves, no other part of the plant can perform photosynthesis. Chloroplast have two membranes, an outer and an inner membrane. These membranes enclose a protein rich semi-liquid called stroma. Within the stroma are a system of membrane bound sacs called thylakoids, stacked on top of each other to form columns called grana. A typical chloroplast has 60 grana consisting of 30-50 thylakoids. - The thylakoid system inside the chloroplast increases the surface area of the thylakoid membrane, therefore, increasing the efficiency of photosynthesis. - Chloroplasts are able to replicate, by division, independently from the cell. 6