Name: Date: Section: Ms. Mallon Cells Study Guide: Know the
advertisement

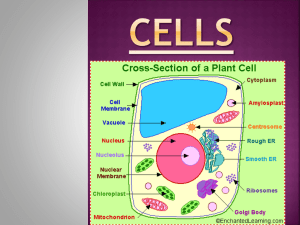
Name: Date: Section: Ms. Mallon Cells Study Guide: Know the following vocabulary: Cell - Basic unit of life Microscopic – something so small it can only be seen through a microscope Cell membrane –thin covering around every cell, controls what goes in and out of the cell Organism – any living thing that maintains vital life processes Nucleus- the “brain” of the cell, it directs all of the cells activities Cytoplasm- jelly like substance inside a cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus that contains chemicals which keep the cell healthy Protist- single celled organism with a nucleus and organelles Chromosome- located inside the nucleus. Contains genetic information about the cell. Cell wall- extra support and protection for the plant cell. Chloroplast- makes food for the plant cell Vacuole- stores food, water, and waste for the cell Mitochondria- the powerhouse of the cell. Releases energy from nutrients Organelle- structures that help keep the cell alive Organ- a group of tissues that work together to perform a certain function Tissue- a group of cells that work together to perform a certain function Organ system- a group of organs th at work together to perform a certain function Ideas and questions to know and be able to answer: How do cells keep organisms alive and healthy? They work together to carry out life processes How are plant and animal cells alike and different? They have most of the same structures, except the plant cell has chloroplast and cell wall, the animal cell does not Know each organelle and where it can be found (in a plant cell, animal cell, or both), and the role that organelle has in the cell: Look at organelles chart. Compare and contrast bacteria and protists: Bacteria- enriches soil by breaking d own dead plants and animals, helping to digest food, and others help make food. Bacterial cells have cell walls, but no nucleus or organelles. Protists- have a nucleus and organelles. Some have cell walls and chloroplast Both- single celled organisms How are bacterial cells different from plant and animal cells? They have no nucleus or organelles Is bacteria good, bad, or both? Why? Bacteria can be good because it helps make food, helps with digestion, and enriches soil. Some bacteria is harmful. Who is Robert Hooke? What did he do? Why is he important? 1665, an English scientist named Robert Hooke observed cork cells through a microscope. The structures looked like tiny rooms so he called them cells. He was actually observing the remains of dead plant cells. He was the first to observe cells. Who is Anton van Leewenhoek? Why is he important? Anton van Leewenhoek was the first to observe living cells. A Dutch trader, van Leewenhoek viewed these cells in 1673 with a very simple microscope. How are microscopes important? What did they enable us to do? Enabled us to discover cells, and know that all living things are made up of cells. These microscopes allowed humans to see things we are unable to see with our eyes, and understand that all cells share some characteristics, and see that different cells do different things. How many cells is your body made out of? Trillions How are cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems related? Cells produce tissues Tissues produce organs Organs produce organ systems Organs systems produce organisms What are the four kinds of tissue in your body? Epithelial, muscle, connective, nervous tissues What is diffusion? Explain it. What experiment demo did we do that helped you understand diffusion? Food coloring demo- Process where particles move from an area where there are a lot of particles of the substance, to an area where there are fewer What is osmosis? What experiment did we do to help you understand osmosis? movement of water and dissolved materials through the cell membrane