30e41e34-1108-4c2c-ab36
advertisement

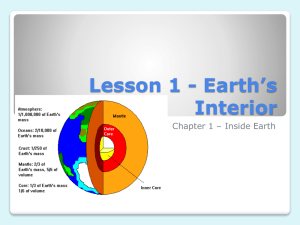
Chaper 10 Dynamic Earth Name: Class: Date: Instructions to students: Please write answers in spaces provided. Multiple-choice questions 1 Marks If a shellfish dies its body decays but its shell remains. Sometimes fine silt gets inside the shell and hardens. Over many years the shell may wear away leaving the shape of the inside of the shell as a fossil. This fossil is said to be: 2 A carbonised B a mould C petrified D a cast Answer: ______ 2 Which one of the following is NOT classified as a fossil? 2 A a leaf impression B a cast of a snail shell C a crystal of quartz D petrified wood Answer: ______ 3 The teeth of animals are often the only remains found as fossils. This is because: 2 A there are more teeth than other structures in the body. B this part of the body is not normally taken away by scavengers. C teeth are very hard and resist weathering. D teeth are the only part of the body not broken down by decomposers. Answer: ______ © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 1 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth 4 The diagrams below show the fossils found at three different road cuttings. The fossils which look the same are the same age. 2 Fossil 5 is a small fish complete with scales and is the only fossil that isn’t a shell. It is very rare, whereas the shells are very common. The most likely reason for its preservation is that: A it probably lived on land. B it was covered quickly by mud and preserved. C it is an invertebrate. D it is much younger than all of the other fossils. Answer: ______ 5 The diagrams below show the fossils found at three road cuttings. The fossils which look the same are the same age. 2 Which one of the following statements is FALSE? A Fossil 1 is older than fossil 5. B Fossil 3 is older than fossil 1. C Fossil 4 is older than fossil 10. D Fossil 10 is older than fossil 8. Answer: ______ © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 2 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth 6 Many fossils are found in caves. The LEAST likely reason for this is that: 2 A many animals use caves for shelter. B there is no light in caves. C there is no wind or rain in caves. D there is little variation of temperature in caves. Answer: ______ 7 The order of the layers from the inside of the Earth outwards is: 2 A inner core, outer core, mantle, crust B outer core, inner core, mantle, crust C inner core, outer core, crust, mantle D mantle, inner core, outer core, crust Answer: ______ 8 This diagram shows several layers of rocks which were exposed when a road cutting was made. 2 The order of events which have occurred to cause this sequence of layers is: A folding, deposition, erosion and further deposition. B deposition, folding, erosion and further deposition. C deposition, folding, further deposition and erosion. D deposition, erosion, further deposition and folding. Answer: ______ 9 The inside of the Earth consists of four major layers. Which is the densest layer? 2 A mantle B inner core C outer core D crust Answer: ______ © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 3 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth 10 The inside of the Earth consists of four major layers. In which layer would the focus of an earthquake occur? 2 A mantle B inner core C outer core D crust Answer: ______ 11 The inside of the Earth consists of four major layers. Which is the only layer that will conduct L (surface) waves? 2 A mantle B inner core C outer core D crust Answer: ______ 12 The inside of the Earth consists of four major layers. Which layer causes the movement of the continents? 2 A mantle B inner core C outer core D crust Answer: ______ 13 When an earthquake occurs the shock waves go out in all directions. These can be detected by seismic stations. 2 On this map the seismic stations are located at points A, B and C near a large lake. The waves were detected at A after 12 minutes, at B after 8 minutes and at C after 6 minutes. Where is the epicentre of the earthquake likely to be? A location 1 B location 2 C location 3 D location 4 Answer: ______ © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 4 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth 14 An earthquake measuring 8 on the Richter scale is stronger than one measuring 6. How much stronger is it? 2 A 1.3 times B 2 times C 10 times D 100 times Answer: ______ Short-answer questions 15 Marks This chart shows when different types of living things have appeared and disappeared from the Earth. 6 Indicate whether each of the following statements is TRUE or FALSE. (a) Mammals could have evolved from dinosaurs. ______ (b) Fish could have evolved from dinosaurs. ______ (c) Humans could have hunted dinosaurs. ______ © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 5 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth (d) Dinosaurs could have helped disperse seeds from flowering plants. ______ (e) Seed ferns existed for about 300 million years before becoming extinct. ______ (f) Too many birds could have caused the extinction of the seed ferns. 