Reference mapping and variant detection
advertisement

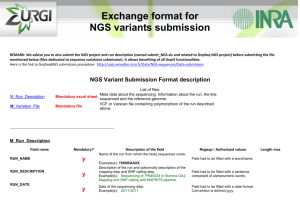
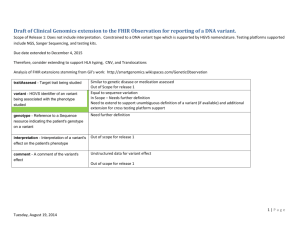
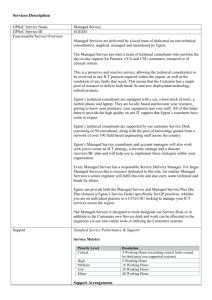
Reference mapping and variant detection Peter Tsai Bioinformatics Institute, University of Auckland Reference mapping The mapping is the process of comparing each read with the reference genome. There are many different software available to perform reference mapping ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Multiple placement of reads (multi-hits) Allow gaps Don’t allow gaps at all Limits on number of mis-matches Assess your mapping results ◦ % of total reads mapped ◦ % of uniquely mapped reads ◦ Coverage statistics, variance in depth Mapped read depth Variant detection Identification of point mutation, short insertion and deletion. We go thought every column of the alignment and see how many alleles are found and how many are different to the reference genome. Reference: ACGAAACGTAGTGAGGAC-GTA sample: ACCAAACGTAGAGAGGACCGTA SNP SNP indels Complexity of variant detection 2nd generation sequencing is NOT single molecule sequencing Due to the PCR amplification, some DNA fragments will be sequenced more often than others => results in uneven coverage across the genome. This would provide false support in variant detection, as we are usually more confident in variants that has higher coverage support. Solution: Mark or remove exact duplicate reads when doing variant detection. Complexity of variant detection Cloning process artifacts (e.g. PCR induced mutations). Error rate associated with the sequence reads. Error rate associated with the mapping. Reliability of the reference genome. Calling a variant A (ref): 0% G: 100% A (ref): 7% T: 93% A hard cut-off in percentage of difference to reference base. 75% as minimum threshold for a variant to be call homozygous variant. Percentage based cut-off assumes you have sufficient coverage. When to call a variant ? A: 18% C: 0% G: 55% T: 27% Alignment considerations Perform local realignment and calculate mapping score to determine which one is better. What depth do I need ? Factors to consider Read length Sequencing depth Require sufficient depth, ~30x Base call quality for each supporting bases Longer reads are more likely to be mapped with high confidences Use high quality bases, Q30 Mapping quality Local realignment to improve variant calling