Answers B1 - B3 - HIS-IGSci-Bio
advertisement

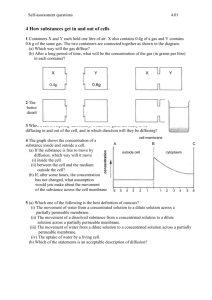
Sections B1, B2 and B3 Revision questions 1. Which one of the following is most likely to be true: To see plant cells with a microscope you usually need a magnification of about A. x5 B. xl0 C. xl00 D. xl000 2. Which one of the following best describes the function of a cell membrane? A. It keeps the cell in shape. B. It controls the substances entering and leaving the cell. C. It controls the substances entering the cell. D. It supports the cell structures. 3. Which of the following structures are i. in plant and animal cells, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus, chromosomes ii. in plant cells but not in animal cells? Cell wall, central vacuole 4. Classify the following under the headings 'Cell structure', 'Tissue', 'Organ' or 'System'. Cell structure: nucleus, mitochondrion, cytoplasm. Tissue: bone, nerve, muscle, epithelium. Organ: brain, stomach, lung. System: skeleton, heart and blood vessels, alimentary canal, lungs and windpipe. 5. A protein molecule which is denatured, has A. split into smaller molecules B. changed its shape C. combined with another molecule D. been diluted 6. Select the most appropriate words from the list in the box to complete the following paragraph: All cells contain enzymes which are proteins and act as catalysts which speed up chemical reactions. The reactions do not which can take part in further reactions. use up the enzymes 7. Enzymes will usually react with only one substance. This can be explained by the 'lock and key' theory. If this theory is correct, which of the following substances, represented by P, Q, R and S would be acted on by enzyme A? A P Q R S 8. If an enzyme-controlled reaction normally takes place at 10ºC, in general terms how will the reaction be affected by i. a fall in temperature to 2°C slow down ii. iii. a rise in temperature to 20°C speed up (by 2x) a rise in temperature to 65°C? stop completely as the enzyme denatures 9) If an enzyme is denatured, why does it no longer work? An enzyme which has been denatured has changed its shape and will no longer combine with its substrate (the substance it acts on). 10) The graph shows the rate of an enzyme reaction at different levels of acidity or alkalinity (pH). From the graph, what is the optimum pH for this enzyme? A. pH 2 B. pH 7 C. pH 10 D. none of the above rate of reaction pH 2 4 6 8 10 11) A protein-digesting enzyme when mixed with starch solution would: A. have no action rate of B. produce amino acids reaction C. produce glucose D. digest the starch 12) Select the most appropriate words from the list in the box to complete the following paragraph. pH 2 4 6 8 10 animals, extra-cellular, intra-cellular, cells, digestive, nuclei, catalysts All enzymes are produced inside cells. Enzymes which do their work outside extra-cellular. Enzymes which do their work inside cells are called intra-cellular Most of our digestive enzymes are examples of extracellular enzymes. cells are called 13) In an investigation to compare the rates at which starch is being broken down by an enzyme i. what test is used? Iodine solution goes blue-black in the presence of starch ii. When the iodine stays orange-brown, all the starch has been broken down into sugars how do you know when the reaction is completed? 14) Containers X and Y each hold one litre of air. X also contains 0.4g of a gas and Y contains 0.6 g of the same gas. The two containers are connected together as shown in the diagram. i. Which way will the gas diffuse? From Y (high concentration) to X (low concentration) ii. After a long period of time, what will be the concentration of the gas (in grams per litre) in each container? 0.5g in each container – evenly distributed / equilibrium X Y 0.4g 0.6g X Y 15) The diagram represents (not to scale) molecules of a salt dissolved in the bottom layer of water in a beaker. Draw two similar diagrams to show the distribution of salt molecules i. after a few minutes i. 16) The graph shows the concentration of a substance inside and outside a cell. (a) If the substance is free to move by diffusion, which way will it move: i. inside the cell from B to C (down the concentration gradient) ii. ii after several hours. cell membrane A concentration ii. B outside cell C cytoplasm between the cell and the medium outside the cell? 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 If the cell membrane were freely permeable, the substance would diffuse out of the cell, from B to A, because its concentration inside is greater than that outside. (b) If, after some hours, the concentration has not changed, what assumption would you make about the movement of the substance across the cell membrane? If there is no change in the concentration, you might assume that the substance was not free to diffuse across the cell membrane and was being taken up by active transport and diffusing across the cytoplasm by passive diffusion. 17) Which one of the following is the best definition of osmosis? A. The movement of water from a concentrated solution to a dilute solution across a partially permeable membrane. . B. The movement of a dissolved substance from a concentrated solution to a dilute solution across a partially permeable membrane. C. The movement of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution across a partially permeable membrane. D. The uptake of water by a living cell. 18) Which of the statements (above) is an acceptable description of diffusion? B. The movement of a dissolved substance from a concentrated solution to a dilute solution membrane 19) The diagram to the right shows a vessel which contains a concentrated and a dilute solution separated by a partially permeable membrane. Draw a similar diagram to show the liquid levels after an hour or two. There will be a rise in level on the right and a corresponding fall on the left as water passes from the dilute to the concentrated solution by osmosis. Membrane dilute solution 6 dilute solution concentrated solution concentrated solution 20) When meat is salted, bacteria cannot grow on it. Suggest a reason for this. The salt lowers the meat's osmotic potential so that water is withdrawn, by osmosis, from the bacterial cytoplasm and so kills the bacteria. dilute concentrated solution solution