CG_FHIR_Obs_v3
advertisement

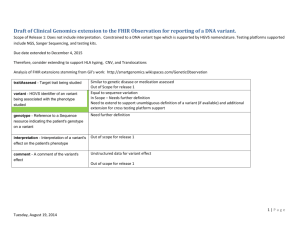
Draft of Clinical Genomics extension to the FHIR Observation for reporting of a DNA variant. Scope of Release 1: Does not include interpretation. Constrained to a DNA variant type which is supported by HGVS nomenclature. Testing platforms supported include NGS, Sanger Sequencing, and testing kits. Due date extended to December 4, 2015 Therefore, consider extending to support HLA typing, CNV, and Translocations Analysis of FHIR extensions stemming from Gil’s work: http://smartgenomics.wikispaces.com/GeneticObservation Similar to genetic disease or medication assessed Out of Scope for release 1 Equal to sequence variation In Scope – Needs further definition Need to extend to support unambiguous definition of a variant (if available) and additional extension for cross testing platform support Need further definition traitAssesed - Target trait being studied variant - HGVS identifier of an variant being associated with the phenotype studied o genotype - Reference to a Sequence resource indicating the patient's genotype on a variant o interpretation - Interpretation of a variant's effect on the patient's phenotype Out of scope for release 1 o comment - A comment of the variant's effect Unstructured data for variant effect Out of scope for release 1 1|Page Tuesday, September 09, 2014 Suggested – preliminary draft Suggested Name (names in bold come from previous HL7 CG standards) Constraints Definition GenomeBuild.version Genomic Reference Sequence Identifier Chromosome GenomicReferenceSequence.version o o o Genomic start o o o Genomic stop o o o Reference allele Observed allele Gene cDNAReferenceSequence.version cDNASequenceVariation using HGVS Nomenclature Exon Gene Identifier Transcript Reference Sequence Identifier DNA Sequence Variation Identifier HGNC NCBI or EBI HGVS DNA Region Name cDNAChangeType DNA Sequence Variation Type Consider linking to SO Ontology terms Consider linking to SO Ontology terms NCBI or EBI HGVS RNAReferenceSequence.version AASequenceVariation using HGVS Nomenclature AAChangeType Amino Acid Change Amino Acid Change Type CommonVariantSynonym Genomic source class Allele Name Genomic source class Allelic State Allelic State Consider linking to SO Ontology terms (germline, somatic, prenatal, unknown genomic origin, likely germline, likely somatic, likely fetal) Heteroplasmic, Homoplasmic, Homozygous, 2|Page Tuesday, September 09, 2014 Heterozygous, Hemizygous Notes from Sept 2, 2014 Continued discussion of tagging some data as derived. Attendees: Grant Wood, Bob Milius, Scott Bolte, Mollie Ullman-Cullere, Larry Babb, and Siew Lam Primary data vs. interpretation --> what the physician gets it the primary data (within the EHR), downstream is the interpretive data --> However, the lab will have different primary data, more upstream . Primary data is the level at which the stakeholder would revert to for a recalculation. If genomic, cDNA, Amino Acid and Allele/Common name are reported from the laboratory, uses should not use one of these elements to recalculate another, because the laboratory likely detected the mutation at one level (genomic) and made decisions at another level (amino acid change). Therefore, the mutation definition should be used in its entirety. If something is inaccurate, the test should be rerun or re-reported. Derived – should not be used to tag the translation to cDNA/AA change or calculation of genomic coordinates (from cDNA). Derived should be used when the presence of a variant is assumed due to presence of another which was measured e.g. * alleles If desire is to denote the initial context of testing, should we use ‘testing platform’ and add ‘providence’ (of the test). providence = source of the information (who e.g. ) (when) what and how LMM’s NGS pipeline 1.0 see how it works here with link to website (e.g. BI pipeline details etc...) In the future this might be held in NCBI’s genetic test registry Look for definition of providence and derived in FHIR Larry – send best representation of variant for additional downstream usage 3|Page Tuesday, September 09, 2014 IOM – establishing data elements and EHR should have to store genetic/genomic information Grant to be attending the meeting Germline list and Somatic elements --> Grant to send out list of somatic elements. Notes from Sept 9 2014 con call Attendees: Amnon Shabo, Grant Wood, Bob Milius, Mollie Ullman-Cullere, Scot Bolte, Siew Lam, Gil Alterovitz, Perry Mar, Vanderbilt: Jonathan Holt, Ari Taylor, Jeremy Warner,Marc Beller How do you support the use cases where the patient is mosaic or there is chimerism (e.g. from a stem cell transplant)? Should germline/somatic designation be at the specimen level? Outcome Germline needs to be well defined. Germline = background genome – – germline/somatic designation should be used at the mutation level - drawing from previous work and maintaining alignment with ClinVar, COSMIC, and other mutation knowledgebases. a qualifier needs to be created and can be used to denote that the mutation is resulting from a ‘chimera’ Qualifier would be mosaic or chimera (preferred) 4|Page Tuesday, September 09, 2014