Evolution guided notes completed
advertisement

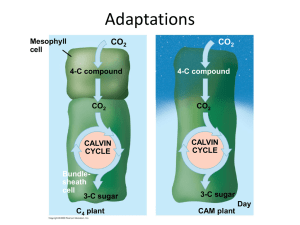
Evolution: A history and a process Charles Darwin= Father of the Theory of Evolution Evolution= all of the changes that have transformed life over an immense time Two ideas persisted before Darwin Species are fixed Earth was less than 10,000 years old and also unchanging Adaptation= an inherited characteristic that improves an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment Ex: the muscular hind legs of a kangaroo Before Darwin… 1800s Jean Baptiste Lamarck Proposed that life evolves and that species are not permanent Process of adaptation Other scientists Charles Lyell- geologist Proposed the gradual and observable geologic processes Erosion, formation of mountains Darwin confirmed this when he witnessed an earthquake in Chile that moved a portion of land above sea level Thomas Malthus Proposed that a population’s growth is influenced by resources Darwin left England as a young graduate He returned as a famous naturalist 1844 Darwin wrote a 200 paper essay that described his idea…but was not published 1858 Alfred Wallace came to the same conclusions as Darwin Within a month, some of Wallace’s, as well as Darwin’s ideas, were presented to the public jointly One year later, Darwin published his book The Origin of Species Darwin made two points in his book: 1. Species on Earth today descended from ancestral species These descendants spread into different habitats around the world and acquired adaptations for a diversity of life “Descent with modification” Ex: jackrabbit and showshoe hare 1. Natural selection is the mechanism for evolution Natural selection is the process by which individuals with inherited characteristics that are ideal to the environment leave more offspring on average than do other individuals Evolution leaves signs Evolution leaves evidence in The fossil record The diverse assortment of modern species Fossil record Fossils= preserved remains or markings left by organisms that lived in the past Found mostly in sedimentary rocks Sedimentation causes rock formation as particles accumulate in layers; any given stratum (layer) is older than the one above it, and younger than those below Paleontologist= scientist who studies fossils Oldest fossil evidence of life consists of chemical traces in rocks that are 3.8 billion years old Found in Greenland Prokaryote fossils have been found and dated as 3.5 billion years old Fossil example: Basilosaurus= an early whale found to have remnants of hind leg bones Geographic Distribution Darwin observed the similarities and differences of organisms from different parts of the world Darwin proposed that organisms present today evolved from ancestral forms Geographic distribution can be used as a clue for the evolution of species Biogeography is the study of the distribution of plants and animals throughout the world The world’s six biogeographical regions have their own distinct mix of living things Continental drift refers to the changing positions of the continents over time Two hundred twenty-five million years ago, all the present land masses belonged to one continent (Pangaea) The distribution of plants and animals is consistent with continental drift Organisms, such as certain seed plant groups or reptiles, are widely distributed throughout the world Other groups, such as mammals that arose after the continents broke up, have great differences in species on different continents Clues to evolutionary history Similarities in Structure Example: mammal forelimb Homologous structures= similar structures in species haring a common ancestor “Descent with modification” Proposed by Darwin Modification of structures to take on new functions Vestigial structures= remnants of structures that may have served an important function in an ancestral species, but have no clear function in some of the modern descendents Often smaller in size Ballene whale Developmental similarities Embryos of closely related species have similar stages of development Bones of the skeleton form in a common pattern The process of comparing how certain structures develop in different organisms is comparative embryology. Molecular biology Comparison of DNA sequences between species If the two species’ sequences match closely then it is thought that the two species are related to a common ancestor If the two species’ sequences have many differences they probably do not share common ancestry Comparison of Hemoglobin Artificial selection= selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to produce offspring with genetic traits that humans value Munchkin cats Artificial Selection In contrast, natural selection favors traits that are beneficial to the organisms in their environment The environment does the “selective breeding” Resulting in evolutionary adaptation Natural Selection of Flies Darwin could not explain how variations passed from one individual to the next Gregor Mendel to the rescue!! Microevolution…a change in a population’s gene pool Gene pool= consists of all the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population Where genetic variation is stored Example: Wild mustangs What leads to genetic variation? Mutations Sexual recombination Natural selection is not random Why? The environment favors combinations of genes that contribute to survival and reproductive success Some alleles may become more common in a gene pool than others Frequency of alleles= how often certain alleles occur in the gene pool Usually expressed as a percentage Microevolution Blending of Mendel’s and Darwin’s theories to look at evolution based on genetics Generation to generation changes (smallest scale) Microevolution What causes gene pools to change (besides natural selection)? 1. Genetic drift= a change in the gene pool of a population due to chance All populations are subject to genetic drift Bottleneck effect…a drastic reduction in the size of a population Usually by natural disaster…and only a few remaining individuals are left to start a new population • Ex: cheetah population in Africa Founder effect…genetic drift in a new colony When a few individuals leave the original population and start a new population Genetic Drift 2. Gene flow= movement of alleles between populations Occurs when fertile individuals mate with individuals from other populations Ex: a wind storm might blow pollen from a population of only red flowers to a population consisting of only white flowers Reduces the genetic differences between populations Can eventually mix the two populations So how did humans evolve? A very lengthy process in which people originated from apelike ancestors. The evolution of humans has occurred over the last 6 million years. Bipedalism – walking on 2 legs – 4 million years ago Most advanced traits have occurred over the last 100 million years. • Apes have a very large, very strong lower jaw to support their carnivorous eating. • As the shape of the human skull evolved to have a smaller lower jaw, this allowed for a larger brain to develop. • With a larger brain, the capacity for language and the manufacture of tools were able to be developed.