Yr 2 Science Medium Term Plan
advertisement

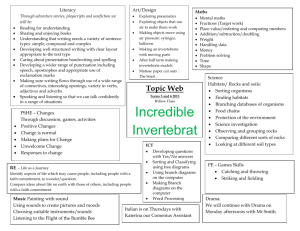
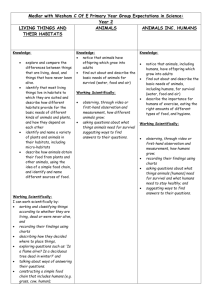
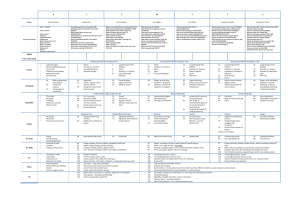
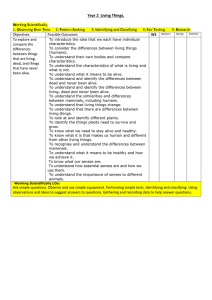
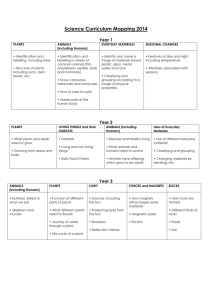
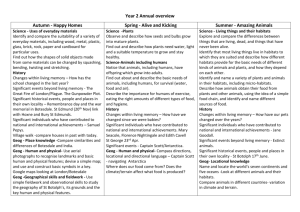
Year 2 Science Medium term plan 2014 – 2015 Term Topic theme Science Objectives Linked Maths Objectives Autumn 1 Magical Potions Plants 1. Observe and describe how seeds and bulbs grow into mature plants. 2. Find out and describe how plants need water, light and a suitable temperature to grow and stay healthy. Working Scientifically 2. Observe closely using simple equipment 4. Identify and classify Measures: length, mass, capacity, moneyTo choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure length/ height in any direction; mass; temperature; volume and capacity to the nearest appropriate unit using rulers, scales, thermometers and measuring vessels. ● To compare and order lengths, mass, volume/capacity and record the results using >, < and =. Spring 1 Can a robot save the world? Materials 1. Identify and compare the suitability of a variety of everyday materials, including wood, metal, plastic, glass, brick, rock, Measures: length, mass, capacity and money ● To choose and Linked Speaking and Listening Objectives use relevant strategies to build their vocabulary listen and respond appropriately to adults and their peers use relevant strategies to build their vocabulary Vocabulary Plants (from Year 1) branches, bud, bulb, deciduous tree, evergreen tree, flowers, fruit, garden/flowering plants, leaves, petals, roots, seed, stem, trunk, wild (new in Year 2): germination, insect pollination, nutrients, pollination, seed dispersal, wind pollination. Working scientifically: changes over time, comparing, contrasting, criteria, data/results, describing, equipment, grouping, identify, name, observations, patterns, record, sorting, test. Everyday materials: absorbent/not absorbent, Resources paper and cardboard for particular uses. 2. Find out how the shapes of solid objects made from some materials can be changed by squashing, bending, twisting and stretching. Working Scientifically 1. Ask simple questions & recognise that they can be answered in different ways. 3. Perform simple tests 5. Use their observations and ideas to suggest answers to questions 6. Gather and record data to help answer questions. use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure length/ height in any direction (m/cm/mm); mass (kg/g); temperature (°C); volume and capacity (litres/ml) to the nearest appropriate unit using rulers, scales, thermometers and measuring vessels. ● To compare and order lengths, mass, volume/capacity and record the results using >, < and =. Solving problems by gathering data and representing in tallies, tables, pictograms and block diagrams •To interpret and construct simple pictograms, tally charts, block diagrams and simple tables. ● To ask and answer simple questions by counting the ask relevant questions to extend their understanding and knowledge use spoken language to develop understanding through speculating, hypothesising, imagining and exploring ideas bending, bendy/not bendy, gas, glass, hard/soft, liquid, metal, plastic, property, rock, rough/smooth, shiny/dull, solid, squashing, stretching, stretchy/stiff, twisting, water, waterproof/not waterproof, wood (New in Year 2): characteristics, classification, manmade, natural, properties. Working scientifically: changes over time, comparing, contrasting, criteria, data/results, describing, equipment, grouping, identify, name, observations, patterns, record, sorting, test. Summer 1 Where could the magic take us? (Polar lands) Living Things and their habitats 1. Explore and compare the differences between things that are living, dead, and things that have never been alive. 2. Identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe how different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other. 3. Identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including micro-habitats 4. Describe how animals obtain their food from plants and other animals, using the idea of a simple food chain, and identify and name different sources of food. Animals Including Humans 1. Notice that animals, including humans, have offspring which grow into adults. 2. Find out about and describe the basic needs of animals, including humans, for survival (water, food and air) 3. Describe the importance for humans of exercise, eating the right amounts of different types of food and hygiene number of objects in each category and sorting the categories by quantity. ● To ask and answer questions about totalling and compare categorical data. Measures: length, mass (weight), capacity and money To choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure length/ height in any direction; mass; temperature; volume and capacity to the nearest appropriate unit using rulers, scales, thermometers and measuring vessels. ● To compare and order lengths, mass, volume/capacity and record the results using >, < and =. Solving problems by gathering data and representing use relevant strategies to build their vocabulary articulate and justify answers, arguments and opinions give wellstructured descriptions, explanations and narratives for different purposes, including for expressing feelings maintain attention and participate actively in collaborative conversations, staying on topic and initiating and responding to comments Living things and their habitats: adaptation, alive, carnivore, characteristics, conditions, consumer, dead, excrete, feed, food chain, grow, habitat, heat, herbivore, life processes, light, living/non-living, micro-habitat, move, ocean, omnivore, pond, producer, rainforest, reproduce, respire, respond to stimuli, seashore, sound, touch, woodland. Animals, including humans: adult, baby, bacteria, balanced diet, in tallies, tables, pictograms and block diagrams To interpret and construct simple pictograms, tally charts, block diagrams and simple tables. ● To ask and answer simple questions by counting the number of objects in each category and sorting the categories by quantity. ● To ask and answer questions about totalling and compare categorical data. carbohydrates, child, circulation, dairy, exercise, fats, fibre, fitness, food groups, germs, growth, healthy, heart rate, infection, life cycle, minerals, nutrition, protein, teenager, toddler, unhealthy, vitamins.