2013-midterm-review-guide-earth

2013-2014 Lab EARTH SCIENCE
MIDTERM EXAMINATION STUDY GUIDE
About the Exam:
The Lab Earth Science Exam will take place on Thursday January 30 th on a regular school day and class period. ALL Science exams will take place that day. If you are absent, the exam must be made up after school, the following week. The EXAM is composed of 50 multiple choice questions. With each question
4 choices will be provided. You must choose the best answer. The exam covers units from the first half of the year, this includes the branches of Earth Science, lab safety, the scientific method, the extinction of the dinosaurs, the layers of the Earth, Earth’s Energy Budget, the ‘sphere’ words, food chains and food webs, Latitude and Longitude, Map Skills, Contour Maps, Seasons, Continental Drift and Plate
Tectonics, Types of Plate Boundaries, Earthquakes and Seismic Waves, Geologic Time Scale , Fossils ,
Minerals and Rocks and the Rock Cycle.
Skills That You Should Practice:
Understand that Science is an evidence based discipline that tries to explain the forces that impact the natural world and prevent or prepare humans for natural disasters. Students will be expected to provide proof or evidence of major Earth Science theories and show how matter and energy cycle through sll the parts of the Earth System. The Earth is a dynamic, changing planet. Students will also be expected to show evidence of the causes and effects of change.
How You Should Prepare For the Exam :
To be SUCCESSFUL on this exam- it is suggested that you begin studying/reviewing at least 2 weeks
before the actual exam (in other words- for several hours). Any/all of the following methods of review are suggested:
Download this study guide to your computer and type in the answers as you complete them, then print out your answers and quiz yourself
Study class notes in your Interactive NOTEBOOK
Review diagrams in the textbook
Review end of chapter/section questions in your textbook
Compare and contrast information
Create mnemonics, rhymes, concept maps or other devices to help in recall of vocabulary and processes learned this semester
Look at previous chapter tests and/or quizzes and lab activities
The Following general tips for studying should help you, no matter what your course of study:
Find a calm and relaxed place to study
Be well rested for studying AND for exam day take regular breaks think positively
Schedule your study time well and set goals for each time you review
Find a study partner bring # 2 pencil(s) with erasers
Eat a good breakfast on the morning of your test
On the test day, dress comfortably and in layers, in case the test site is warm or cool
Answer ALL quations on the study guide and have a family member or friend test you on it
Chapters covered by the exam:
Chapter 1- Intro to Earth Science Chapter 8 Fossil (last section only pp 197-200)
Chapter 2- The Earth as a System
Chapter 3 Models of Earth
Chapter 5 Minerals
Chapter 6 Rocks
Chapter 9 Geologic Time Scale (1st section only)
Chapter 10 plate Tectonics
Chapter 12 Earthquakes (2 nd section only)
Chapter 26 Seasons (2 nd only pp 667-673)
Practice Questions :
1.
Explain what the acronym O.M.E.G.A. means and give examples ( pp 8-9)
2.
Safety in the science lab is mainly based on ______________ ___________ (pp10-11)
3.
How did the dinosaurs become extinct? Give 4 pieces of evidence to support the meteorite impact hypothesis. What would happen to this idea if new technology discovered some conflicting evidence that made it hard to accept? ( pp 12-13, Ch. 1)
4.
On the day of the midterm, the sun will rise at 7:07 a.m. and set at 5:13 p.m. How many
__________hours and _____________minutes of daylight will we have that day? Why is it changing? ( p 14)
5.
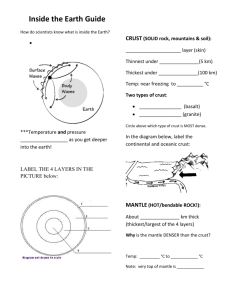
Label the layers of the Earth with the terms below.
Continental Crust - the thick parts of the Earth's crust, not located under the ocean.
Lithosphere - the crust plus the rigid, upper mantle.
Lower Mantle (semi-rigid) - the deepest parts of the mantle, just above the core.
Mohorovicic discontinuity - separates the crust and the upper mantle.
Ocean - large bodies of water sitting atop oceanic crust.
Oceanic Crust - thin parts of the Earth's crust located under the oceans.
