14-1 PowerPoint Notes
advertisement

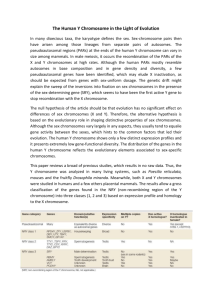
Biologist ___________________________ Date ______________ 14-1 PowerPoint - Human Chromosomes Karyotypes A ___________ is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA. A study of any genome starts with ___________, the bundles of DNA and protein found in the nuclei of eukaryotic cells. Karyotypes A geneticist will cut out the chromosomes from photographs of cells in ___________ (usually blood cells) and arrange them in a picture known as a karyotype. It shows the complete ___________ set of chromosomes grouped together in pairs, arranged in order of decreasing size. A karyotype from a typical human cell, which contains ___ chromosomes, is arranged in ___ pairs. Sex Chromosomes _____ of the 46 chromosomes in the human genome are known as sex chromosomes, because they determine an individual’s sex. Females have two copies of the ___ chromosome. Males have one ___ chromosome and one ___ chromosome. Sex Chromosomes Males and females are born in a roughly ____:____ ratio. This ensures that just about half the ___________ will be males and half will be females. Sex Chromosomes More than _________ genes are found on the X chromosome, some of which are shown. The human Y chromosome is much smaller than the X chromosome and contains only about _______ genes, most of which are associated with ________ sex determination and sperm development. Autosomal Chromosomes The remaining ____ human chromosomes are known as autosomal chromosomes, or autosomes. The complete human genome consists of _____ chromosomes, including 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes. To quickly summarize the total number of chromosomes present in a human cell, biologists write ____________ for females and _____________ for males. Dominant and Recessive Alleles Many human traits follow a pattern of ___________ (or simple) dominance. For example, a gene known as ___________ helps determine skin and hair color. Red hair results from ___________ MC1R genes while ___________ alleles for the MC1R gene help produce darker hair colors. Codominant and Multiple Alleles The alleles for many human genes display ___________ inheritance. One example is the _______ blood group, determined by a gene with three alleles: IA, IB, and I (or A, B, and o) Sex-Linked Inheritance The genes located on the ___ and ___ chromosomes show a pattern of inheritance called sexlinked. A ___________ gene is a gene located on a sex chromosome. Genes on the ___ chromosome are found only in males and are passed directly from father to son. Genes located on the ___ chromosome are found in both sexes, but the fact that men have just one X chromosome leads to some interesting consequences. Sex-Linked Inheritance For example, humans have three genes responsible for ________ vision, all located on the X chromosome. It affects about 1 in ____ males (red-green colorblindness) and only 1 in _____ females since females have two X chromosomes. The recessive phenotype of a sex-linked genetic disorder tends to be much more common among ___________ than among ___________. X-Chromosome Inactivation If just one X chromosome is enough for cells in males, how does the cell “adjust” to the extra X chromosome in female cells? In female cells, most of the genes in one of the X chromosomes are randomly switched _____, forming a dense region in the nucleus known as a ________ body. Barr bodies are generally _____ found in males because their single X chromosome is still active. X-Chromosome Inactivation X-chromosome inactivation also happens in other mammals. In _______, a gene that controls the color of coat spots is located on the X chromosome. Different parts of their body will turn different X chromosomes off or on resulting in a mixture of orange and _________ spots. Human Pedigrees To analyze the pattern of inheritance followed by a particular trait, you can use a chart, called a pedig___________ ree, which shows the relationships within a family. A pedigree shows the presence or absence of a trait according to the ___________ between parents, siblings, and offspring. Human Pedigrees The information gained from pedigree analysis makes it possible to determine the ___________ of genes and alleles associated with inherited human traits. Based on a pedigree, you can often determine if an allele for a trait is ___________ or ___________, ___________ or ___________. Example #1 – Dominant or Recessive, Sex-linked or Autosomal Example #2 – Dominant or Recessive, Sex-linked or Autosomal Example #3 – Dominant or Recessive, Sex-linked or Autosomal