Physical versus Chemical Properties
advertisement

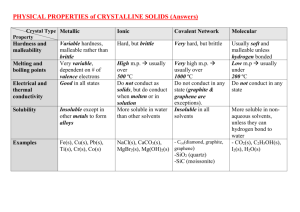
Physical Properties What are they? Expectation: The student will be able to distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Prerequisite: What are physical properties? Bellwork: Look at your pencil—what are some properties that you can observe about your pencil? List these in your journal. Pencil Properties • • • • • Solid Wood or plastic (depending on the type) Color may vary Size will vary Shape- generally longer than your palm, thinner than your fingers • Solid matter – These are all properties of the pencil—physical properties! Reviewing MATTER • Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space – Mass – the amount of matter in something – Volume – the amount of space something occupies • Which of the following is matter? – A car? – A box? – You? What is a property? • Property: a characteristic of a substance that can be observed What a Physical Property is NOT: Chemical Properties • Chemical property: a property that can only be observed by changing the identity of the substance Examples: •flammability •ability to rust •reactivity with vinegar Physical Property Physical property: a property that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance. Examples: • luster-The shine from the surface of a mineral. It is usually characterized as metallic, glassy, pearly, or dull. • malleability: the ability to be hammered into a thin sheet • conductivity-ability to conduct energy • melting point • boiling point • density • volume • mass • solubility Special Physical Properties • Melting point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid at a given pressure water = 0oC • Boiling point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas at a given pressure water = 100oC Physical Properties That Can Easily Be Observed with Your Senses • • • • • • • Shape Size (in comparison to other things) Color Texture Odor State of Matter Length Solubility • Measure of how much of one substance can dissolve in another. – Salt & sugar—very soluble in water • Salt is not soluble in alcohol – Oil, sand, rock—not soluble Conductivity • A material’s ability to carry energy. – Two types: • electrical conductivity– carries electricity • heat conductivity- carries heat • Metals—good electrical and heat conductors mostly • Rubber--- poor conductivity both • Ceramic cup—poor electrical; good heat conductivity Quick Review • Name at least 4 observable physical properties of matter. • Which of these do you think is not a physical property? – – – – A. solubility B. Conductivity C. Shine D. Reactivity to another substance Mass • A measure of the amount of matter in an object or a material. (Grams (g) or Kilograms (kg) – A larger object contains more matter than a smaller one of the same material so the larger one has a greater mass. – Use a scale/balance to measure an object’s mass. 1 gram=1 paperclip Volume • The amount of space a sample of matter takes up. – Volume of a solid can be measured in cubic centimeters. – Liquid volumes are measured in liters (L) or milliliters (mL) • One cubic centimeter=one milliliter Volume • You can find volume of a solid by multiplying its length x width x height. • To find the volume of an odd shaped solid, sink it in water in a beaker or graduated cylinder. The object’s volume equals the increase in the water level. Density • Density is the amount of mass per unit of volume. • Density can be used to identify a substance. • The density of water is 1.0g/mL • To find the density, find the mass and then divide it by its volume. Density Calculations • Calculations: D = m/V = g/mL = g/cm3 • Ex: A cube has a mass of 2.8 g and occupies a volume of 3.67 ml. Would this object float or sink in water? Mass = 2.8 g Volume = 3.67 mL D = 2.8g/3.67 mL= 0.76 g/mL – This object would float in water because its density is less than water (1.0 g/mL). More Density Calculations • Ex: A liquid has a mass of 25.6 g and a volume of 31.6 mL. Use the table below to identify the substance. Substance Density (g/mL) D = 25.6 g/31.6 mL Mercury 13.6 D= 0.81 g/mL Water 1.00 Ethanol 0.81 M=25.6 g V=31.6 mL The substance is ethanol. Expectation: The student will be able to distinguish between physical and chemical properties. Prerequisite: What are physical properties? • Create a concept circle to define what physical properties are. – Include at least two not statements.