Upper Mantle (rigid) - the uppermost part of the mantle, part of the Lithosphere.
Upper Mantle (flowing) = Asthenosphere - the lower part of the upper mantle that exhibits plastic (flowing) properties. It is located below the lithosphere (the crust and upper mantle).
6.
The Earth also has an Iron and Nickel core. How do we know this if no one has been able to dig down that far? Distinguish between the Outer and Inner Core.(pp16-17)
7.
What is the shape of the Earth ______________ ___________________ (p 19) What is the Circumference of the Earth __________________ the diameter?_______________
8.
The Earth is a ___________________(open/closed) system in terms of Energy and an
____________________ (open/closed) system in terms of Matter. (p21)
9.
What are the 4 main energy sources for the Earth system? (p 21 – Chapter 2)
10.
Define the term RESERVOIR- ( p23) What is the main reservoir for the following substances that cycle through the Earth System- Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and
Water ( p23)
11.
Create two possible food chains from the food web depicted below:
12.
How are food chains different from food webs ( pp24-25)
13.
Fill in the blanks below.
1.
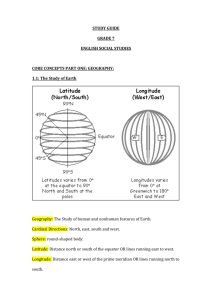
There are _____ seconds in a minute, _____ minutes in a degree, and _____degrees in a circle.
2. Latitude measures distance _____ and _____ of the _____.
3. Longitude measures distance _____ and _____ of the ______________ which runs through __________.
4. Latitude measures as high as _____ which represents the ________ and longitude measures as high as _____.
5. At the poles, all lines of longitude (meridians) __________.
6. The coordinates of the north pole are _____ and of the south pole are _____.
2.
Using the map on the next page- fill in the Latitude and Longitude of the labeled spots in the table below: letter Latitude Longitude
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
14.
On the map, the blue represents streams, the brown lines are contours. The elevation of one point is given as 537 feet above sea level.
1.
Determine towards which direction the stream is flowing.
2.
Label all contours.
3.
Calculate the average gradient along the stream from the red dot at A to the red dot at B.
4.
Determine the range of possible elevations for the pink dots at C, D and E. ( see pp 34-37)
15.
Match the maps with their corresponding mountain profiles. Imagine that you are viewing the mountain from the southern end (bottom) of the map (as indicated by the eye).
( see pp 38-39)
View 1 matches View ____ View 2 matches View ____ View 3 matches View ____
View 4 matches View _____View 5 Matches View ____ View 6 matches View _______
1 2 3 4 5
A B C D E
16.
Why do we have seasons? ( 3 reasons) Give the date and name for each season- what happens to the period of daylight and darkness as the Earth moves around the Sun? What season are we in now? ( PP42-43)
17.
List 8 pieces of evidence to support Alfred Wegener’s theory of CONTINENTAL DRIFT. ((p45)
18.
Put the steps in the breakup of PANGEA in order ( p 44)
19.
What is the SUPERCONTINENT CYCLE? ( p46)
20.
Fill in this table describing the 4 kinds of plate boundaries and the geologic features that form there.(pp52-53)
TYPE OF BOUNDARY
CONVERGENT
DIVERGENT
TRANSFORM
Geologic Features examples
HOT SPOT
21.
Use the EARTHWEEK story to plot current Earthquake and Volcanic Activity. ( p 55)
22.
How do seismologists pinpoint the epicenter of an earthquake?
23.
Put these terms in order from largest unit to smallest unit of Geologic Time (p62)
AGE EON EPOCH ERA PERIOD
24.
We live in the _________________________ ERA
25.
What pattern do you observe in the complexity and variability of life on Earth as you move from the beginning of Geologic Time to the present? ( p 62)
26.
How old is the Earth ______________________________
27.
How do Fossils form? ( p 64)
28.
What are 4 types of fossils? (p 65)
29.
What is a mineral? ( (p 69)
30.
What are some common properties and tests that can be done to identify minerals? ( pP70-71)
31.
Describe the characteristics and give 3 examples of IGNEOUS Rocks ( p 73)
32.
Describe the characteristics and give 3 examples of SEDIMENTARY Rocks (p75)
33.
Describe the characteristics and give 3 examples of Metamorphic Rocks ( p77)