physical properties of solids (student handout
advertisement
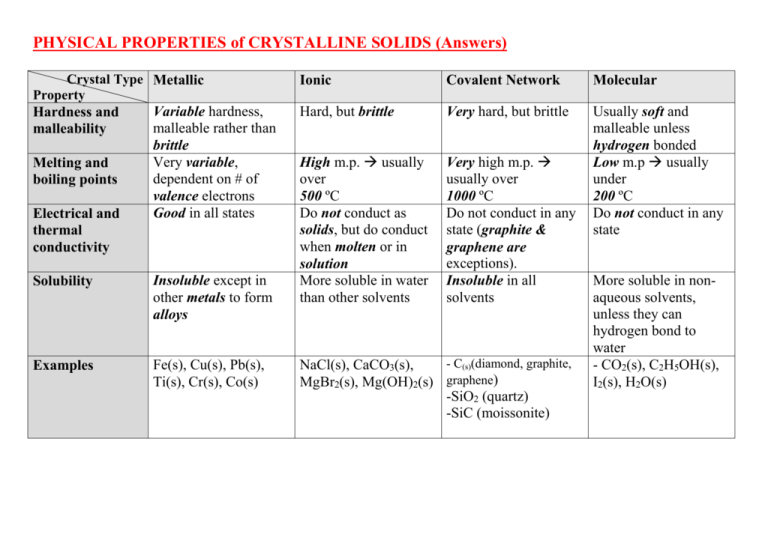
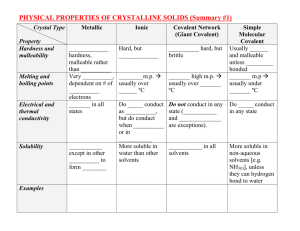
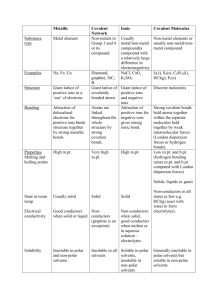
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES of CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS (Answers) Crystal Type Metallic Property Hardness and malleability Melting and boiling points Electrical and thermal conductivity Variable hardness, malleable rather than brittle Very variable, dependent on # of valence electrons Good in all states Solubility Insoluble except in other metals to form alloys Examples Fe(s), Cu(s), Pb(s), Ti(s), Cr(s), Co(s) Ionic Covalent Network Molecular Hard, but brittle Very hard, but brittle High m.p. usually over 500 ºC Do not conduct as solids, but do conduct when molten or in solution More soluble in water than other solvents Very high m.p. usually over 1000 ºC Do not conduct in any state (graphite & graphene are exceptions). Insoluble in all solvents Usually soft and malleable unless hydrogen bonded Low m.p usually under 200 ºC Do not conduct in any state - C(s)(diamond, graphite, NaCl(s), CaCO3(s), MgBr2(s), Mg(OH)2(s) graphene) -SiO2 (quartz) -SiC (moissonite) More soluble in nonaqueous solvents, unless they can hydrogen bond to water - CO2(s), C2H5OH(s), I2(s), H2O(s) SUMMARY #2 (Answers) IONIC COMPOUNDS Volatility Solubility in polar solvent, e.g. water Low Soluble Solubility in nonpolar solvent, e.g. hexane Electrical Conductivity Non-soluble Conduct when molten(l) or dissolved in water(aq) POLAR COVALENT COMPOUNDS Higher Solubility increases as polarity increases Solubility increases as polarity decreases Non-conductors NON-POLAR COVALENT COMPOUNDS Highest Non-soluble GIANT COVALENT Soluble Non-soluble Non-conductors Non-conductors except graphite, graphene and semiconductivity of silicon and (molecular) fullerene, C60 Low Non-soluble Definitions: (i) VOLATILE A substance is volatile if it evaporates at a low temperature (under 100°C). [*e.g. Acetone (CH3COCH3) and gasoline are volatile liquids.] (ii) SEMICONDUCTOR A solid substance that has a conductivity between that of an insulator and that of most metals, either due to the addition of an impurity or because of temperature effects.