Word Document
advertisement

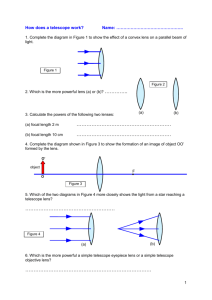
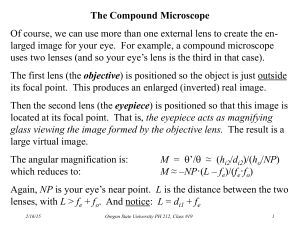
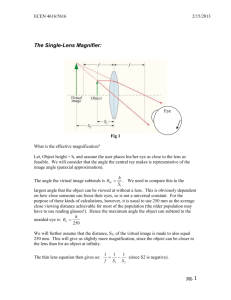
Laboratory Exercise 4 In this laboratory exercise students will build a simple Keplerian telescope, a simple Galilean telescope, and a compound microscope. Equipment: Optical track 50 cm focal length 2'' diameter converging lens 5 cm focal length 1'' diameter converging lens 5 cm focal 1'' diameter length diverging lens 3.8 cm focal length 2'' diameter converging lens Meter Stick, Ruler Various viewing targets Experiment 1: A Keplerian Telescope Build a Keplerian telescope with a magnifying power of ~10. Use a 2'' lens with a focal length of 50 cm for the objective and a 1'' lens with a focal length of 5 cm for the eyepiece. Use plano-convex lenses with one flat side and one curved side. Let the center to center distance between the lenses be ~55cm and let the flat sides of the lenses face each other. Build your telescope on the optical rail. You can easily slide the components along the rail without destroying the alignment. Screw the objective to the rail. Place your eye approximately 5 cm away from the eyepiece and move the eyepiece back and forth until you can see a sharp image of a distant target. Look at the most distant target you can find considering the size limitations of the laboratory. Evaluate the performance of your telescope. Can you see features of the target through the telescope that you cannot see when you view the target from the same distance with the naked eye? Is the image upright or inverted? How does your field of view (the biggest angle in your view away from the center line from your eye to the target) change when you switch from looking at the target with your naked eye to looking through the telescope? A Keplerian telescope Images of targets with a camera replacing the eye Experiment 2: A Galilean Telescope Build a Galilean telescope with a magnifying power MP ~10. Use a plano-convex 2'' lens with a focal length of 50 cm for the objective and a plano-concave 1'' lens with a focal length of -5cm for the eyepiece. Let the center to center distance between the lenses be ~45cm and let the flat sides of the lenses face each other. Build your telescope on the optical rail. Place your eye as close as possible to the eyepiece and move the eyepiece back and forth until you can see a sharp image of a distant target. Look at the most distant target you can find considering the size limitations of the laboratory. Evaluate the performance of your telescope. Can you see features of the target through the telescope that you cannot see when you view the target from the same distance with the naked eye? Is the image upright or inverted? How does your field of view change when you switch from looking at the target with your naked eye to looking through the telescope? Compare this telescope with the Keplerian telescope and comment on advantages and disadvantages. A Galilean telescope An image with a camera replacing the eye Experiment 3: A Compound Microscope Design a simple compound microscope with a tube length g of 16 cm and a magnifying power MP ~20. 16 cm is the most common tube length for laboratory microscopes. Use the 38 cm focal length 2'' converging lens as the objective and the 5 cm focal length 1'' diameter converging lens as the eyepiece. Let the center to center distance between the lenses be ~25cm. Place the target ~5 cm in front of the objective. Build your microscope on the optical rail. Place your eye as close as possible to the eyepiece and move the object back and forth until you can see a sharp image of the object. (If necessary, adjust the position of the eyepiece.) Evaluate the performance of your compound microscope. A compound microscope An image with a camera replacing the eye Laboratory 2 Report: Name: E-mail address: In a few words, describe the experiment. Comment on the procedure. Did you encounter difficulties or surprises? Evaluate the performance of your Keplerian telescope, your Galilean telescope, and your compound microscope.