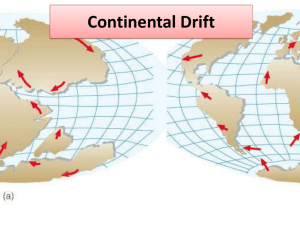
What is the continental shelf? What is the continental slope? What is
What is the continental shelf?
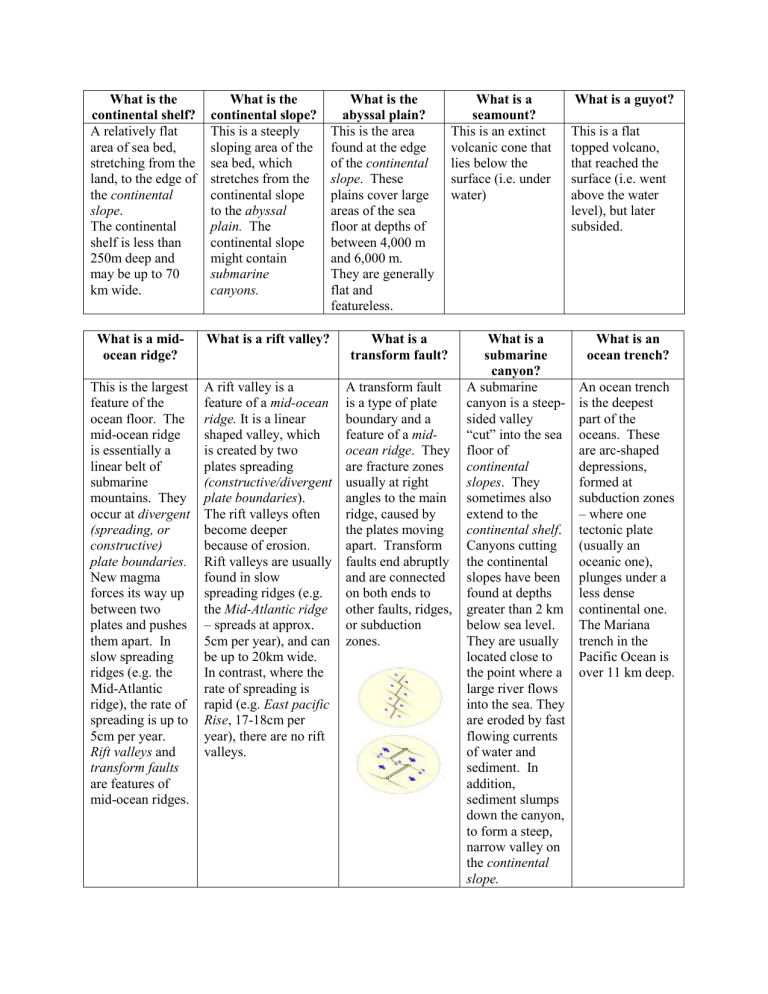
A relatively flat area of sea bed, stretching from the land, to the edge of the continental slope .
The continental shelf is less than
250m deep and may be up to 70 km wide.
What is the continental slope?
This is a steeply sloping area of the sea bed, which stretches from the continental slope to the abyssal plain.
The continental slope might contain submarine canyons.
What is the abyssal plain?
This is the area found at the edge of the continental slope . These plains cover large areas of the sea floor at depths of between 4,000 m and 6,000 m.
They are generally flat and featureless.
What is a midocean ridge?
What is a rift valley? What is a transform fault?
What is a seamount?
This is an extinct volcanic cone that lies below the surface (i.e. under water)
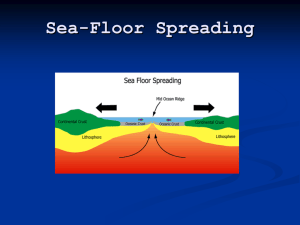
This is the largest feature of the ocean floor. The mid-ocean ridge is essentially a linear belt of submarine mountains. They occur at divergent
(spreading, or constructive) plate boundaries.
New magma forces its way up between two plates and pushes them apart. In slow spreading ridges (e.g. the
Mid-Atlantic ridge), the rate of spreading is up to
5cm per year.
Rift valleys and transform faults are features of mid-ocean ridges.
A rift valley is a feature of a mid-ocean ridge.
It is a linear shaped valley, which is created by two plates spreading
(constructive/divergent plate boundaries ).
The rift valleys often become deeper because of erosion.
Rift valleys are usually found in slow spreading ridges (e.g. the Mid-Atlantic ridge
– spreads at approx.
5cm per year), and can be up to 20km wide.
In contrast, where the rate of spreading is rapid (e.g. East pacific
Rise , 17-18cm per year), there are no rift valleys.
A transform fault is a type of plate boundary and a feature of a midocean ridge . They are fracture zones usually at right angles to the main ridge, caused by the plates moving apart. Transform faults end abruptly and are connected on both ends to other faults, ridges, or subduction zones.
What is a guyot?
This is a flat topped volcano, that reached the surface (i.e. went above the water level), but later subsided.
What is a submarine canyon?
A submarine canyon is a steepsided valley
“cut” into the sea floor of continental slopes . They sometimes also extend to the continental shelf .
Canyons cutting the continental slopes have been found at depths greater than 2 km below sea level.
They are usually located close to the point where a large river flows into the sea. They are eroded by fast flowing currents of water and sediment. In addition, sediment slumps down the canyon, to form a steep, narrow valley on the continental slope.
What is an ocean trench?
An ocean trench is the deepest part of the oceans. These are arc-shaped depressions, formed at subduction zones
– where one tectonic plate
(usually an oceanic one), plunges under a less dense continental one.
The Mariana trench in the
Pacific Ocean is over 11 km deep.