16 ______ This paragraph has some missing words. Their positions are numbered. 7 A fossil is any remains or trace of any (1) thing. Sometimes they are turned to stone (or (2) ) and sometimes they are turned to carbon (or (3) ). If a footprint is filled with silt and hardens it forms a (4) , whereas if a jellyfish rots away to leave a space it is called a (5) . Usually the soft fleshy parts of an animal (6) but the (7) are left behind. Which word goes in which position? Choose the correct word from the jumbled list at right by writing each one in the correct numbered position: (1) _________________________ (2) _________________________ (3) _________________________ (4) _________________________ (5) _________________________ (6) _________________________ (7) _________________________ 17 petrified carbonised living mould bones, shell or teeth decompose cast This paragraph has some missing words. Their positions are numbered. 8 An earthquake occurs when parts of the Earth’s (1) move past each other. The place where the movement occurs is called the (2) and the point on the Earth’s crust directly above it is called the (3) . The vibrations sent out are measured by a (4) which makes a record called a (5) . The strength of the shock waves is measured on the (6) scale. On this scale each successive number means a (7) times increase in (8) . Which word goes in which position? Choose the correct word from the jumbled list on the right by writing each one in the correct numbered position: (1) _________________________ (2) _________________________ (3) _________________________ (4) _________________________ (5) _________________________ (6) _________________________ (7) _________________________ (8) _________________________ © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition Richter epicentre ten crust magnitude seismograph focus seismogram 6 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth 18 There are three types of shock waves involved in earthquakes. Fill in the blanks to complete their names. 4 (a) ‘P’ or _____________________ waves (b) ‘S’ or _____________ waves (c) ‘L’ or ______ waves. (d) The waves which cause most damage are the _______ waves. (Use P, S or L). Long-answer questions 19 Marks You are out camping with friends in sandhills near the beach and you find a piece of rock with tiny bones in it. The shape of the animal looks as though it is a small fish. 5 Draw simple diagrams in the space below to explain how this fossil was formed and then exposed, and write a brief paragraph to explain the process. © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 7 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth 20 The diagram below represents four layers in the Earth’s crust: F 4 F (a) Draw another diagram on the right showing what will happen to these layers if they are pushed at each end by strong inward forces (F), causing them to bend. (b) Write a short paragraph about this type of Earth movement. 21 The diagram below represents four layers in the Earth’s crust with a major weakness across the layers as shown by the dotted line. F 4 F (a) Draw another diagram showing what will happen to these layers if they are pushed at each end by strong inward forces (F), causing them to break. © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 8 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth (c) Write a short paragraph about this type of Earth movement. 22 (a) Label the parts A, B, C and D indicated by arrows on the diagram below, using these words: continental plate mid-ocean ridge oceanic plate 4 volcano (b) Using the terms in (a), which you should underline, write a paragraph to explain why earthquakes usually occur where plates meet. © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 2 9 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth 23 The hypothesis suggesting that continents were once joined together and have drifted apart was first proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1915. It is now widely accepted as part of ‘Plate Tectonics theory’. Discuss two types of evidence that support Wegener’s original hypothesis. 24 An earthquake occurs and the time of arrival of S and P waves is recorded by seismograph stations in three Australian cities, as shown in the table below (h: hours, min: minutes, s: seconds). (a) Use this data to work out the difference in the time of arrival of the P and S waves, which you should enter in column 4 of the table above. Then use the graph below to calculate the distance of each city from the epicentre, which you should enter in column 5 of the table. (Hint: Convert the difference in time of arrival to seconds to make it easier to use the y-axis scale.) © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition 4 12 (8) 10 Chapter 10: Dynamic Earth (b) From the information in (a), use a ruler and geometric compass to find the location of the epicentre on the map below. © Macmillan Education Australia 2012 ScienceWorld 9 Australian Curriculum edition (4) 11