Grid Steve Lara Spring II
advertisement

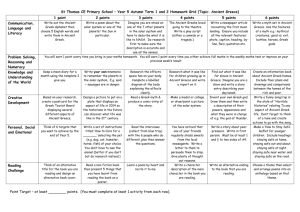
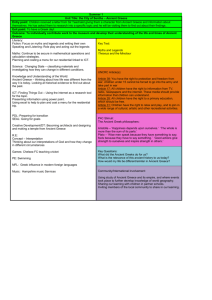
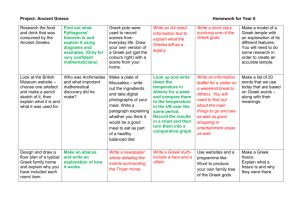
Teacher: Unit Title: Esteban Lara Ancient Greece, 6th Grade Unit Objectives: The students will be able to analyze the geographic, political, economic, religious, and social structures of the early civilizations of Ancient Greece. Standards Addressed: Social Studies 6.4 Students analyze the geographic, political, economic, religious, and social structures of the early civilizations of Ancient Greece. 1. Discuss the connections between geography and the development of city-states in the region of the Aegean Sea, including patterns of trade and commerce among Greek city-states and within the wider Mediterranean region. 2. Trace the transition from tyranny and oligarchy to early democratic forms of government and back to dictatorship in ancient Greece, including the significance of the invention of the idea of citizenship (e.g., from Pericles' Funeral Oration). 3. Explain the significance of Greek mythology to the everyday life of people in the region and how Greek literature continues to permeate our literature and language today, drawing from Greek mythology and epics, such as Homer's Iliad and Odyssey, and from Aesop's Fables. 4. Outline the founding, expansion, and political organization of the Persian Empire. 5. Compare and contrast life in Athens and Sparta, with emphasis on their roles in the Persian and Peloponnesian Wars. 6. Trace the rise of Alexander the Great and the spread of Greek culture eastward and into Egypt. Mathematics Content Standards Number Sense 1.0 Students compare and order positive and negative fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers. Students solve problems involving fractions, ratios, proportions, and percentages: 1.1 Compare and order positive and negative fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers and place them on a number line. 1.2 Interpret and use ratios in different contexts (e.g., batting averages, miles per hour) to show the relative sizes of two quantities, using appropriate notations ( a/b, a to b, a:b ). 1.3 Use proportions to solve problems (e.g., determine the value of N if 4/7 = N/ 21, find the length of a side of a polygon similar to a known polygon). Use cross-multiplication as a method for solving such problems, understanding it as the multiplication of both sides of an equation by a multiplicative inverse. 1.4 Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discounts at sales, interest earned, and tips. 2.0 Students calculate and solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division: 2.3 Solve addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems, including those arising in concrete situations, that use positive and negative integers and combinations of these operations. English Language Arts READING1.0 Word Analysis, Fluency, and Systematic Vocabulary Development Word Recognition 1.1 Read aloud narrative and expository text fluently and accurately and with appropriate pacing, intonation, and expression. Vocabulary and Concept Development 1.2 Recognize the origins and meanings of frequently used foreign words in English and use these words accurately in speaking and writing. 1.0 Writing Strategies Organization and Focus 1.1 Choose the form of writing (e.g., personal letter, letter to the editor, review, poem, report, narrative) that best suits the intended purpose. 1.2 Use a variety of effective and coherent organizational patterns, including comparison and contrast; organization by categories; and arrangement by spatial order, order of importance, or climactic order. Research and Technology 1.4 Use organizational features of electronic text (e.g., bulletin boards, databases, keyword searches, e-mail addresses) to locate information. 1.5 Compose documents with appropriate formatting by using wordprocessing skills and principles of design (e.g., margins, tabs, spacing, columns, page orientation). Evaluation and Revision 1.6 Revise writing to improve the organization and consistency of ideas within and between paragraphs. Verbal/ Linguistic Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Students use Greek vocabulary to assume roles of Greek generals at battle of Thermopylae vs Persia then give verbal and written Students make maps of ancient Greek trade routes with cities, lands as well as goods to be traded with each city labeled. Write about what would happen if Greeks lose war with Persia. How will lives of Greeks change. Create a play to act out battle of Thermopylae as well as Greek life before and after the battle. Use Power Point and verbal presentation to convince class to vote yes or no on war with Persia and why. Students vote on whether to go to war with Persia and write explanation of why they voted as they did. Interpersonal BodilyKinesthetic Intrapersonal reports on the progress of the battle each day for several days. Work in groups to build Sparta or Athens out of 3D paper buildings, ships etc with different groups making different parts of the city. In a play, act out the visit of the Persian envoy requesting Greek surrender as in the movie 300. Pretend to be a citizen of Ancient Athens or Sparta during peace and during war and list possible occupations. Each class group working together makes a different part of the city economy, such as ships, maps, temples, farmhouse, market etc. Act out the battle of Thermopylae including the vote on whether to go to war. Write to describe what occupation you would like and another you would not like. Each group makes a verbal group presentation to a meeting of citizens to convince us why their group’s activity or building is important to the city economy and to the citizens. Students act out a democratic meeting of Ancient Greek citizens and listen to presentations to convince us to vote yea or nay on war with Persia. With a partner, classify city buildings or activities as religious, economic, or political. Each group makes a group presentation defending and describing their activity to the rest of the citizens (the class). With a partner compare Athens to Sparta in a voice thread for the class to see on a computer. Like a Greek general, use pointer to show on a map where Persia is attacking and ask class of Greek citizens what we can do about it. Organize a Write in a journal list of what ancient occupations occupation you would into those choose in you would Ancient like and Greece. those youwould not like. Have class make and eat Greek food especially that eaten in ancient times. Compare and contrast the physical activities of Ancient Greece to our own today. Compare slavery and manual labor jobs such as mining for gold etc. back then to life today. Participate in a class Olympics. Create a model of an Ancient Greek object you would like to sell or trade back then. Explain in writing why student chose the ancient Greek occupation they dod. Naturalist VisualSpatial Make a list of animals that ancient Greeks had. Make a list of raw materials the Ancient Greeks used. Make a list of the bad things about slavery in Ancient Greece and who benefited from slavery. Identify tools used in each ancient occupations. Draw a map Students create 3D paper models of ancient Greek ships, trade goods, shields and buildings to make a city they will defend at a recreation of battle of Thermopylae. Sing a song about why Sparta is better than Athens. Make a list Musical of Rhythmic occupations Ancient Greeks would sing about. Write down Logical how many Mathematical Greek soldiers get killed each day during battle of Make a song about Ancient Greece. Write down how many Persians die each day of the battle of Thermopyle Create a map of Ancient Sparta or Athens with important buildings Classify a group of objects into those used in Ancient Times and those used today Compare life today to that in Acient Greece. Draw an ancient Greek house with the tools it wyou havefe Compare life back then to life today. Make a song about why Athens is better than Sparta. Consider why Alexander the Great should have attacked Persia. Survey Hypothesize what would a Greek soldier eat during a battle. Make a recommendation of which city is best and why. cla ss to fin d out wh ich cit y is bes t. Design your Compare own Ancient Anceient Spara Greek city to Athens. using the best parts of Sparta and Athens then make a poster telling us why we should live in that city.