PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS (Summary #1)
advertisement

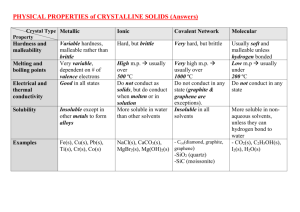
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS (Summary #1) Crystal Type Property Hardness and malleability Melting and boiling points Electrical and thermal conductivity Solubility Examples Metallic _____________ hardness, malleable rather than __________ Very __________, dependent on # of __________ electrons _______ in all states ___________ except in other __________ to form ________ Ionic Covalent Network (Giant Covalent) Simple Molecular Covalent Usually ______ and malleable unless _________ bonded _______ m.p usually under _______ ºC Hard, but _____________ __________ hard, but brittle ________m.p. usually over ______ ºC _______ high m.p. usually over _______ ºC Do _____ conduct as __________, but do conduct when __________ or in ___________ More soluble in water than other solvents Do not conduct in any state (___________ and ______________ are exceptions). Do _____ conduct in any state ___________ in all solvents More soluble in non-aqueous solvents [e.g. NH3(l)], unless they can hydrogen bond to water SUMMARY #2 IONIC COMPOUNDS POLAR COVALENT COMPOUNDS NON-POLAR COVALENT COMPOUNDS GIANT COVALENT Volatility Solubility in polar solvent, e.g. water Solubility increases as polarity ______________ Solubility in nonpolar solvent, e.g. hexane Solubility increases as polarity _______________ Electrical Conductivity Conduct when ___________(l) or dissolved in ____________(aq) Non-conductors except _________, ___________ and semi-conductivity of _________ and (molecular) ____________ (C60) Definitions: (i) VOLATILE A substance is volatile if it evaporates at a low temperature (under 100°C). [*e.g. Acetone (CH3COCH3) and gasoline are volatile liquids.] (ii) SEMICONDUCTOR A solid substance that has a conductivity between that of an insulator and that of most metals, either due to the addition of an impurity or because of temperature effects.