Chemistry C1 playing cards
advertisement

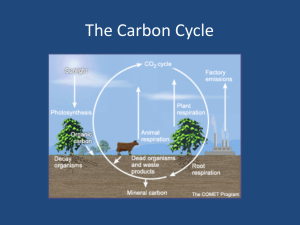
Methane CH4 Ethane C2H6 Fractional Distillation Separating mixtures of liquids because they boil (and condense) at different temperatures Examples: crude and vegetable oil separation Alkane (CnH2n+2) Dodecane C12H26 Alkane (CnH2n+2) Rule: any liquid will boil and condense at the same temperature Ethene C2H4 Cracking Type of thermal decomposition that requires heat and catalyst Alkane (CnH2n+2) Alkene (CnH2n) Propene C3H6 Propane C3H8 Heating breaks down the chemical bonds between the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon compound to make new smaller sized hydrocarbon compounds CaCO3 CaO+CO2 Thermal decomposition Process requires Alkene (CnH2n) Alkane (CnH2n+2) heat Carbon Carbon Dioxide C Also exists as Carbon Coke or as Carbon particulates Calcium Carbonate Complete Combustion CO2 (burning with plenty of oxygen) Calcium Oxide C+O2CO2 e.g. carbon coke in blast CaCO3 Also known as CaO Exothermic limestone Also is the cloudy white precipitate when CO2 gas furnace Also known as Quicklime reaction (generates heat) reacts with limewater Calcium Hydroxide Water Ca(OH)2 H20 Also known as limewater Thermal Decomposition Heating breaks down the chemical bonds in the compound to make new substances Octane C8H18 also known as Gasoline (Petrol) Alkane (CnH2n+2) Poly(ethene) Ethanol C2H5OH Made from renewable and non-renewable sources C12H26 C8H18+2C2H4 Cracking dodecane to give octane(petrol) Polymerisation Hydration polymerisation equation Incomplete Combustion (burning with limited oxygen) Multiple monomer molecules (e.g. ethene) are joined together to make a longer molecule called a polymer CH4+2O2 CO2+2H20 H20 formed in U-tube turns blue cobalt chloride paper pink Chemical reaction in which water (H20) is added C2H4+H20 C2H5OH Ethene reacts with steam Requires 300C, 60atm and phosphoric acid catalyst Non-renewable source Glucose C6H12O6 Energy source in most organisms Is a product of plant photosynthesis Plants store glucose as starch C6H12O6 2C2H5OH+2CO2 Formation of ethanol from glucose by fermentation Renewable source of ethanol Hydrogen gas Fermentation H2 H-H Anaerobic (without oxygen) respiration of yeast Single covalent bond Carbon Monoxide CO Made from combustion of carbon (coke) or incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons Cell Respiration Aerobic (with oxygen) Toxic clear odourless gas Electrolysis Carbon Dimming Global Warming Caused by excessive Caused by excessive atmospheric Carbon atmospheric CO2 particulates (soot) Fe2O3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO2 Redox C+O2CO2 2C+CO22CO 2C+O22CO Reduction & Oxidation Reactions occurring in a Blast Furnace Type of chemical Reaction C6H12O6+6O2 6CO2+6H20 Generates energy(heat) in all living organisms Technically, cellular respiration is a combustion reaction Occurs in cell mitochondria Fossil fuels Coal Crude oil Natural gas formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms Electrolysis of brine (sodium chloride, NaCl) 2NaCl+2H20 Cl2+H2+2NaOH 6CO2+6H20 C6H12O6+6O2 Reaction occurring in plant chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll pigments Photosynthesis Light-dependent reaction Sulfur dioxide SO2 Sulfur can be removed from fuels prior to burning the fuel Sulfur dioxide emissions from fossil fuel power plants can Contain hydrocarbons be reduced by reacting SO2 with CaO (quicklime) Also contain sulfur and heavy metal (e.g. lead) impurities 2NO22O2+N2 2CO+O22CO2 Redox reaction occurring in a platinum or palladium catalytic converter Nitrogen gas Nitrogen dioxide N2 NO2 78% of atmosphere is N2 For use by industry, nitrogen is made by the fractional distillation of liquid air Liquid nitrogen is a cryogenic liquid (boils at -195 C, 78 K) Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 Formed naturally from SO2 emissions (burning fossil fuels) Formed industrially by combining SO2 with O2 to make sulfur trioxide SO3 CaCO3+H2SO4 CaSO4+H2O+CO2 Explains why limestone statues corrode (gradually dissolve away) by acid rain (e.g sulfuric acid) Catalytic converter (e.g. in car exhaust) Air pollutant that arise from any combustion process that uses air N2+O22NO 2NO+O22NO2 Acid Rain Biodiesel Formed when SO2 or NO2 gases, produced from combustion processes, dissolve in atmospheric water vapour Renewable source of energy made from plant (e.g palm oil) or animal products (e.g. animal fats, sewage) Bromine water test Br2 Bromine water is ORANGE Test which shows the difference between unsaturated and saturated carbon bonds in organic compounds Br2 water, stays orange (saturated e.g. alkanes, single C-C bond) Br2 water, turns clear (unsaturated e.g. alkenes, double C=C bond) Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O CaO(s)+H20(l) Ca(OH)2(s) Quicklime reacts exothermically (generates heat) with water to produce slaked lime Ca(OH)2(s) Recycling plastic polymers 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O Combustion of hydrogen gas Ca(OH)2(s) + (aq) Ca(OH)2(aq) Hydrogen is a clean fuel as the product (water) is nonpollutant Solid slaked lime dissolves in Highly exothermic (generates heat) reaction water (aq) to give aqueous limewater Ca(OH)2(aq) Ca(OH)2+CO2 CaCO3+H2O Bubble CO2 gas through limewater to give the cloudy white precipitate of calcium carbonate Compound A molecule that is made up of two or more different atoms (elements) that are joined together by chemical bonds Examples include: Sodium Chloride (NaCl), Water (H2O), hydrocarbons (e.g. methane CH4) Unsaturated vegetable oils Extracted from seeds, nuts and fruits by pressing or by distillation Hydrogenation Hardening of unsaturated vegetable oils Contain C=C double bonds Higher boiling points than water (food cooks at higher temp in oils so food cooks faster in oil than in water) Hydrogenated oils have higher melting points because they are more saturated so they are solids at room temperature, making them useful as spreads and in cakes and pastries. by reacting them with hydrogen at 60C with a nickel catalyst Mixture A combination of two or more elements or compounds which are NOT chemically combined Examples include: crude oil (a mixture of alkanes), sand & water, breakfast!