S2 Fig. - Figshare
advertisement
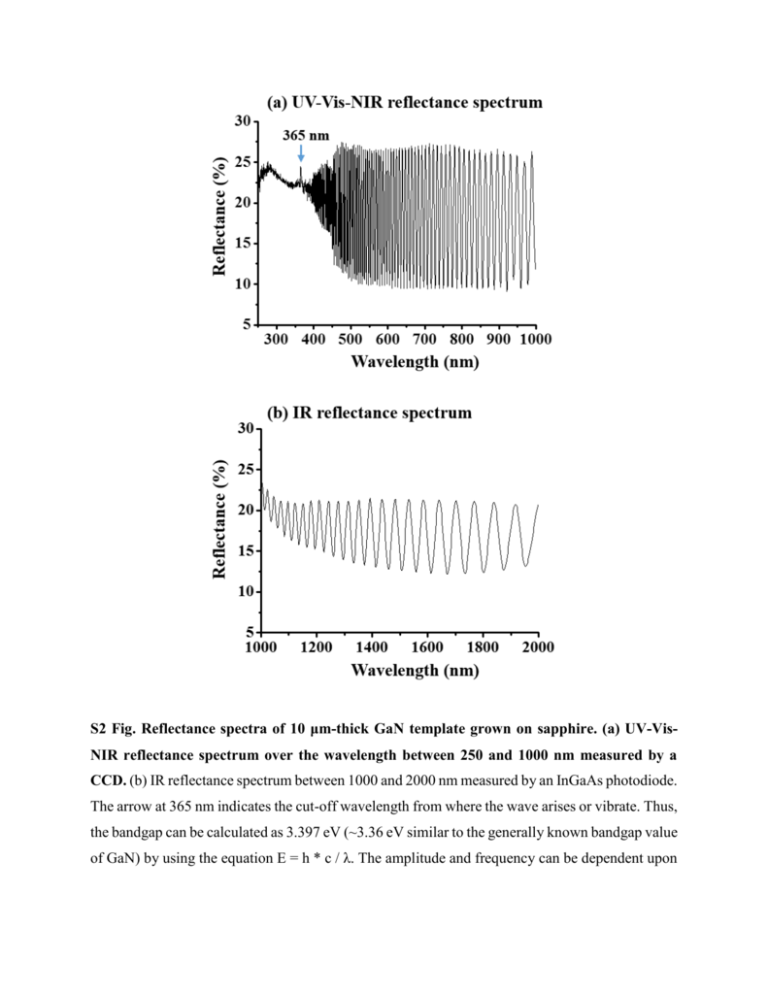
S2 Fig. Reflectance spectra of 10 μm-thick GaN template grown on sapphire. (a) UV-VisNIR reflectance spectrum over the wavelength between 250 and 1000 nm measured by a CCD. (b) IR reflectance spectrum between 1000 and 2000 nm measured by an InGaAs photodiode. The arrow at 365 nm indicates the cut-off wavelength from where the wave arises or vibrate. Thus, the bandgap can be calculated as 3.397 eV (~3.36 eV similar to the generally known bandgap value of GaN) by using the equation E = h * c / λ. The amplitude and frequency can be dependent upon the thickness of GaN template. [1] The oscillation of 10 μm-thick GaN/sapphire template shows the increased amplitude and frequency as compared with the thinner GaN/sapphire template.[1] Reference [1]. C. X.Lian, X. Y. Li and J. Liu, “Optical anisotropy of wurtzite GaN on sapphire characterized by spectroscopic ellipsometry” Semiconductor science and technology, 19, 417 (2004).


![Structural and electronic properties of GaN [001] nanowires by using](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007592263_2-097e6f635887ae5b303613d8f900ab21-300x300.png)